
Name the compound
$C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_3}$
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: This is the example of unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atoms. The term unsaturated means more hydrogen atoms may be added to the hydrocarbons to make it saturated.
Complete step by step answer:
$C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_3}$
This is a But-2-ene compound. It is named so because it has a double bond on the second carbon atom .
(1) The chemical formula for butane is: ${C_4}{H_8}$ which means it is made up of four carbon atoms and eight hydrogen atoms. The $ene$ part of the name refers to an alkene. So we know that butane’s structure must include a carbon double bond.
(2) There are several different isomers or molecular structures, that this compound can form:
Additional information:
The relationships between each of these isomers are mostly constitutional, which means they have the same molecular formula but have different bond connections (Order).
Meaning to transform them, you would have to just move around the hydrogen and carbons in other words the atoms and functional groups.
Note:
These isomers of butane are made up from the same materials, they each have different properties.
With cis-beta-butylene and trans-beta-butylene the atoms are in the same order, but the polarities are not same . The $cis$ isomer is polar, with both $C{H_3}$ groups on the same side. This makes it really bulky and difficult to stack.
Complete step by step answer:
$C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_3}$
This is a But-2-ene compound. It is named so because it has a double bond on the second carbon atom .
(1) The chemical formula for butane is: ${C_4}{H_8}$ which means it is made up of four carbon atoms and eight hydrogen atoms. The $ene$ part of the name refers to an alkene. So we know that butane’s structure must include a carbon double bond.
(2) There are several different isomers or molecular structures, that this compound can form:
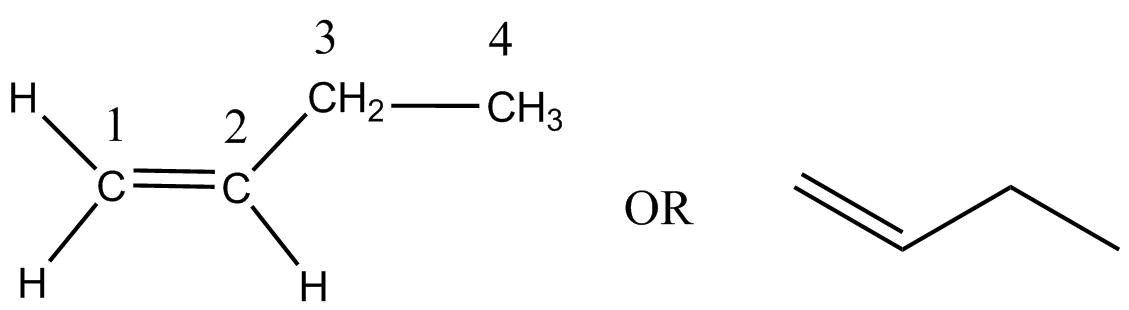
Alpha-butylene $\left( {but - 1 - ene} \right)$

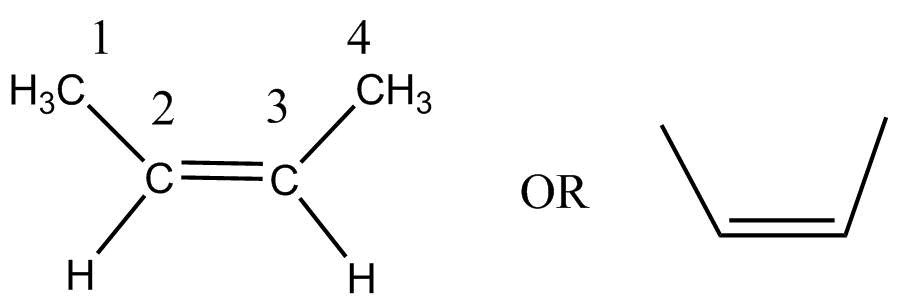
$C$ is beta-butylene- $\left( {\left( {2z} \right) - but - 2 - ene} \right)$

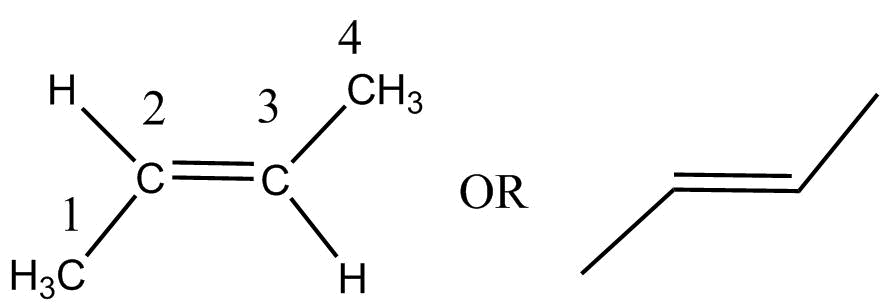
Trans-beta-butylene- $\left( {\left( {2E} \right) - but - 2ene} \right)$

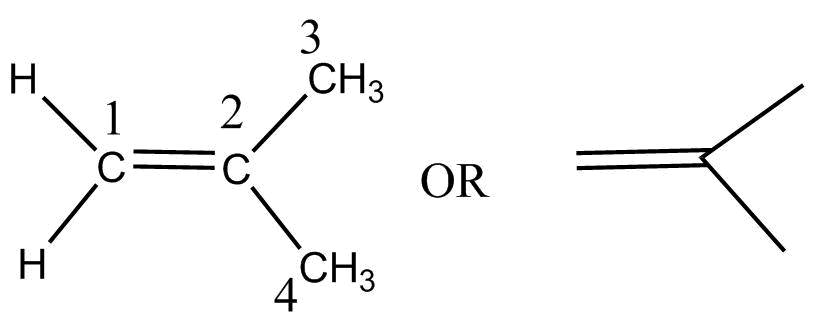
Iso butylene $\left( {2 - methylprop - 1 - ene} \right)$

Additional information:
The relationships between each of these isomers are mostly constitutional, which means they have the same molecular formula but have different bond connections (Order).
Meaning to transform them, you would have to just move around the hydrogen and carbons in other words the atoms and functional groups.
Note:
These isomers of butane are made up from the same materials, they each have different properties.
With cis-beta-butylene and trans-beta-butylene the atoms are in the same order, but the polarities are not same . The $cis$ isomer is polar, with both $C{H_3}$ groups on the same side. This makes it really bulky and difficult to stack.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




