
Nitration and Chlorination of benzene are:
(A) Nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution respectively
(B) Electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution respectively
(C) Electrophilic substitution in both the reactions
(D) Nucleophilic substitution in both the reactions
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: The substitution reaction in which benzene acts as a nucleophile and attacks on the electrophile is called electrophilic substitution reactions. An electrophile is characterized by its electron-deficient nature.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s see the mechanism of those reactions in order to find out which type of reaction it is.
1) Nitration of benzene:
- When we allow benzene to react with the mixture of concentrated nitric and sulphuric acid, we obtain nitrobenzene as a final product.
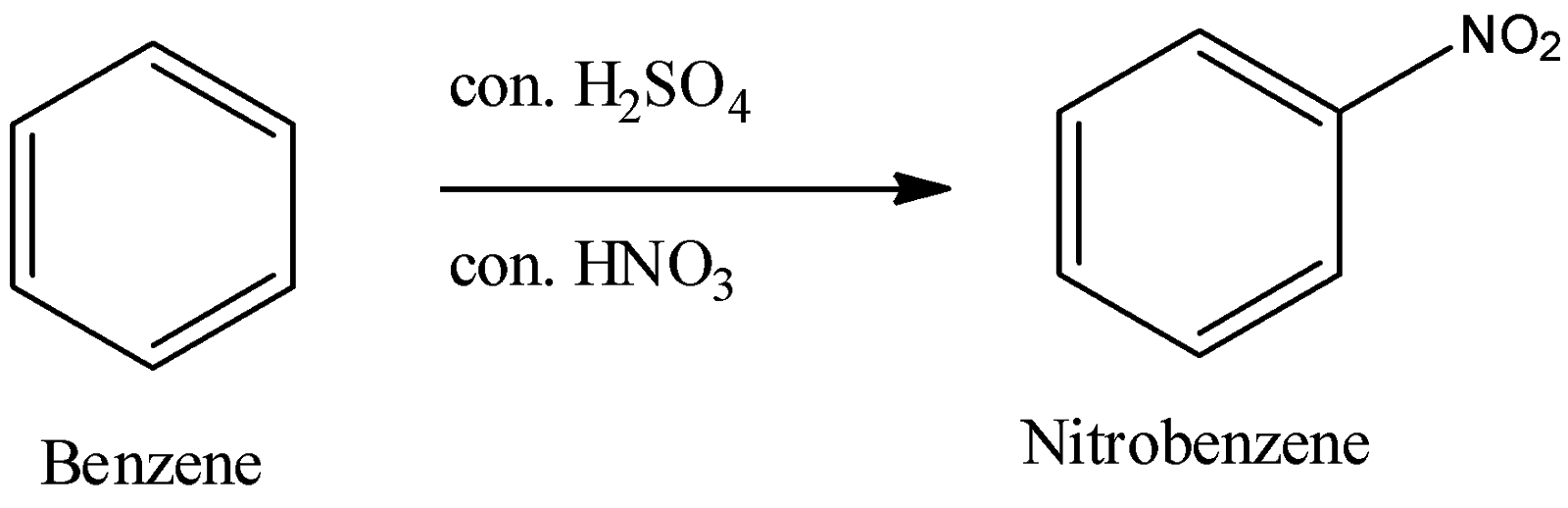
Now, let’s see what happens as sulphuric acid and nitric acid react.
