
Rate constant k of a reaction varies with temperature according to the equation \[{\text{log}}\,{\text{k}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{constant}}\,{\text{ - }}\,\dfrac{{{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}}}{{{\text{2}}{\text{.303}}}}\,{\text{ \times }}\,\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}\] where \[{E_a}\] is the energy of activation for the reaction. When a graph is plotted for \[{\text{log}}\,{\text{k}}\] vs \[\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}\] a straight line with a slope \[ - 6670\,K\] is obtained. The activation energy for this reaction will be: \[(R\, = \,8.314\,J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}})\]
\[A.\,122.65\,kJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
\[B.\,127.71\,kJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
\[C.\,142.34\,kJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
\[D.\,150.00\,kJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
Answer
546k+ views
Hint:The minimum amount of extra energy required by a reacting molecule to get converted into product is called the activation energy. In the presence of a catalyst, the activation energy decreases a bit. The activation energy can also be described as the minimum amount of energy needed to activate molecules or atoms so that they can undergo a chemical reaction. Activation energy is denoted by \[{E_a}\] . It is usually measured in joules \[\left( J \right)\] and or \[k\,J\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\] or \[k\,cal\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:The given Arrhenius equation;
\[{\text{log}}\,{\text{k}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{constant}}\,{\text{ - }}\,\dfrac{{{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}}}{{{\text{2}}{\text{.303}}}}\,{\text{ \times }}\,\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}\]
Let’s write constant as \[log{\text{ }}A\] ;
Now, we know that the plotted graph is a straight line; which means,
\[y\, = \,c\, + \,mx\]
Therefore, \[y\] will be \[\log \,k\], \[c\] will be \[\,{\text{constant}}\,\]i.e., \[log{\text{ }}A\] and the remaining term \[mx\] will be \[{\text{ - }}\,\dfrac{{{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}}}{{{\text{2}}{\text{.303}}}}\,{\text{ \times }}\,\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}\] where \[x\]will be \[\left[ {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}} \right]\].
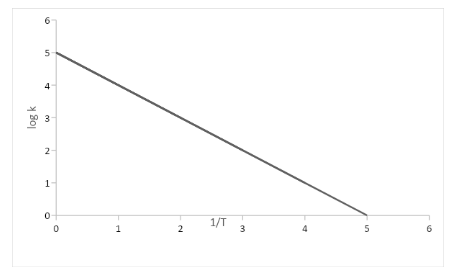
In this graph, we are able to observe that \[\left[ {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}} \right]\] which is on \[x\] axis and \[\log \,k\] values on \[y\] axis.
Where the given intercept value which will be our term \[c\] .
\[ = \, - \,\dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303\,R}}\]
Now, we need to find \[{E_a}\], i.e., activation energy.
So, let’s write the reaction in which the values are given;
slope \[ = \, - 6670\,K\]
let’s observe the equation, we need to find activation and we have the value of slope.
So,
Slope of the line \[ = \, - \,\dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303\,R}}\]
\[{E_a}\, = \, - 2.303\,R\, \times \,slope\,of\,the\,line\]
\[slope\, = \, - 6670\,K\]
\[{E_a}\, = \, - 2.303\,R\, \times \,8.314\, \times \,( - 6670)\]
\[ = 127711.4\]
\[ = 127.71\,KJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
So, the activation energy is \[127.71\,KJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option \[B.\,127.71\,kJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
Note:A catalyst is a chemical substance that either increases or decreases the rate of a chemical reaction. In the case of activation energy, a catalyst lowers it. Since, the energies of the reactants will remain the same. A catalyst only changes the activation energy. There can be positive catalysts or else negative catalysts too.
Complete step-by-step answer:The given Arrhenius equation;
\[{\text{log}}\,{\text{k}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{constant}}\,{\text{ - }}\,\dfrac{{{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}}}{{{\text{2}}{\text{.303}}}}\,{\text{ \times }}\,\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}\]
Let’s write constant as \[log{\text{ }}A\] ;
Now, we know that the plotted graph is a straight line; which means,
\[y\, = \,c\, + \,mx\]
Therefore, \[y\] will be \[\log \,k\], \[c\] will be \[\,{\text{constant}}\,\]i.e., \[log{\text{ }}A\] and the remaining term \[mx\] will be \[{\text{ - }}\,\dfrac{{{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}}}{{{\text{2}}{\text{.303}}}}\,{\text{ \times }}\,\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}\] where \[x\]will be \[\left[ {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}} \right]\].

In this graph, we are able to observe that \[\left[ {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{T}}}} \right]\] which is on \[x\] axis and \[\log \,k\] values on \[y\] axis.
Where the given intercept value which will be our term \[c\] .
\[ = \, - \,\dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303\,R}}\]
Now, we need to find \[{E_a}\], i.e., activation energy.
So, let’s write the reaction in which the values are given;
slope \[ = \, - 6670\,K\]
let’s observe the equation, we need to find activation and we have the value of slope.
So,
Slope of the line \[ = \, - \,\dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303\,R}}\]
\[{E_a}\, = \, - 2.303\,R\, \times \,slope\,of\,the\,line\]
\[slope\, = \, - 6670\,K\]
\[{E_a}\, = \, - 2.303\,R\, \times \,8.314\, \times \,( - 6670)\]
\[ = 127711.4\]
\[ = 127.71\,KJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
So, the activation energy is \[127.71\,KJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option \[B.\,127.71\,kJmo{l^{ - 1}}\]
Note:A catalyst is a chemical substance that either increases or decreases the rate of a chemical reaction. In the case of activation energy, a catalyst lowers it. Since, the energies of the reactants will remain the same. A catalyst only changes the activation energy. There can be positive catalysts or else negative catalysts too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




