
Name the common ancestor of the great apes and man.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Biological or organic evolution refers to the changes in the properties of organisms or groups of such populations over a number of generations. It is the process of cumulative change in living populations and in the descendent populations of organisms, i.e. descent with modification.
Complete answer:
1. The common ancestor of apes and man is a primate Dryopithecus, that lived 15 million years ago.
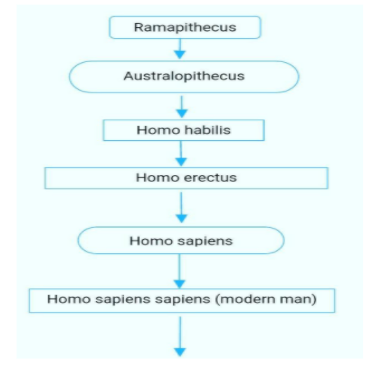
The next stage in the hominid evolution is Ramapithecus.
2. Both Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus were hairy and walked like gorillas and chimpanzees, but Ramapithecus was more manlike and is the forerunner of hominid evolution.
Human evolution is as follows:
3. Australopithecus: Their fossils were found in Tanzania and Ethiopia. They had a brain capacity of 450- 600 cc. They were probably about four feet tall and walked nearly upright. They hunted with stone weapons but essentially ate fruits.
4. Homo habilis: They lived in East African grasslands. They had a brain capacity of 650 - 800 cc. They probably did not eat meat.
5. Homo erectus: Their fossils were found in Java (Java man). They had a brain capacity of about 900cc. They probably ate meat.
6. Homo sapiens (primitive man): The fossils were found in east and central Asia. Neanderthal man ( Homo sapiens neanderthalensis) had a brain capacity of about 1400cc. They used hides to protect the body and buried the dead. They became extinct 25000 years before.
7. Homo sapiens sapiens (Modern man ): Homo sapiens arose during the ice age between 75000 - 10000 years ago. He spread all over the globe and learned to cultivate plants and domesticate animals. Prehistoric cave art developed about 18000 years before. Agriculture started around 10,000 years back. Human settlements and civilization started.
Note: Evolution of man from ape-like ancestors is supported by molecular and anatomical evidence besides the fossil evidence. The main changes that occurred in the evolution of man include erect posture, bipedal locomotion, grasping hands, binocular vision, enlargement of the brain, rounding of the cranium, broadening of the forehead, flattening of face, etc.
Complete answer:
1. The common ancestor of apes and man is a primate Dryopithecus, that lived 15 million years ago.
The next stage in the hominid evolution is Ramapithecus.
2. Both Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus were hairy and walked like gorillas and chimpanzees, but Ramapithecus was more manlike and is the forerunner of hominid evolution.
Human evolution is as follows:
3. Australopithecus: Their fossils were found in Tanzania and Ethiopia. They had a brain capacity of 450- 600 cc. They were probably about four feet tall and walked nearly upright. They hunted with stone weapons but essentially ate fruits.
4. Homo habilis: They lived in East African grasslands. They had a brain capacity of 650 - 800 cc. They probably did not eat meat.
5. Homo erectus: Their fossils were found in Java (Java man). They had a brain capacity of about 900cc. They probably ate meat.
6. Homo sapiens (primitive man): The fossils were found in east and central Asia. Neanderthal man ( Homo sapiens neanderthalensis) had a brain capacity of about 1400cc. They used hides to protect the body and buried the dead. They became extinct 25000 years before.
7. Homo sapiens sapiens (Modern man ): Homo sapiens arose during the ice age between 75000 - 10000 years ago. He spread all over the globe and learned to cultivate plants and domesticate animals. Prehistoric cave art developed about 18000 years before. Agriculture started around 10,000 years back. Human settlements and civilization started.

Note: Evolution of man from ape-like ancestors is supported by molecular and anatomical evidence besides the fossil evidence. The main changes that occurred in the evolution of man include erect posture, bipedal locomotion, grasping hands, binocular vision, enlargement of the brain, rounding of the cranium, broadening of the forehead, flattening of face, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




