
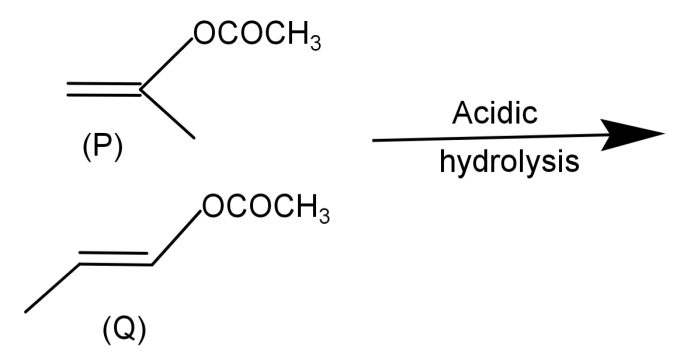
Product formed by (P) and (Q) can be differentiated by:
(A) 2,4-DNP
(B) Lucas reagent ($ZnC{l_2} + conc.HCl$)
(C) $NaHS{O_3}$
(D) Fehling’s solution

Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Acid hydrolysis of esters results in the formation of an enol group first, which further undergoes tautomerism to form ketone or aldehyde according to the groups present on the double bond. Now we need to find out which of the tests given in the options are used to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all let us start by seeing what are the products of acid hydrolysis of (P) and (Q).
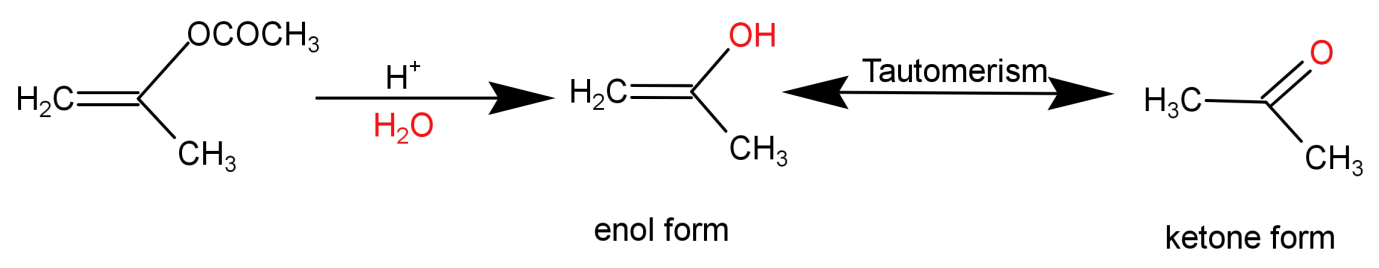
For (P): This is an ester. An ester on acid hydrolysis gives an enol form as shown in the reaction below, which further undergoes tautomerism and leads to the formation of a ketone. The reaction is shown below:
For (Q): This is also an ester and so on acid hydrolysis it gives an enol form as shown in the reaction below, this further undergoes tautomerism leading to the formation of aldehyde. The reaction is shown below:

-Now we will check the options regarding which one of them can separate a ketone from an aldehyde.
For (A): 2,4-DNP is not used for differentiation of aldehydes and ketones. It tests for carbonyl groups which can be for both aldehydes and ketones.
For (B): Lucas reagent ($ZnC{l_2} + conc.HCl$) is done to differentiate between tertiary, primary and secondary alcohols. Tertiary alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent very fast while primary alcohol does not react with it noticeably.
For (C): $NaHS{O_3}$ can also react with both aldehydes and methyl ketones. And the product of compound (P) is a methyl ketone, hence $NaHS{O_3}$ cannot be used to differentiate between the products of compound (P) and (Q).
For (D): Fehling’s solution: This test can be used to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones. Fehling’s reagent oxidises aldehyde and gives a positive result, but ketones do not give a positive result unless they are α-hydroxy ketones. So, Fehling’s solution can be used to distinguish between the products of compound (P) and (Q).
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Acid hydrolysis is basically the reverse of esterification. Also do not get confused between option (C) and option (D) since both can be used to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones. But since the product of (P) is a methyl ketone it would react with $NaHS{O_3}$ as well and so it cannot be used to differentiate here. Both (P) and (Q) are esters but the formation of ketone in (P) and an aldehyde in (Q) is due to difference in the methyl group at the double bond.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all let us start by seeing what are the products of acid hydrolysis of (P) and (Q).
For (P): This is an ester. An ester on acid hydrolysis gives an enol form as shown in the reaction below, which further undergoes tautomerism and leads to the formation of a ketone. The reaction is shown below:

For (Q): This is also an ester and so on acid hydrolysis it gives an enol form as shown in the reaction below, this further undergoes tautomerism leading to the formation of aldehyde. The reaction is shown below:

-Now we will check the options regarding which one of them can separate a ketone from an aldehyde.
For (A): 2,4-DNP is not used for differentiation of aldehydes and ketones. It tests for carbonyl groups which can be for both aldehydes and ketones.
For (B): Lucas reagent ($ZnC{l_2} + conc.HCl$) is done to differentiate between tertiary, primary and secondary alcohols. Tertiary alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent very fast while primary alcohol does not react with it noticeably.
For (C): $NaHS{O_3}$ can also react with both aldehydes and methyl ketones. And the product of compound (P) is a methyl ketone, hence $NaHS{O_3}$ cannot be used to differentiate between the products of compound (P) and (Q).
For (D): Fehling’s solution: This test can be used to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones. Fehling’s reagent oxidises aldehyde and gives a positive result, but ketones do not give a positive result unless they are α-hydroxy ketones. So, Fehling’s solution can be used to distinguish between the products of compound (P) and (Q).
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Acid hydrolysis is basically the reverse of esterification. Also do not get confused between option (C) and option (D) since both can be used to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones. But since the product of (P) is a methyl ketone it would react with $NaHS{O_3}$ as well and so it cannot be used to differentiate here. Both (P) and (Q) are esters but the formation of ketone in (P) and an aldehyde in (Q) is due to difference in the methyl group at the double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




