
How do pi and sigma bonds relate to hybridization?
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: We know that a single bond formed between the two atoms containing one sigma bond, a double bond formed between the two atoms containing one sigma and one pi bond. A triple bond formed between the two atoms containing one sigma and two pi bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
The property by which the atomic orbitals fuse with each other to form new hybridized orbitals is known as hybridization. From the hybridization of the central atom, one can know the number of sigma bonds around the central atom.
For the first atom, we can see that it forms three sigma bonds, two of them are formed with two hydrogen atoms and one of them is with the adjacent carbon atom. We can see the double bond present between and the second carbon atom, the second bond is a pi bond that involves the sideways overlap of the hybridized orbitals.
It needs only one orbital for the sideways overlap and hence it will be $ s{{p}^{2}} $ hybridized. An example for pi and sigma bond hybridization is the structure of propadiene so that we will get an idea about the hybridization of the carbon atoms based on any single, double, and triple bonds that are present in the molecule. The structure of propadiene is as follows:
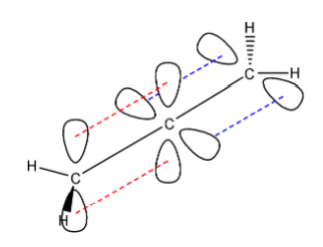
Here, we can see that the solid black bond between the carbon atoms is the sigma bond. The dashed red lines form the pi bond between the first and the second carbon atom, and the dashed blue lines form the pi bond between the second and the third carbon atom.
Note:
Remember that although the central carbon atom has only double bonds involved, it is hybridized. We should always consider the number of pi bonds that the carbon atom is forming and not just the type of bonds that it is forming.
Complete step by step solution:
The property by which the atomic orbitals fuse with each other to form new hybridized orbitals is known as hybridization. From the hybridization of the central atom, one can know the number of sigma bonds around the central atom.
For the first atom, we can see that it forms three sigma bonds, two of them are formed with two hydrogen atoms and one of them is with the adjacent carbon atom. We can see the double bond present between and the second carbon atom, the second bond is a pi bond that involves the sideways overlap of the hybridized orbitals.
It needs only one orbital for the sideways overlap and hence it will be $ s{{p}^{2}} $ hybridized. An example for pi and sigma bond hybridization is the structure of propadiene so that we will get an idea about the hybridization of the carbon atoms based on any single, double, and triple bonds that are present in the molecule. The structure of propadiene is as follows:

Here, we can see that the solid black bond between the carbon atoms is the sigma bond. The dashed red lines form the pi bond between the first and the second carbon atom, and the dashed blue lines form the pi bond between the second and the third carbon atom.
Note:
Remember that although the central carbon atom has only double bonds involved, it is hybridized. We should always consider the number of pi bonds that the carbon atom is forming and not just the type of bonds that it is forming.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




