
On catalytic reduction $\text{(}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{/Pd)}$ how many alkenes will give $\text{2-methyl butane}$?
(A)$1$
(B)$2$
(C)$3$
(D)$4$
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: The process which involves gain of electrons (or hydrogen atom) by an atom or molecule is called reduction.
Catalytic hydrogenation of alkene is an electrophilic addition reaction.
Complete answer:
The substance which donates electrons in chemical reactions is called reducing agent. There are many reducing organic compounds like$\text{(}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{/Pd)}$, $\text{LiAl}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{,}\,\text{NaB}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$which causes reduction of organic compounds like alkene, and other carboxy compounds.
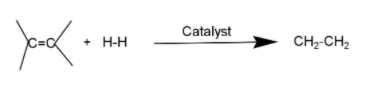
In catalytic hydrogenation alkene get reduced to alkenes with the help of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$in the presence of metal like platinum (Pt.), palladium (Pd), nickel (Ni) or rhodium (Rh).
In this reaction new sigma$\text{(C-H)}$bonds are formed. In this reaction a hydrogen atom takes place in alkene.
This reaction also forms an experimental basis of heat of hydrogenation which is used to explain the stability of isomeric alkenes. Alkynes are less reactive to catalytic hydrogenation in respect to alkene, because of the presence of stronger pi bond.
Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes takes place in three steps –
(i) absorption of hydrogen gas on the metal surface. In the presence of catalyst cleavage of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ takes place and each hydrogen atom forms attachment with the metal ion.
(ii) alkene shows an approach toward the hydrogen atom on the metal surface. Metal catalysts attract the alkene and transfer hydrogen atoms to the alkene.
(iii) Alkene reacts with the H-atom and gets reduced by forming two new $\text{C-H}$ bonds.
Two alkene molecules $\text{2-methyl-2-}\,\,\text{butene}$ and $\text{2-methyl-1-}\,\,\text{butene}$ gives $\text{2-methyl butane}$ after catalytic hydrogenation.
So, option (B) is the correct option.
Note
$\text{(}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{/Pd)}$ acts as a weak reducing agent. It reduces alkene, aldehyde and ketone but cannot reduce the carboxylic acid, ester and amides. It reduces aldehyde and ketones into corresponding alcohols.
Catalytic hydrogenation of alkene is an electrophilic addition reaction.
Complete answer:
The substance which donates electrons in chemical reactions is called reducing agent. There are many reducing organic compounds like$\text{(}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{/Pd)}$, $\text{LiAl}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{,}\,\text{NaB}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$which causes reduction of organic compounds like alkene, and other carboxy compounds.

In catalytic hydrogenation alkene get reduced to alkenes with the help of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$in the presence of metal like platinum (Pt.), palladium (Pd), nickel (Ni) or rhodium (Rh).
In this reaction new sigma$\text{(C-H)}$bonds are formed. In this reaction a hydrogen atom takes place in alkene.
This reaction also forms an experimental basis of heat of hydrogenation which is used to explain the stability of isomeric alkenes. Alkynes are less reactive to catalytic hydrogenation in respect to alkene, because of the presence of stronger pi bond.
Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes takes place in three steps –
(i) absorption of hydrogen gas on the metal surface. In the presence of catalyst cleavage of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ takes place and each hydrogen atom forms attachment with the metal ion.
(ii) alkene shows an approach toward the hydrogen atom on the metal surface. Metal catalysts attract the alkene and transfer hydrogen atoms to the alkene.
(iii) Alkene reacts with the H-atom and gets reduced by forming two new $\text{C-H}$ bonds.
Two alkene molecules $\text{2-methyl-2-}\,\,\text{butene}$ and $\text{2-methyl-1-}\,\,\text{butene}$ gives $\text{2-methyl butane}$ after catalytic hydrogenation.
So, option (B) is the correct option.
Note
$\text{(}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{/Pd)}$ acts as a weak reducing agent. It reduces alkene, aldehyde and ketone but cannot reduce the carboxylic acid, ester and amides. It reduces aldehyde and ketones into corresponding alcohols.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