\[{H_2}S{O_4} + HN{O_3} \to {H_2}O + N{O_2}^ + + HS{O_4}^ - \]
Here, we can see one of the products is nitronium ion. This nitronium is attacked by the benzene ring and substitution reaction occurs there. That can be shown as:
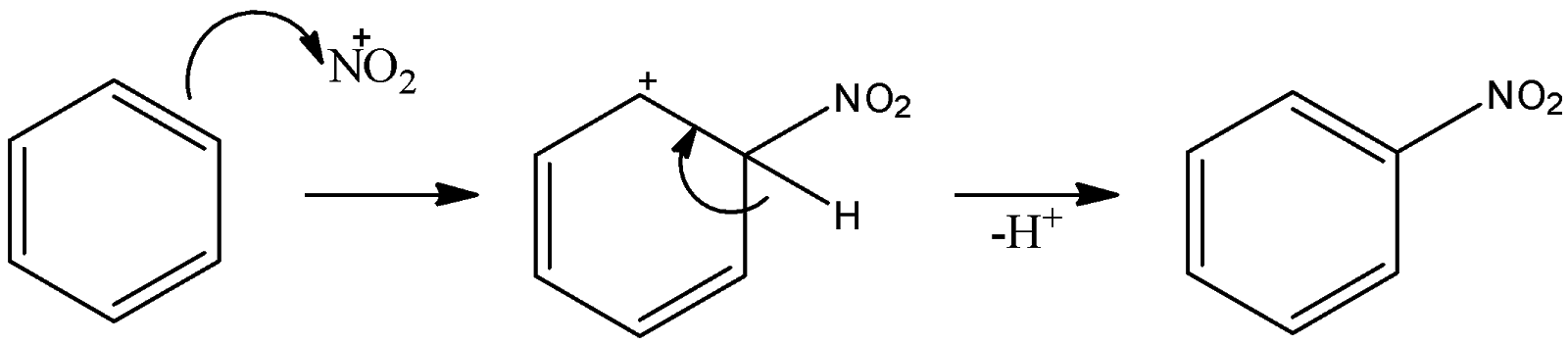
Thus, nitronium ion is an electrophile because it has a positive charge on it. These nitronium ions substitute hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring. So, we can say that an electrophile has substituted the hydrogen atom. So, this is an electrophilic substitution of benzene rings.
2) Chlorination of benzene:
The reaction of chlorination of benzene is:
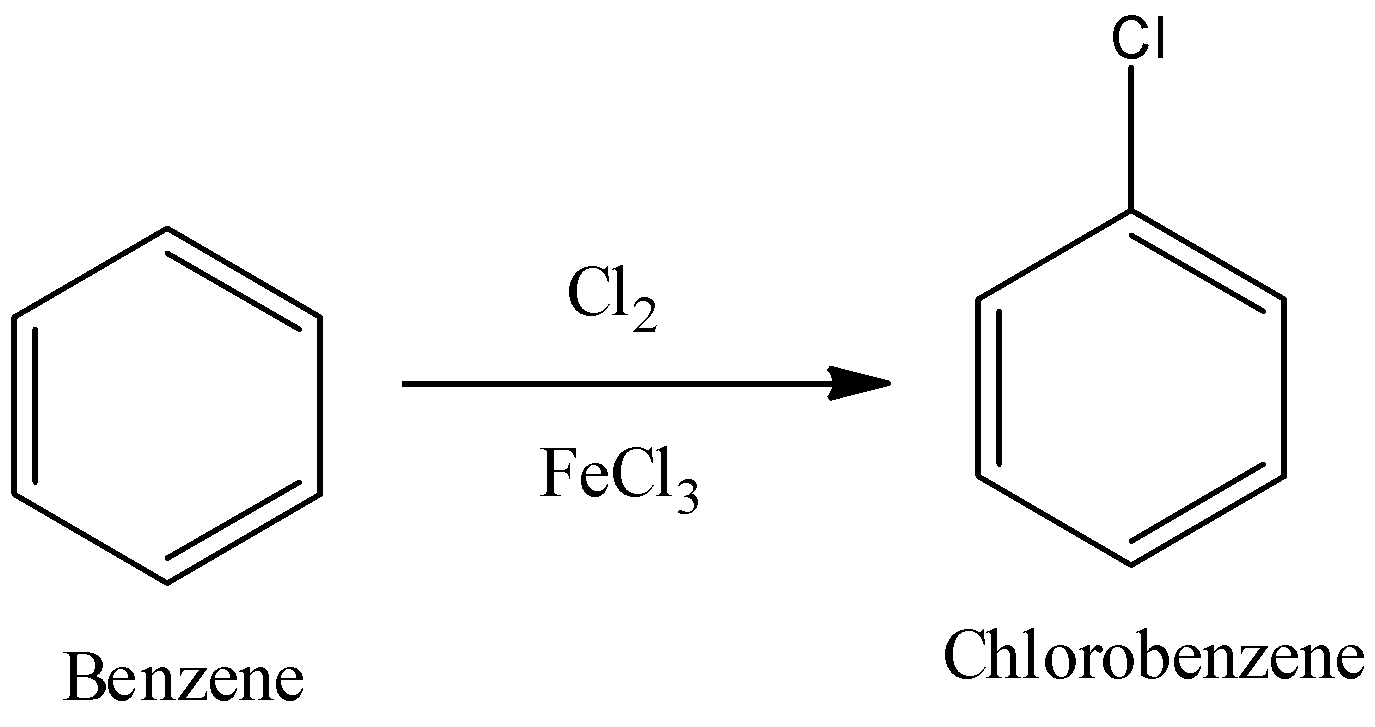
Now, we will see how ferric chloride which is a lewis acid and chlorine gas reacts. Lewis acid accepts the basic chloride ion from the chlorine gas and we get chlorine cation as one of the products.
