
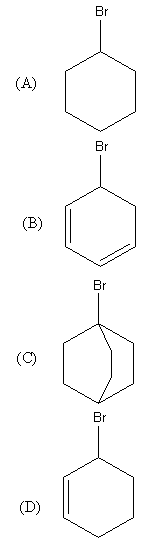
Rate of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$will be negligible in:

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint:: To determine the answer we should the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2} $reaction and factor affecting the rate of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction. The ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction removal of a nucleophile and the attack of another nucleophile take place simultaneously. So, the reaction requires a less sterically hindered environment.
Complete step by step solution:
The full name of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. In ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction, a nucleophile substitutes another nucleophile. The whole reaction takes place in one step.
As the nucleophile removes from the reactant another nucleophile attacks from the opposite side. The formed structure is known as a transition state in which both nucleophiles remain bound with weak bonds. Due to the attack from the opposite side the stereo of the product changes. This is known as Walden inversion.
The attacking nucleophile can approach the reactant easily if the reactant has less steric hindrance and thus facilitate the reaction via the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ mechanism. The compound with less steric hindrance will give the${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction faster. As the steric hindrance decreases the rate of reaction via ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ mechanism increases.
The order of increasing steric hindrance in alkyl halide is as follows:
${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$
The order of decreasing reactivity of alkyl halide towards the${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction is as follows:
${1^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{3^ \circ }$
So, we have to find the most sterically hindered ${3^ \circ }$aryl bromide.
The structure of the given aryl bromides are as follows:
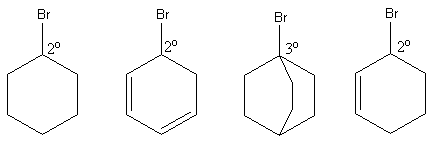
So, the C is ${3^ \circ }$aryl bromide as it has three alkyl groups.
So, the rate of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$will be negligible in compound C.
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Note:The rate of the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$reaction depends upon both of the reactants. The carbon atom that has a bromide group, is attached with only one carbon then it is known as ${1^ \circ }$ carbon. The ${3^ \circ }$aryl halide favours substitution via ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}$mechanism in which a carbocation forms as intermediate. So, the reactivity depends upon the stability of the carbocation. The order of decreasing reactivity of alkyl halide towards the${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}$reaction is as follows: ${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$.
Complete step by step solution:
The full name of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. In ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction, a nucleophile substitutes another nucleophile. The whole reaction takes place in one step.
As the nucleophile removes from the reactant another nucleophile attacks from the opposite side. The formed structure is known as a transition state in which both nucleophiles remain bound with weak bonds. Due to the attack from the opposite side the stereo of the product changes. This is known as Walden inversion.
The attacking nucleophile can approach the reactant easily if the reactant has less steric hindrance and thus facilitate the reaction via the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ mechanism. The compound with less steric hindrance will give the${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction faster. As the steric hindrance decreases the rate of reaction via ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ mechanism increases.
The order of increasing steric hindrance in alkyl halide is as follows:
${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$
The order of decreasing reactivity of alkyl halide towards the${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction is as follows:
${1^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{3^ \circ }$
So, we have to find the most sterically hindered ${3^ \circ }$aryl bromide.
The structure of the given aryl bromides are as follows:

So, the C is ${3^ \circ }$aryl bromide as it has three alkyl groups.
So, the rate of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$will be negligible in compound C.
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Note:The rate of the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$reaction depends upon both of the reactants. The carbon atom that has a bromide group, is attached with only one carbon then it is known as ${1^ \circ }$ carbon. The ${3^ \circ }$aryl halide favours substitution via ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}$mechanism in which a carbocation forms as intermediate. So, the reactivity depends upon the stability of the carbocation. The order of decreasing reactivity of alkyl halide towards the${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}$reaction is as follows: ${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




