
How is phenol converted to salicylic acid?
Answer
519.3k+ views
Hint :Benzene attached to a hydroxyl functional group is called phenol. Salicylic acid is a derivative of phenol itself with an additional carboxylic acid functional group attached to a position ortho to the hydroxyl group of phenol.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Salicylic acid is an important industrial organic compound that can be derived from phenol through two different types of reactions. It contains the same structure as that of phenol with an additional carboxylic acid group $ (COOH) $ placed at the ortho position (adjacent position) of the hydroxyl group of phenol.
The two methods of converting phenol to salicylic acid are as follows:
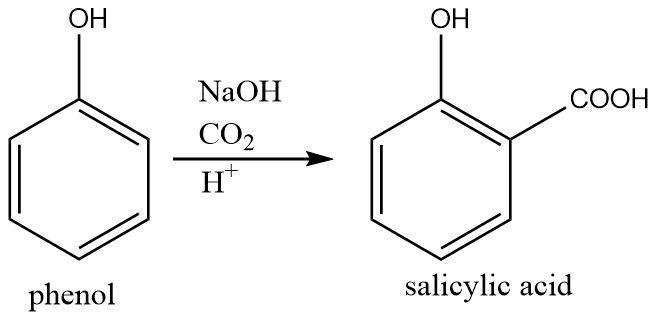
Kolbe-Schmitt reaction: This reaction involves the conversion of acidic phenol into a phenoxide ion in presence of sodium hydroxide base. This is followed by the attack of phenoxide ion of the electrophilic carbon dioxide gas resulting in a carboxylate group getting attached at the ortho position. The reaction ends with a mild acidic hydrolysis that gives salicylic acid.
Thus it is a base facilitated carboxylation of phenol.
The overall reaction can be written as follows:
$ {\text{phenol}}\xrightarrow[{{H^ + }}]{\begin{subarray}{l}
NaOH \\
C{O_2}
\end{subarray} }{\text{salicylic acid}} $
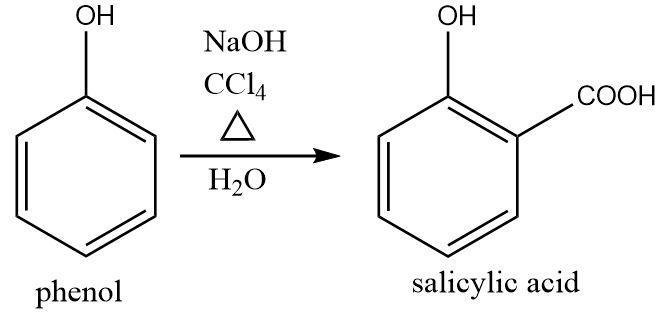
Reimer–Tiemann reaction: This reaction involves the conversion of phenol to salicylic acid by treatment of phenol at high temperatures with carbon tetrachloride in the presence of an alkali followed by mild hydrolysis.
The reaction can be written as follows:
$ {\text{phenol}}\xrightarrow[{{H_2}O}]{\begin{subarray}{l}
NaOH \\
CC{l_4}
\end{subarray} }{\text{salicylic acid}} $
Note :
The Reimer–Tiemann reaction can be performed with both chloroform as well as carbon tetrachloride. The reaction in the presence of chloroform as a reagent gives salicylaldehyde, however that in the presence of carbon tetrachloride gives salicylic acid as the desired product.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Salicylic acid is an important industrial organic compound that can be derived from phenol through two different types of reactions. It contains the same structure as that of phenol with an additional carboxylic acid group $ (COOH) $ placed at the ortho position (adjacent position) of the hydroxyl group of phenol.
The two methods of converting phenol to salicylic acid are as follows:
Kolbe-Schmitt reaction: This reaction involves the conversion of acidic phenol into a phenoxide ion in presence of sodium hydroxide base. This is followed by the attack of phenoxide ion of the electrophilic carbon dioxide gas resulting in a carboxylate group getting attached at the ortho position. The reaction ends with a mild acidic hydrolysis that gives salicylic acid.
Thus it is a base facilitated carboxylation of phenol.
The overall reaction can be written as follows:
$ {\text{phenol}}\xrightarrow[{{H^ + }}]{\begin{subarray}{l}
NaOH \\
C{O_2}
\end{subarray} }{\text{salicylic acid}} $

Reimer–Tiemann reaction: This reaction involves the conversion of phenol to salicylic acid by treatment of phenol at high temperatures with carbon tetrachloride in the presence of an alkali followed by mild hydrolysis.
The reaction can be written as follows:
$ {\text{phenol}}\xrightarrow[{{H_2}O}]{\begin{subarray}{l}
NaOH \\
CC{l_4}
\end{subarray} }{\text{salicylic acid}} $

Note :
The Reimer–Tiemann reaction can be performed with both chloroform as well as carbon tetrachloride. The reaction in the presence of chloroform as a reagent gives salicylaldehyde, however that in the presence of carbon tetrachloride gives salicylic acid as the desired product.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




