
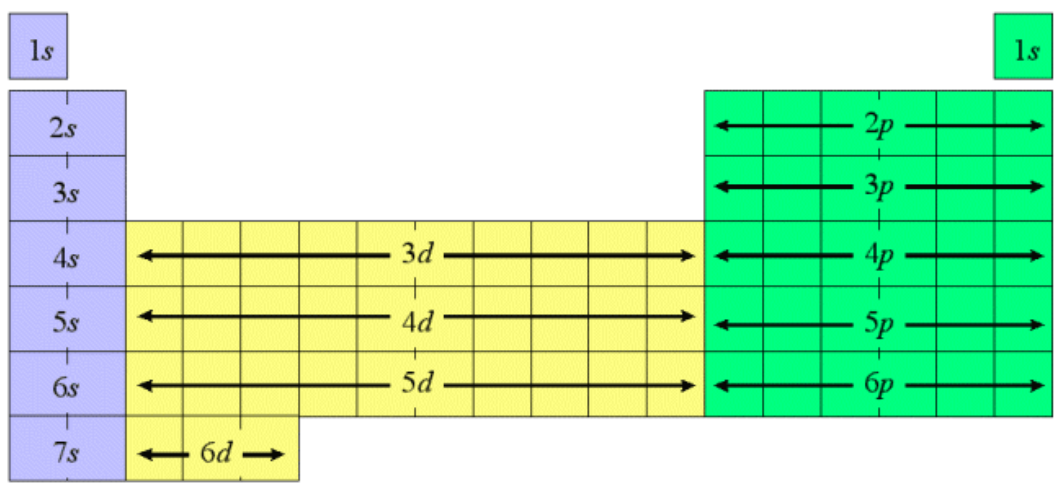
How do you read the electronic configuration periodic table? For example, if you want to find Mg what would its configuration be?

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint To solve this question first we have to understand the meaning of the term orbital. Orbitals refers to the dimensional motion of an electron around the nucleus in 3-D motion. The number of orbitals can be determined using the electronic configuration. Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbital.
Complete step by step solution:
To write the electronic configuration, first we will write the subshell notation of that atom.
For magnesium = 2,8,2
We know that magnesium is present in group 2 and period 3. Hence, the energy level is 3.
Hence, the electronic configuration of Mg will be
\[Mg=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}\]
Similarly, we can write the electronic configuration for other elements, by writing down the total number of electrons.
Additional information:
Aufbau principle states that in the ground state of an atom or ion, the electrons are filled on the basis of the increasing energy levels, this means that the orbital having low energy will be filled first. Pauli’s exclusion principle states that no two electrons have the same set of all the four quantum numbers. And according to the hund's rule of maximum multiplicity, pairing of electrons will be done only when all the degenerate orbitals are singly occupied.
Note: In case when the value of $ (n+l)$ is the same for two orbitals, then the orbital having lower value of n i.e. the principal quantum number will be filled first.
Complete step by step solution:
To write the electronic configuration, first we will write the subshell notation of that atom.
For magnesium = 2,8,2
We know that magnesium is present in group 2 and period 3. Hence, the energy level is 3.
Hence, the electronic configuration of Mg will be
\[Mg=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}\]
Similarly, we can write the electronic configuration for other elements, by writing down the total number of electrons.
Additional information:
Aufbau principle states that in the ground state of an atom or ion, the electrons are filled on the basis of the increasing energy levels, this means that the orbital having low energy will be filled first. Pauli’s exclusion principle states that no two electrons have the same set of all the four quantum numbers. And according to the hund's rule of maximum multiplicity, pairing of electrons will be done only when all the degenerate orbitals are singly occupied.
Note: In case when the value of $ (n+l)$ is the same for two orbitals, then the orbital having lower value of n i.e. the principal quantum number will be filled first.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




