
What is primarily responsible for the hardness of Diamond?
A. Hydrogen bonding
B. Ionic Bonding
C. Network Bonding
D. London dispersion force
E. Metallic Bonding
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the knowledge of binding forces that held the atoms together to form a substance. Diamond is the allotrope of carbon that has vast structure and it is a network solid. It creates some unique properties in diamond and it has wide applications in different fields.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrogen Bonding: this is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction force can only be present in the compound where hydrogen is attached to a highly electronegative atom like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. Because of the difference in electronegativity electrons of the bond will be partially shifted towards the high electronegative atom and that will create partial negative charge on the highly electronegative atom and hydrogen will be having partial positive charge. Now this positively charged hydrogen will be attracted towards the negatively charge atom of adjacent molecule and will form a weak bond that is known as Hydrogen bonding.
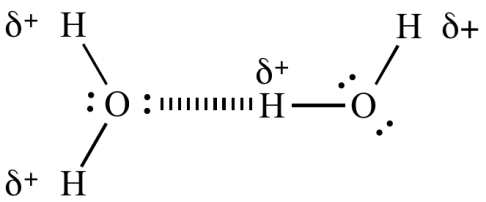
- Ionic Bonding: when a metal atom and a nonmetal atom come together to form a bond, metal loses its electron and forms a positively charged ion called cation and nonmetal atom gains that electron and forms a negatively charged ion called anion. Now these oppositely charged ions will be attracted towards each-other and held together by strong electrostatic forces and this bonding is known as ionic bonding.
- Network Bonding: This type of bonding is present in the compounds where atoms have the tendency of catenation and form long branches. Carbon has a unique property of catenation that’s why it's allotrope and compounds form long networks extended throughout the materials. Allotrope of Carbon like diamond and graphite are network solids having vast structure and their way of networking gives its allotrope some unique features.
- London dispersion force: It is a type of van der waals force. It weakest intermolecular forces act between two induced dipoles, that’s why it is also called as induced dipole- induced dipole attraction force. This type of attraction force is found in non-polar molecules and noble gases.
- Metallic bonding: This type of bonding is generally present between metal atoms. In this type of bond collective sharing of sea of valence electrons between many positively charged metal ions. Because of the presence of these free electrons metals are the good conductor of heat and electricity.
In diamond, Carbon atoms are arranged tetrahedrally. It has a three dimensional structure that results in an infinite network of atoms and this network bonding is responsible for the hardness of diamond.
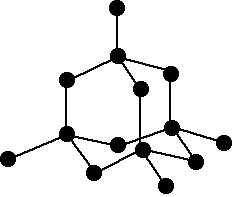
The correct answer is option “C” .
Additional Information :
- Other than the hardness diamond has following physical properties:
- Low Coefficient of friction
- High thermal conductivity
- High electrical resistivity
- Low thermal expansion coefficient
- High strength
- Biologically compatible
- Resistant to corrosion
Note: Whenever you have to find out the binding forces those are responsible for the certain specific characteristic into a substance then observe it closely. If metal and non-metal are together then that compound will be ionic and all the major properties of that compound will be the attribution of strong electrostatic forces or ionic forces. If Hydrogen is attached to a highly electronegative atom then hydrogen bonding may be the reason for some unique properties. In case of non-polar compounds, attraction force between their particles will be London dispersion forces. In pure metals metallic bonding is responsible for their properties and in network solids like diamond, graphite, silica etc. network bonding gives them unique features.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrogen Bonding: this is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction force can only be present in the compound where hydrogen is attached to a highly electronegative atom like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. Because of the difference in electronegativity electrons of the bond will be partially shifted towards the high electronegative atom and that will create partial negative charge on the highly electronegative atom and hydrogen will be having partial positive charge. Now this positively charged hydrogen will be attracted towards the negatively charge atom of adjacent molecule and will form a weak bond that is known as Hydrogen bonding.
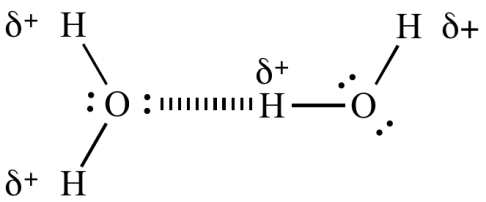
- Ionic Bonding: when a metal atom and a nonmetal atom come together to form a bond, metal loses its electron and forms a positively charged ion called cation and nonmetal atom gains that electron and forms a negatively charged ion called anion. Now these oppositely charged ions will be attracted towards each-other and held together by strong electrostatic forces and this bonding is known as ionic bonding.
- Network Bonding: This type of bonding is present in the compounds where atoms have the tendency of catenation and form long branches. Carbon has a unique property of catenation that’s why it's allotrope and compounds form long networks extended throughout the materials. Allotrope of Carbon like diamond and graphite are network solids having vast structure and their way of networking gives its allotrope some unique features.
- London dispersion force: It is a type of van der waals force. It weakest intermolecular forces act between two induced dipoles, that’s why it is also called as induced dipole- induced dipole attraction force. This type of attraction force is found in non-polar molecules and noble gases.
- Metallic bonding: This type of bonding is generally present between metal atoms. In this type of bond collective sharing of sea of valence electrons between many positively charged metal ions. Because of the presence of these free electrons metals are the good conductor of heat and electricity.
In diamond, Carbon atoms are arranged tetrahedrally. It has a three dimensional structure that results in an infinite network of atoms and this network bonding is responsible for the hardness of diamond.

The correct answer is option “C” .
Additional Information :
- Other than the hardness diamond has following physical properties:
- Low Coefficient of friction
- High thermal conductivity
- High electrical resistivity
- Low thermal expansion coefficient
- High strength
- Biologically compatible
- Resistant to corrosion
Note: Whenever you have to find out the binding forces those are responsible for the certain specific characteristic into a substance then observe it closely. If metal and non-metal are together then that compound will be ionic and all the major properties of that compound will be the attribution of strong electrostatic forces or ionic forces. If Hydrogen is attached to a highly electronegative atom then hydrogen bonding may be the reason for some unique properties. In case of non-polar compounds, attraction force between their particles will be London dispersion forces. In pure metals metallic bonding is responsible for their properties and in network solids like diamond, graphite, silica etc. network bonding gives them unique features.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




