
What is the normal ray in a convex lens at a given point?
Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint : In this question we have to find the point on the convex lens where normal ray passes, it is that point of the convex lens whose distance from optical centre is two times of radius of curvature of the lens, and normal ray always passes through this point whenever ray diagram formation of lenses is done.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In optics normal ray is ray along which when light passes then light remains undeviated either in mirror or lenses .Whenever light ray goes along this ray they never deviate from its path in mirror they bounces back along the same line and when it goes in lens these ray straight without any bending of light.
On a curved surface either of mirror or lens.
Normal ray always passes through a point called the centre of curvature.
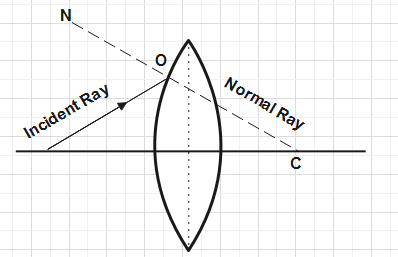
Centre of curvature is a point whose distance from the optical centre is two times the radius of that curvature. It is defined as the reflecting or refracting surface of a spherical mirror or lens from a part of a sphere. It has a centre, which is known as centre of curvature.
A lens, either a convex lens or a concave lens has two spherical surfaces. Each of these surfaces forms a part of the sphere. The centre of these two spheres are called centre of curvature
Let \[R\] is representing the distance of radius of curvature
so \[2R\] is the distance between the optical centre and centre of curvature.
In the given figure, the point where the incident ray and normal ray intersect each other at point is called point of incidence.
If the surface is plane like glass then the normal ray is perpendicular to that surface and if the surface is curved then it also perpendicular to that surface.
So we conclude that the Normal ray in a convex lens passes at a point called centre of curvature and this diagram is representing the normal ray for a convex lens.
Note: Refraction is due to change in the speed of light as it enters from one transparent medium to another. Speed of light DECREASES as the beam of light travels from the rarer medium to the denser medium. Speed of light INCREASES as the beam of light travels from denser medium to the rarer medium.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In optics normal ray is ray along which when light passes then light remains undeviated either in mirror or lenses .Whenever light ray goes along this ray they never deviate from its path in mirror they bounces back along the same line and when it goes in lens these ray straight without any bending of light.
On a curved surface either of mirror or lens.
Normal ray always passes through a point called the centre of curvature.

Centre of curvature is a point whose distance from the optical centre is two times the radius of that curvature. It is defined as the reflecting or refracting surface of a spherical mirror or lens from a part of a sphere. It has a centre, which is known as centre of curvature.
A lens, either a convex lens or a concave lens has two spherical surfaces. Each of these surfaces forms a part of the sphere. The centre of these two spheres are called centre of curvature
Let \[R\] is representing the distance of radius of curvature
so \[2R\] is the distance between the optical centre and centre of curvature.
In the given figure, the point where the incident ray and normal ray intersect each other at point is called point of incidence.
If the surface is plane like glass then the normal ray is perpendicular to that surface and if the surface is curved then it also perpendicular to that surface.
So we conclude that the Normal ray in a convex lens passes at a point called centre of curvature and this diagram is representing the normal ray for a convex lens.
Note: Refraction is due to change in the speed of light as it enters from one transparent medium to another. Speed of light DECREASES as the beam of light travels from the rarer medium to the denser medium. Speed of light INCREASES as the beam of light travels from denser medium to the rarer medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




