
What is the Ratio of bond pair-lone pair electrons in ${\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_2}$ ?
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint:To determine the ratio of bond pair-lone pair we have to determine the bond pair and lone pair first. For this we will write the Lewis geometry. Lewis structure shows the electron pairs around the atoms of a molecule. The Lewis structure includes both bonded as well as nonbonding electron density.
Complete step by step solution:The rules to write the Lewis structure are as follows:
Write the basic structure. Write the central atom around which writes all atoms of the molecule. The least electronegative atom is the central atom.
Count total valence electrons.
Two electrons are used in the formation of a bond.
Count the total electron used in bond formation.
Subtracts the electrons used in bond formation from the total valence electrons.
The Lewis structure of ${\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_2}$ is as follows:
Total valence electrons are as follows:
$ = \,\left( {8 \times 1} \right) + \left( {6 \times 1} \right) + \left( {7 \times 2} \right)$
$ = \,28$
The basic arrangement of atoms are as follows:
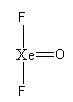
Xenon is forming four bonds, so the total electron used in the bonds are $8$.
The remaining valence electrons are,
$ = 28 - 8$
$ = \,20$
We will arrange the $20$ electrons to complete the octet of each atom.
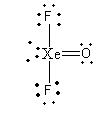
So, the number of bond pairs of xenon is $4$and lone pairs are $2$. So, the ratio of bond pair-lone pair electrons is,
$ = 4/2$
$ = 2$
Therefore, the ratio of bond pair-lone pair electrons ${\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_2}$ is $2$.
Note: Each atom requires eight electrons to complete an octet except hydrogen. The hydrogen requires two electrons to complete the octet. The electron pair involved in bond formation is known as bond pair. The electron pair which remains non-bonded is known as lone pair. In a bond pair, each electron comes from each bonded atom. The electron density of lone pairs lies only on one atom. Electronegativity of xenon is less than oxygen and fluorine.
Complete step by step solution:The rules to write the Lewis structure are as follows:
Write the basic structure. Write the central atom around which writes all atoms of the molecule. The least electronegative atom is the central atom.
Count total valence electrons.
Two electrons are used in the formation of a bond.
Count the total electron used in bond formation.
Subtracts the electrons used in bond formation from the total valence electrons.
The Lewis structure of ${\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_2}$ is as follows:
Total valence electrons are as follows:
$ = \,\left( {8 \times 1} \right) + \left( {6 \times 1} \right) + \left( {7 \times 2} \right)$
$ = \,28$
The basic arrangement of atoms are as follows:
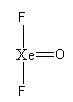
Xenon is forming four bonds, so the total electron used in the bonds are $8$.
The remaining valence electrons are,
$ = 28 - 8$
$ = \,20$
We will arrange the $20$ electrons to complete the octet of each atom.

So, the number of bond pairs of xenon is $4$and lone pairs are $2$. So, the ratio of bond pair-lone pair electrons is,
$ = 4/2$
$ = 2$
Therefore, the ratio of bond pair-lone pair electrons ${\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_2}$ is $2$.
Note: Each atom requires eight electrons to complete an octet except hydrogen. The hydrogen requires two electrons to complete the octet. The electron pair involved in bond formation is known as bond pair. The electron pair which remains non-bonded is known as lone pair. In a bond pair, each electron comes from each bonded atom. The electron density of lone pairs lies only on one atom. Electronegativity of xenon is less than oxygen and fluorine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




