
Predict the shape of \[N{H_3}\] and \[PC{l_3}\].
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory abbreviated as VSEPR theory is based on the premise that there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a manner in which this electron pair repulsion is minimalized. This arrangement of the atom determines the geometry of the resulting molecule. The VSEPR theory is used to predict the shape of the molecules from the electron pairs that surround the central atoms of the molecule. VSEPR theory is based on the assumption that the molecule will take a shape such that electronic repulsion in the valence shell of that atom is minimized.
Complete answer:
Using VSEPR theory, let us try to predict the shapes of \[N{H_3}\] and \[PC{l_3}\]:
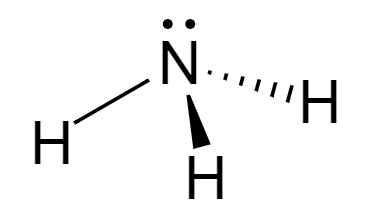
\[N{H_3}\] is ammonia that has 3 Hydrogens attached to it. It has 1 lone pair and 3 \[\sigma \] bonds. Its hybridization is given by:
$ Hybridisation = {\text{ }}Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ }}bonds + Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}lone{\text{ }}pairs \\
Hybridisation = 3 + 1 = 4 \\ $
Therefore, it is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized and arranged in tetrahedral geometry.
The shape of \[N{H_3}\] is trigonal pyramidal.
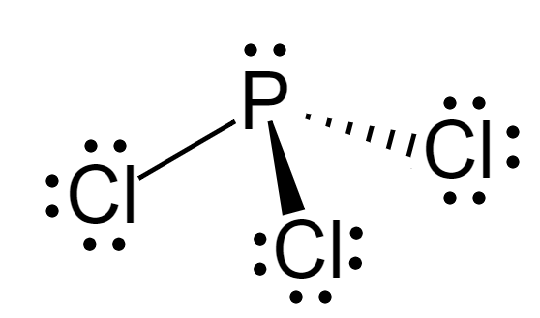
\[PC{l_3}\] is phosphorus trichloride that has 3 chlorine atoms attached to it. It has 1 lone pair and 3 \[\sigma \] bonds. Its hybridization is given by:
$ Hybridisation = {\text{ }}Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ }}bonds + Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}lone{\text{ }}pairs \\
Hybridisation = 3 + 1 = 4 \\ $
Therefore, it is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized and arranged in tetrahedral geometry.
The shape of \[PC{l_3}\] is trigonal pyramidal.
Hence, the shape of \[N{H_3}\] and \[PC{l_3}\] is trigonal pyramidal.
Note:
Bond angle possessed by \[PC{l_3}\] is approximately equal to \[{100^ \circ }\]which is mainly due to the disproportionate influence or greater repulsion of the phosphorus lone pair which makes it deviate from the ideal angle of $109^o$. Whereas in case of \[N{H_3}\], the bond angle is equal to \[{107^ \circ }\].
Complete answer:
Using VSEPR theory, let us try to predict the shapes of \[N{H_3}\] and \[PC{l_3}\]:
\[N{H_3}\] is ammonia that has 3 Hydrogens attached to it. It has 1 lone pair and 3 \[\sigma \] bonds. Its hybridization is given by:
$ Hybridisation = {\text{ }}Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ }}bonds + Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}lone{\text{ }}pairs \\
Hybridisation = 3 + 1 = 4 \\ $
Therefore, it is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized and arranged in tetrahedral geometry.
The shape of \[N{H_3}\] is trigonal pyramidal.

\[PC{l_3}\] is phosphorus trichloride that has 3 chlorine atoms attached to it. It has 1 lone pair and 3 \[\sigma \] bonds. Its hybridization is given by:
$ Hybridisation = {\text{ }}Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ }}bonds + Number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}lone{\text{ }}pairs \\
Hybridisation = 3 + 1 = 4 \\ $
Therefore, it is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized and arranged in tetrahedral geometry.
The shape of \[PC{l_3}\] is trigonal pyramidal.

Hence, the shape of \[N{H_3}\] and \[PC{l_3}\] is trigonal pyramidal.
Note:
Bond angle possessed by \[PC{l_3}\] is approximately equal to \[{100^ \circ }\]which is mainly due to the disproportionate influence or greater repulsion of the phosphorus lone pair which makes it deviate from the ideal angle of $109^o$. Whereas in case of \[N{H_3}\], the bond angle is equal to \[{107^ \circ }\].
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




