
Out of the given diagram, the correctly labelled diagram showing budding in yeast is :
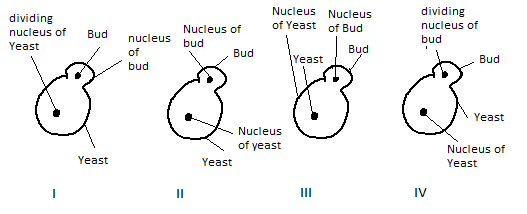
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Answer
556.2k+ views
Hint: In an asymmetric separation mechanism called budding, most yeasts replicate asexually. Next, the parent cell develops a small protuberance that expands to a full size and forms a bud. The nucleus divides into a daughter nucleus of the parent cell and migrates to the daughter cell.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction mode of reproduction by budding, where the parent cell develops a small bud (also known as a bleb or daughter cell), is the most common mode of yeast vegetative growth. The nucleus splits into the parent cell's daughter nucleus and migrates to the daughter cell.
This differs but may be as short as one hour, with the pressure, the growth medium, and the temperature. At this point, in one day, a single cell will develop to become a barely visible colony. In yeast cultures, the growth activity is close to that of bacteria.
The essential characteristics of asexual reproduction include the following:
1)A single parent is involved.
2)No fertilization or development of the gamete takes place.
3)This replication process takes place during a relatively brief amount of time.
4)Organisms rapidly replicate and expand.
5)The offspring are genetically equivalent.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: There are differences between budding in yeast and hydra:
1)Although hydra is a multicellular organism, yeast is a single-cell organism.
2)The bud originates in the yeast from a tiny protuberance on the parent body, while the bud occurs because of the repeated mitotic division in hydra.
3)The yeast gets its daughter nuclei and it may or may not differentiate from the parent body, while the daughter buds are multicellular in hydra and daughter buds do not grow.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction mode of reproduction by budding, where the parent cell develops a small bud (also known as a bleb or daughter cell), is the most common mode of yeast vegetative growth. The nucleus splits into the parent cell's daughter nucleus and migrates to the daughter cell.
This differs but may be as short as one hour, with the pressure, the growth medium, and the temperature. At this point, in one day, a single cell will develop to become a barely visible colony. In yeast cultures, the growth activity is close to that of bacteria.
The essential characteristics of asexual reproduction include the following:
1)A single parent is involved.
2)No fertilization or development of the gamete takes place.
3)This replication process takes place during a relatively brief amount of time.
4)Organisms rapidly replicate and expand.
5)The offspring are genetically equivalent.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: There are differences between budding in yeast and hydra:
1)Although hydra is a multicellular organism, yeast is a single-cell organism.
2)The bud originates in the yeast from a tiny protuberance on the parent body, while the bud occurs because of the repeated mitotic division in hydra.
3)The yeast gets its daughter nuclei and it may or may not differentiate from the parent body, while the daughter buds are multicellular in hydra and daughter buds do not grow.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




