
On what factors does the induced electromotive force depend?
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint:An electromotive force is induced by a change in magnetic flux, according to Faraday's law of induction. A voltage is formed when the magnetic flux through a coil is altered. The induced emf is the name given to this voltage. The current can only flow if the magnetic field changes.
Complete answer:
The induced electromotive force depends upon the following factors;
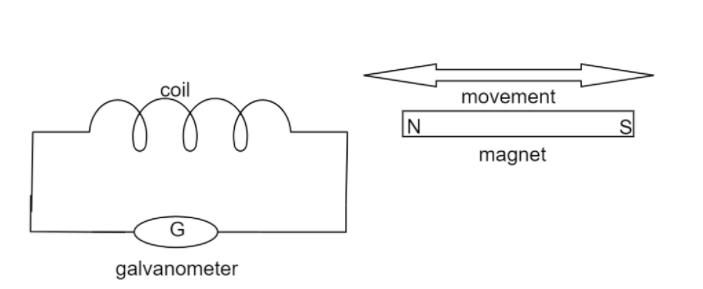
This was the setup to find the induced electromotive force. Here a coil has $N$ number of turns which is connected to a galvanometer. A magnet or the coil is moved which causes a change in the magnetic field in the coil. From this we observed, $N$ , the total number of turns in the coil, is directly proportional to the induced electromotive force.
The induced electromotive force is proportional to $A$ , which is the coil's cross-sectional area.$B$ , the strength of the magnetic field in which the coil is revolving, is directly proportional to the induced electromotive force. The induced electromotive force is proportional to ' $\omega $ ' the coil's angular velocity.
The induced electromotive force changes throughout time and is dependent on the instant '$t$'. When the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field $B$ , the induced electromotive force is greatest, and when the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field $B$ , the induced electromotive force is zero.
Note:The coil is unaffected by a steady magnetic field, yet current flows when the field changes. A galvanometer is a device that uses the deflection of a moving coil to measure a small electrical current or a function of the current.
Complete answer:
The induced electromotive force depends upon the following factors;

This was the setup to find the induced electromotive force. Here a coil has $N$ number of turns which is connected to a galvanometer. A magnet or the coil is moved which causes a change in the magnetic field in the coil. From this we observed, $N$ , the total number of turns in the coil, is directly proportional to the induced electromotive force.
The induced electromotive force is proportional to $A$ , which is the coil's cross-sectional area.$B$ , the strength of the magnetic field in which the coil is revolving, is directly proportional to the induced electromotive force. The induced electromotive force is proportional to ' $\omega $ ' the coil's angular velocity.
The induced electromotive force changes throughout time and is dependent on the instant '$t$'. When the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field $B$ , the induced electromotive force is greatest, and when the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field $B$ , the induced electromotive force is zero.
Note:The coil is unaffected by a steady magnetic field, yet current flows when the field changes. A galvanometer is a device that uses the deflection of a moving coil to measure a small electrical current or a function of the current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




