
What do you mean by incomplete dominance? Give examples
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: It is a method of Gene interaction in which both alleles of a gene at a locus are partly expressed, often resulting in a transitional or different phenotype. It is also known as partial dominance. Incomplete dominance occurs because neither of the two alleles is completely dominant over the other. This results in a phenotype that is a combination of both.
Complete answer:
Researchers did again Mendel’s pea experiment on other plants. Amazingly, they noted that the F1 Generation showed variation from the normal pattern of inheritance. The monohybrid cross resulted in F1 progeny which didn’t show any likeness to either of the parents, but an in-between progeny.
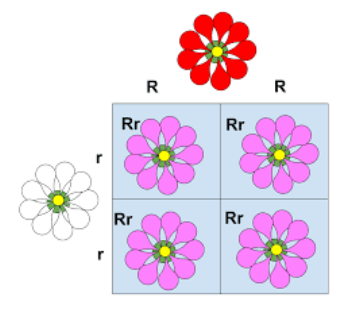
A Monohybrid cross occurred between the red and white-colored flowers of the Snapdragon plant. Initially, true-breeding red (RR) and white (rr) colored flowers of snapdragon were crossed. The F1 generation created a pink-colored flower with Rr pair of alleles.
At that time the F1 progeny was self-pollinated. This is caused in red (RR), pink (Rr), and white (rr) flowers in the ratio of 1:2:1.
Summon up that the genotype ratio of F2 generation in the monohybrid cross by Mendel also gave the same ratio of 1:2:1. But, the phenotype ratio has changed from 3:1 to 1:2:1. The motive for this variation is the incomplete dominance of the allele R over the allele r. This is directed to the blending of color in flowers.
Note: You can also give another example of incomplete dominance is chickens with blue feathers. When a black and a white chicken replicate and neither allele is fully dominant, then the outcome is a blue-feathered bird. The fruit color of eggplants is an added example of incomplete dominance. Blending deep purple eggplants with white eggplants leads to eggplants of a light violet color.
Complete answer:
Researchers did again Mendel’s pea experiment on other plants. Amazingly, they noted that the F1 Generation showed variation from the normal pattern of inheritance. The monohybrid cross resulted in F1 progeny which didn’t show any likeness to either of the parents, but an in-between progeny.
A Monohybrid cross occurred between the red and white-colored flowers of the Snapdragon plant. Initially, true-breeding red (RR) and white (rr) colored flowers of snapdragon were crossed. The F1 generation created a pink-colored flower with Rr pair of alleles.
At that time the F1 progeny was self-pollinated. This is caused in red (RR), pink (Rr), and white (rr) flowers in the ratio of 1:2:1.
Summon up that the genotype ratio of F2 generation in the monohybrid cross by Mendel also gave the same ratio of 1:2:1. But, the phenotype ratio has changed from 3:1 to 1:2:1. The motive for this variation is the incomplete dominance of the allele R over the allele r. This is directed to the blending of color in flowers.

Note: You can also give another example of incomplete dominance is chickens with blue feathers. When a black and a white chicken replicate and neither allele is fully dominant, then the outcome is a blue-feathered bird. The fruit color of eggplants is an added example of incomplete dominance. Blending deep purple eggplants with white eggplants leads to eggplants of a light violet color.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




