
What do you mean by polar molecules and nonpolar molecules? Give one example each.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: If the bonds of a molecule are asymmetrical, that is on the one end there is more electronegative element and on the other end there is electropositive element, the molecule is polar. When there is no charge separation, as there is not much electronegativity differences between the atoms of the compounds, those molecules will be non-polar.
Complete answer:
Polar molecules are framed by components whose ions have various electronegativities. The electrons shaping the bonds will tend to be pulled in nearer to the more electronegative component. On such occasions, covalent particles build up some ionic character and are called polar atoms.
Because of polarity, a little negative charge ${ \delta }^{ - }$ shows up on the more electronegative iota and a little electropositive charge ${ \delta }^{ + }$ shows up on the less electronegative particle. For instance: In HCl particles, the Cl molecule is more electronegative. Therefore it procures a ${ \delta }^{ - }$ charge and H gains a ${ \delta }^{ - }$ charge. In this manner, it is a polar atom.
Non-polar molecules are those in which there is no partition of charge and it is evenly appropriated in the atom. Consequently, the principal distinction among polar and nonpolar atoms lies in the partition of charges. In polar particles, there is a partition of positive and negative charge while in non-polar atoms there is no charge division. The case of non-polar particles incorporates ${ CH }_{ 4 }$, the electronegativity values of carbon and hydrogen are close, and hence it is a non-polar molecule. There isn't a lot of electronegativity contrast among carbon and hydrogen, because of which the holding electrons are similarly shared among carbon and hydrogen. So there is no improvement in positive and negative charges.

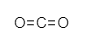
Note:
The polar molecules are soluble in polar solvents such as water while non-polar molecules are soluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene. This is because the polar molecules have charge separation and the polar solvents also have charge separation. The negative charge of the solvent attracts the positive charge of the molecule and vice versa. This is why they become soluble. This is not the case for non polar solvents. That's why they don’t dissolve in polar solvents.
Complete answer:
Polar molecules are framed by components whose ions have various electronegativities. The electrons shaping the bonds will tend to be pulled in nearer to the more electronegative component. On such occasions, covalent particles build up some ionic character and are called polar atoms.
Because of polarity, a little negative charge ${ \delta }^{ - }$ shows up on the more electronegative iota and a little electropositive charge ${ \delta }^{ + }$ shows up on the less electronegative particle. For instance: In HCl particles, the Cl molecule is more electronegative. Therefore it procures a ${ \delta }^{ - }$ charge and H gains a ${ \delta }^{ - }$ charge. In this manner, it is a polar atom.
Non-polar molecules are those in which there is no partition of charge and it is evenly appropriated in the atom. Consequently, the principal distinction among polar and nonpolar atoms lies in the partition of charges. In polar particles, there is a partition of positive and negative charge while in non-polar atoms there is no charge division. The case of non-polar particles incorporates ${ CH }_{ 4 }$, the electronegativity values of carbon and hydrogen are close, and hence it is a non-polar molecule. There isn't a lot of electronegativity contrast among carbon and hydrogen, because of which the holding electrons are similarly shared among carbon and hydrogen. So there is no improvement in positive and negative charges.

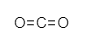
Note:
The polar molecules are soluble in polar solvents such as water while non-polar molecules are soluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene. This is because the polar molecules have charge separation and the polar solvents also have charge separation. The negative charge of the solvent attracts the positive charge of the molecule and vice versa. This is why they become soluble. This is not the case for non polar solvents. That's why they don’t dissolve in polar solvents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




