
What is polarisation of light? Explain polarisation of light by reflection with the suitable diagram and hence derive Brewster’s law.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: Light waves can have vibrations in several planes. Polarised light has vibration in only one plane. Refraction can be used to polarise light. There is a specific angle in which the polarization due to reflection is maximum. That angle is given by the Brewster’s law.
Complete step by step answer:
Light waves can have multiple planes of vibrations. When the light wave has vibrations in several planes, it is called unpolarized light. Now, we can restrict the vibration into specific planes. When the light has only one plane of motion, that is called polarized light. The process of converting unpolarized light into polarized light is called polarization of light. The following diagram shows the polarization of light.
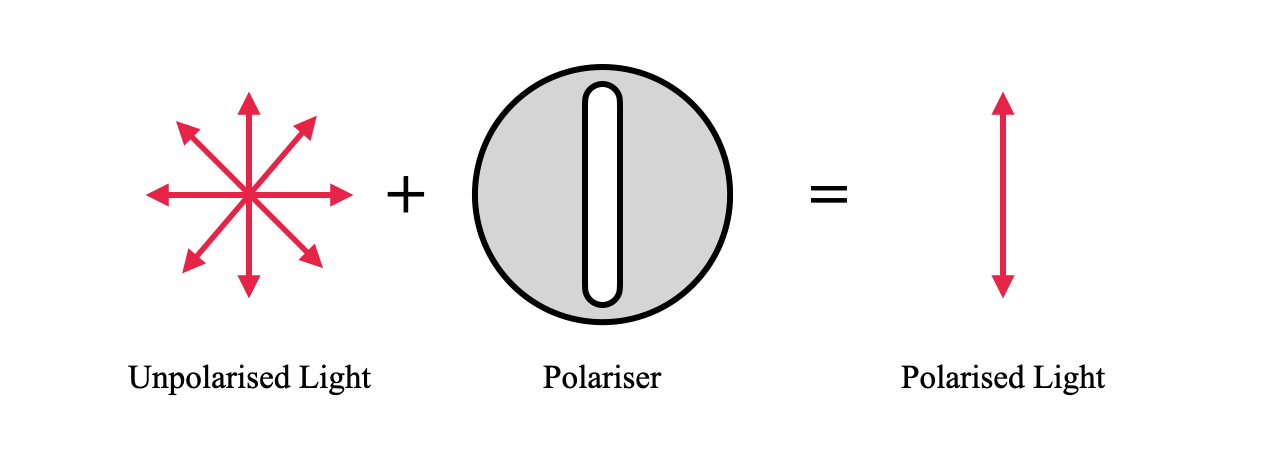
This diagram shows the polarization using a polarizing filter.
Polarization By Reflection:
If light incidents on a refractive surface so that the refracted light and the reflected light are at 90° angle, then the reflected light will be linearly polarized, and the plane of polarization will be parallel to the plane of the interface.
The following diagram shows the polarization by reflection.
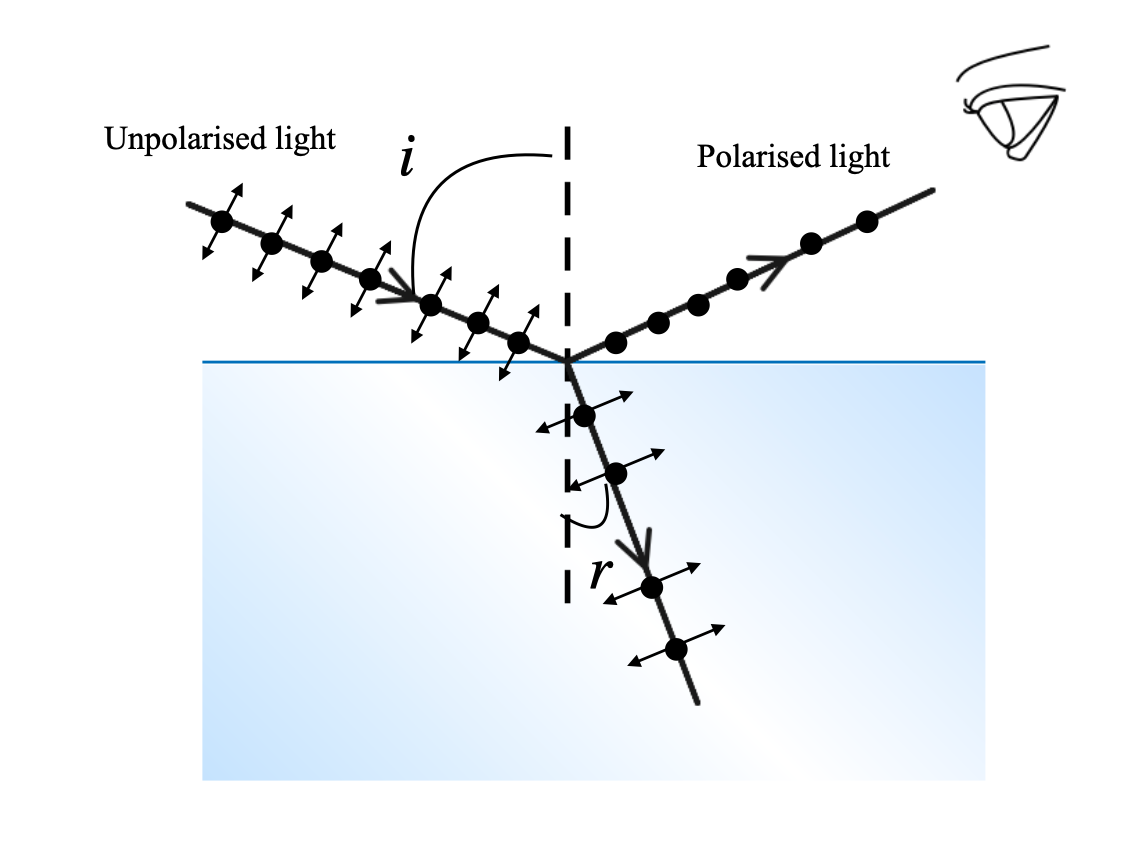
The angle of incidence that produces 90° angle between the refracted and reflected light wave is called Brewster angle.
When the light falls on the medium at Brewster angle, the reflected wave has no electric field vectors that are parallel to the refracted ray. The only direction possible for the light wave is perpendicular to the plane of the image. So, the reflected wave is completely polarized. Whereas, the refracted wave is partially polarized.
Brewster’s law formula is given by, $\mu =\tan i$
Where,
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the material
$i$ is the polarization angle.
We can write from Snell’s law,
$\mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$.............(1)
The reflected light and refracted light should be perpendicular to each other.
Hence, we can write,
$i+r+90=180$
$\Rightarrow r=90-i$
Hence, we can modify equation (1) such that,
$\mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin (90-i)}$
$\Rightarrow \mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\cos i}$
$\Rightarrow \mu =\tan i$
This is the formula of Brewster’s law.
