
What is megasporogenesis? Explain the development of eight nucleate embryo sacs in flowering plants.
Answer
501k+ views
Hint: The term megasporogenesis, in layman’s language can be termed as the process of generation of megaspores.
The 8 nucleate embryo sac development for 80% flowering plants occurs through monosporic embryo sac development type.
Complete answer:
The process of formation of a megaspore mother cell is known as megasporogenesis. The megaspore mother cell or MMC is a large cell containing dense cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus.
The MMC undergoes reductional division or meiosis and forms four haploid megaspores. Out of those four, only one remains functional, and the other three from the micropylar end degenerate.
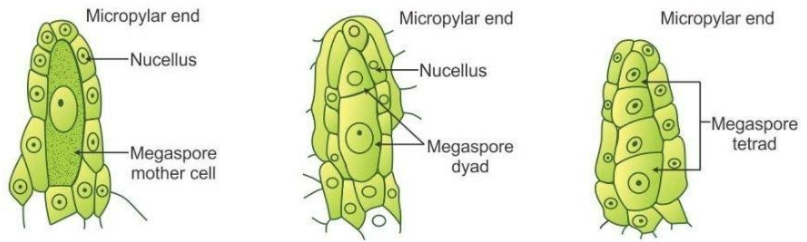
Now, in the majority of the angiosperms, only one of the four megaspores develops into a female gametophyte and the rest three degenerate. This particular type of development is known as monosporic embryo sac development.
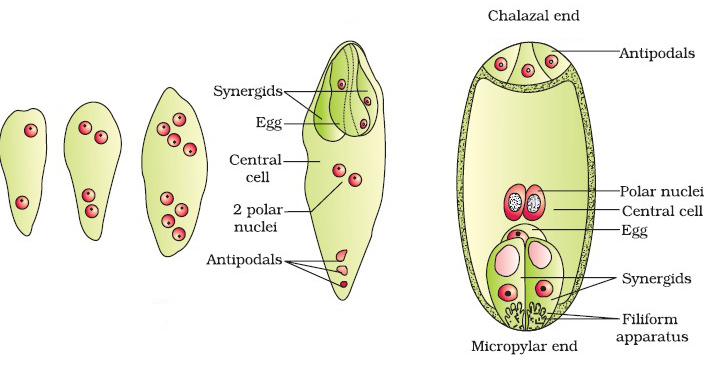
The nucleus of the chalazal functional megaspore (4th megaspore from the micropylar end) divides mitotically into two nuclei which move to opposite poles, forming the 2-nucleate (binucleate) embryo sac.
Again, two subsequent mitotic divisions in these cells result in formation of an 8-nucleate cell. One nucleus from each pole moves into the middle where they form polar nuclei.
Then, at this stage, cytokinesis results in, and the following changes are observed:
Three of the nuclei get organized at the micropylar end and form the egg apparatus (n). One becomes the egg cell (n), and the other two become the synergids (n).
Three nuclei form the antipodal cells (n) at the chalazal end.
Two nuclei in the center are called polar nuclei (n + n).
This ultimately results in a 7-celled and 8-nucleated embryo sac.
Note:
Embryo sac development can be of three basic types based on the number of megaspores that participate in the process:
Monosporic: Only 1 megaspore participates. E.g., Polygonum, Oenothera, etc.
Bisporic: Only 2 megaspores participate. E.g., Allium, Endymion, etc.
Tetrasporic: All the 4 megaspores are involved. E.g., Adoxa, Plumbago, Drusa, etc.
The embryo sac nuclear division is termed as free nuclear division, where karyokinesis is immediately not followed by cytokinesis. After all the nuclei division phases are complete, then only cytokinesis creeps in.
The 8 nucleate embryo sac development for 80% flowering plants occurs through monosporic embryo sac development type.
Complete answer:
The process of formation of a megaspore mother cell is known as megasporogenesis. The megaspore mother cell or MMC is a large cell containing dense cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus.
The MMC undergoes reductional division or meiosis and forms four haploid megaspores. Out of those four, only one remains functional, and the other three from the micropylar end degenerate.

Now, in the majority of the angiosperms, only one of the four megaspores develops into a female gametophyte and the rest three degenerate. This particular type of development is known as monosporic embryo sac development.
The nucleus of the chalazal functional megaspore (4th megaspore from the micropylar end) divides mitotically into two nuclei which move to opposite poles, forming the 2-nucleate (binucleate) embryo sac.
Again, two subsequent mitotic divisions in these cells result in formation of an 8-nucleate cell. One nucleus from each pole moves into the middle where they form polar nuclei.
Then, at this stage, cytokinesis results in, and the following changes are observed:
Three of the nuclei get organized at the micropylar end and form the egg apparatus (n). One becomes the egg cell (n), and the other two become the synergids (n).
Three nuclei form the antipodal cells (n) at the chalazal end.
Two nuclei in the center are called polar nuclei (n + n).
This ultimately results in a 7-celled and 8-nucleated embryo sac.

Note:
Embryo sac development can be of three basic types based on the number of megaspores that participate in the process:
Monosporic: Only 1 megaspore participates. E.g., Polygonum, Oenothera, etc.
Bisporic: Only 2 megaspores participate. E.g., Allium, Endymion, etc.
Tetrasporic: All the 4 megaspores are involved. E.g., Adoxa, Plumbago, Drusa, etc.
The embryo sac nuclear division is termed as free nuclear division, where karyokinesis is immediately not followed by cytokinesis. After all the nuclei division phases are complete, then only cytokinesis creeps in.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