\[FeC{l_3} + C{l_2} \to {[FeC{l_4}]^ - } + C{l^ + }\]
Now, this positively charged chlorine atom is an electrophile and this reacts with benzene to give electrophilic substitution reaction.
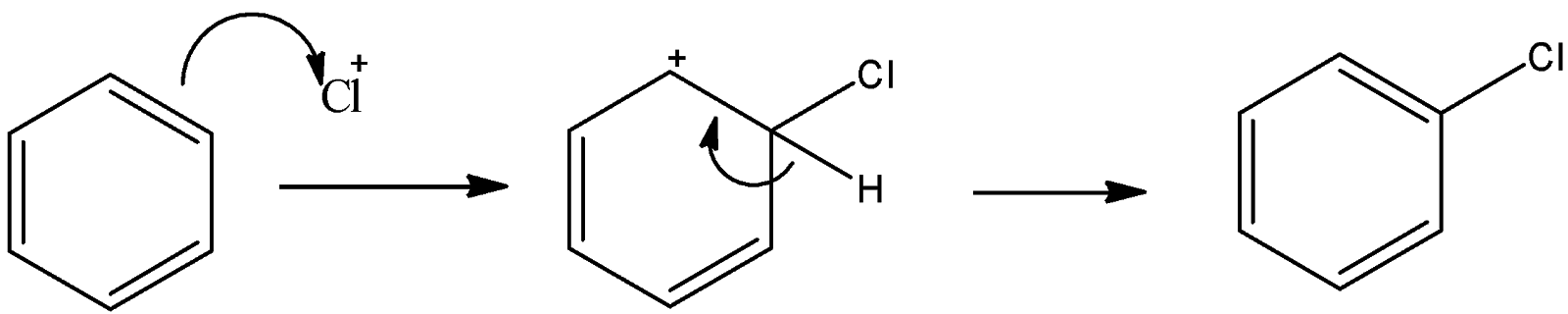
So, here also an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom. So, this is also an electrophilic substitution reaction.
So, the correct answer is (C).
Note: Note that on chlorination of benzene, we use Lewis acid to generate an electrophile from the halogen gas only. Lewis acid there can be $AlC{l_3}{\text{ or }}FeC{l_3}$ or any other metal chloride which can act as a Lewis acid.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s see the mechanism of those reactions in order to find out which type of reaction it is.
1) Nitration of benzene:
- When we allow benzene to react with the mixture of concentrated nitric and sulphuric acid, we obtain nitrobenzene as a final product.

Now, let’s see what happens as sulphuric acid and nitric acid react.
\[{H_2}S{O_4} + HN{O_3} \to {H_2}O + N{O_2}^ + + HS{O_4}^ - \]
Here, we can see one of the products is nitronium ion. This nitronium is attacked by the benzene ring and substitution reaction occurs there. That can be shown as:

Thus, nitronium ion is an electrophile because it has a positive charge on it. These nitronium ions substitute hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring. So, we can say that an electrophile has substituted the hydrogen atom. So, this is an electrophilic substitution of benzene rings.
2) Chlorination of benzene:
The reaction of chlorination of benzene is:

Now, we will see how ferric chloride which is a lewis acid and chlorine gas reacts. Lewis acid accepts the basic chloride ion from the chlorine gas and we get chlorine cation as one of the products.
\[FeC{l_3} + C{l_2} \to {[FeC{l_4}]^ - } + C{l^ + }\]
Now, this positively charged chlorine atom is an electrophile and this reacts with benzene to give electrophilic substitution reaction.

So, here also an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom. So, this is also an electrophilic substitution reaction.
So, the correct answer is (C).
Note: Note that on chlorination of benzene, we use Lewis acid to generate an electrophile from the halogen gas only. Lewis acid there can be $AlC{l_3}{\text{ or }}FeC{l_3}$ or any other metal chloride which can act as a Lewis acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