Note: There are several methods to polarise a light. Polarization by reflection is one of the easiest ways to polarize a light beam. Other methods include - polarization by scattering, polarizer, refraction etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Light waves can have multiple planes of vibrations. When the light wave has vibrations in several planes, it is called unpolarized light. Now, we can restrict the vibration into specific planes. When the light has only one plane of motion, that is called polarized light. The process of converting unpolarized light into polarized light is called polarization of light. The following diagram shows the polarization of light.

This diagram shows the polarization using a polarizing filter.
Polarization By Reflection:
If light incidents on a refractive surface so that the refracted light and the reflected light are at 90° angle, then the reflected light will be linearly polarized, and the plane of polarization will be parallel to the plane of the interface.
The following diagram shows the polarization by reflection.

The angle of incidence that produces 90° angle between the refracted and reflected light wave is called Brewster angle.
When the light falls on the medium at Brewster angle, the reflected wave has no electric field vectors that are parallel to the refracted ray. The only direction possible for the light wave is perpendicular to the plane of the image. So, the reflected wave is completely polarized. Whereas, the refracted wave is partially polarized.
Brewster’s law formula is given by, $\mu =\tan i$
Where,
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the material
$i$ is the polarization angle.
We can write from Snell’s law,
$\mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$.............(1)
The reflected light and refracted light should be perpendicular to each other.
Hence, we can write,
$i+r+90=180$
$\Rightarrow r=90-i$
Hence, we can modify equation (1) such that,
$\mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin (90-i)}$
$\Rightarrow \mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\cos i}$
$\Rightarrow \mu =\tan i$
This is the formula of Brewster’s law.
Note: There are several methods to polarise a light. Polarization by reflection is one of the easiest ways to polarize a light beam. Other methods include - polarization by scattering, polarizer, refraction etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




