
What is the order of acidic strength of the given molecules?
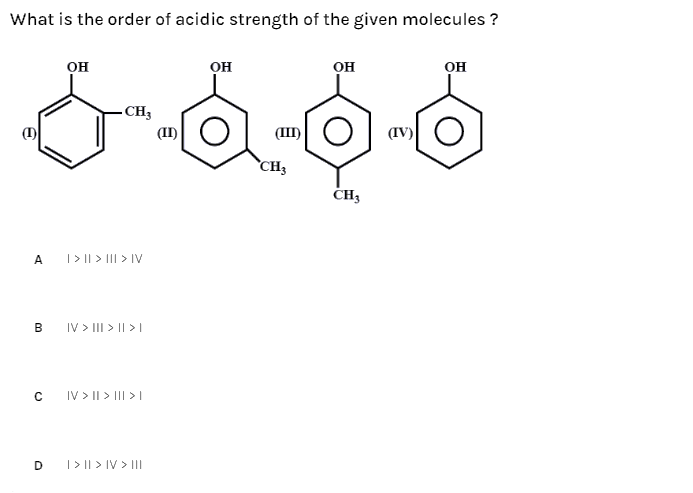
(A)- I > II > III > IV
(B)- IV > III > II > I
(C)- IV > II > III > I
(D)- I > II > IV > III

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The resonance stability of a molecule can be affected by the addition of a substituent through its inductive and hyperconjugation effect by changing the electron–density in the O-H group.
Complete step by step answer:
The molecules given are o-cresol, m-cresol, p-cresol and phenol where the cresol is formed by adding a methyl group to the ortho-, para-, meta- position of the phenol molecule.
As the acids have a tendency to give away protons easily. In order to determine the acidic strength of given molecules the ease with which they lose their proton in the O-H bond is observed.
- The phenol molecule having the -OH group bonded to the benzene ring is an electron-donating group. But the carbon in the benzene ring to with the hydroxyl group is attached is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised and attracts the electron in the C – OH bond towards itself, decreasing the electron density over the oxygen atom and thus, increasing the polarity of the O – H bond.
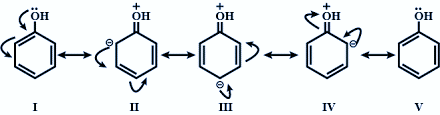
Through resonance it is seen that the electrons attracted by $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised carbon move around the ring creating partial positive charge on the oxygen atom. Hence, making the O - H bond more polar and easily loses its proton forming the phenoxide ion which is further stabilised by resonance in the benzene ring. Therefore, in phenol only resonance effect decides its acidic strength.

- Whereas, in the cresol molecule, the methyl group substituent is also an electron-donating group which affects the acidic strength of the phenol molecule on substitution by increasing the electron density on the O-H bond.
The two phenomenons incorporating hyperconjugation and inductive effects by the $-C{{H}_{3}}$ group inhibit the acidic strength of phenol molecules.
The inductive effect by methyl- group is found in all the three positions of ortho-, meta-, para- positions. But, the inductive effect at the ortho- position is more because the methyl group is close to the -OH group. Thus, increasing the electron density at this position and making the o-cresol less acidic.
Whereas, the negative charge found delocalised at the ortho- and para- positions in the phenol resonance structures, the hyperconjugation by the methyl- group affects only at the ortho- and para- and not the meta- position. So, m-cresol is only affected by the inductive effect.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Phenol > m - cresol > p - cresol > o - cresol
Note: The $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised carbon in benzene due to the greater s-character present in it holds the electrons close to the nucleus, enabling it to attract more electrons due to the increase in its electronegativity.
Complete step by step answer:
The molecules given are o-cresol, m-cresol, p-cresol and phenol where the cresol is formed by adding a methyl group to the ortho-, para-, meta- position of the phenol molecule.
As the acids have a tendency to give away protons easily. In order to determine the acidic strength of given molecules the ease with which they lose their proton in the O-H bond is observed.
- The phenol molecule having the -OH group bonded to the benzene ring is an electron-donating group. But the carbon in the benzene ring to with the hydroxyl group is attached is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised and attracts the electron in the C – OH bond towards itself, decreasing the electron density over the oxygen atom and thus, increasing the polarity of the O – H bond.
Through resonance it is seen that the electrons attracted by $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised carbon move around the ring creating partial positive charge on the oxygen atom. Hence, making the O - H bond more polar and easily loses its proton forming the phenoxide ion which is further stabilised by resonance in the benzene ring. Therefore, in phenol only resonance effect decides its acidic strength.


- Whereas, in the cresol molecule, the methyl group substituent is also an electron-donating group which affects the acidic strength of the phenol molecule on substitution by increasing the electron density on the O-H bond.
The two phenomenons incorporating hyperconjugation and inductive effects by the $-C{{H}_{3}}$ group inhibit the acidic strength of phenol molecules.
The inductive effect by methyl- group is found in all the three positions of ortho-, meta-, para- positions. But, the inductive effect at the ortho- position is more because the methyl group is close to the -OH group. Thus, increasing the electron density at this position and making the o-cresol less acidic.
Whereas, the negative charge found delocalised at the ortho- and para- positions in the phenol resonance structures, the hyperconjugation by the methyl- group affects only at the ortho- and para- and not the meta- position. So, m-cresol is only affected by the inductive effect.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Phenol > m - cresol > p - cresol > o - cresol
Note: The $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised carbon in benzene due to the greater s-character present in it holds the electrons close to the nucleus, enabling it to attract more electrons due to the increase in its electronegativity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




