
Match list-I and list-II
List I List II A. Hypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) 1. Non-reducing B. Isohypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) 2. P in +4 state C. Pyrophosphorous acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_5}\]) 3. P in +3 state D. Pyrophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7}\]) 4. P-P bond 5. P-O-P bond
a. A-1,2,4; B-3,5; C-3,5; D-1,5
b. A-1,2; B-3,4; C-3,5; D-5
c. A-2; B-3,5; C-3; D-1,4
d. A-4; B-1,3,5; C-4,5; D-2,5
| List I | List II |
| A. Hypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) | 1. Non-reducing |
| B. Isohypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) | 2. P in +4 state |
| C. Pyrophosphorous acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_5}\]) | 3. P in +3 state |
| D. Pyrophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7}\]) | 4. P-P bond |
| 5. P-O-P bond |
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:Draw the structure of all acids. Acid which does not contain \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond is known as non-reducing acid. Use the oxidation number rules to determine the oxidation state of P atom.
Complete answer:
A. The structure of hypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) is as follows:
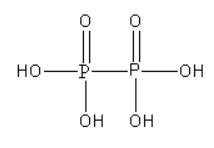
From the structure of hypophosphoric acid, we can say that there is a P-P bond present in it. However, there is no P-O-P bond in it.
As hypophosphoric acid does not contain \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond it is known as non-reducing.
In hypophosphoric acid, both P atoms are surrounded by the same groups so we can determine the oxidation state P atom using the oxidation number rules.
According to the oxidation number rule, the oxidation state of oxygen is -2 and the oxidation state of hydrogen is +1.
In hypophosphoric acid, there are two P atoms, four H atoms and six O atoms.
(Number of P atoms) (Oxidation state of P) + (Number of O atoms) (Oxidation state of O) + (Number of H atom)(oxidation state of H atom)= 0
2 (Oxidation state of P) + 6(-2)+ 4(+1) = 0
Oxidation state of P = +4
Thus, Hypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) matches with 1, 2, 4 from list II.
Hence, for hypophosphoric acid A-1, 2, 4 is the correct answer.
B. The structure of Isohypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) is as follows:

From the structure of isohypophosphoric acid we can say that there is a P-O-P bond present in it. However, there is no P-P bond in it.
As isohypophosphoric acid contains the \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond it is known as reducing.
Both P atoms are surrounded by different groups so the oxidation state of both P atoms is different.
The oxidation state of P atom bonded to H atom is +3 while the oxidation state of another P atom is +5.
Thus, isohypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) matches with 3,5 from list II.
Hence, for isohypophosphoric acid B-3,5 is the correct answer.
C. The structure of pyrophosphorous acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_5}\]) is as follows:
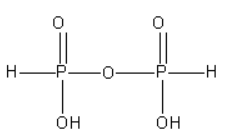
From the structure of pyrophosphorous acid, we can say that there is a P-O-P bond present in it. However, there is no P-P bond in it.
As of pyrophosphorous acid contains the \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond it is known as reducing.
In pyrophosphorous acid, both P atoms are surrounded by the same groups. The oxidation state of both P atoms is +3.
Thus, of pyrophosphorous acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_5}\]) matches with 3,5 from list II.
Hence, for pyrophosphorous acid C-3,5 is the correct answer.
D. The structure of pyrophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7}\]) is as follows:
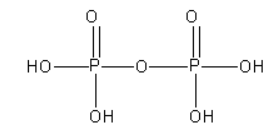
From the structure of pyrophosphoric acid, we can say that there is a P-O-P bond present in it. However, there is no P-P bond in it.
As pyrophosphoric acid does not contain \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond it is known as non-reducing.
In pyrophosphoric acid, both P atoms are surrounded by the same groups. The oxidation state of both P atoms is +5.
Thus, of pyrophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7}\]) matches with 1,5 from list II.
Hence, for pyrophosphoric acid D-1,5 is the correct answer.
Thus, correct option is (a) A-1, 2, 4; B-3, 5; C-3, 5; D-1, 5
Note:
Acids are proton donor species. Proton bonded to the oxygen atom is known as an acidic proton. Proton bonded directly to the central atom is known as reducing proton.
Complete answer:
A. The structure of hypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) is as follows:

From the structure of hypophosphoric acid, we can say that there is a P-P bond present in it. However, there is no P-O-P bond in it.
As hypophosphoric acid does not contain \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond it is known as non-reducing.
In hypophosphoric acid, both P atoms are surrounded by the same groups so we can determine the oxidation state P atom using the oxidation number rules.
According to the oxidation number rule, the oxidation state of oxygen is -2 and the oxidation state of hydrogen is +1.
In hypophosphoric acid, there are two P atoms, four H atoms and six O atoms.
(Number of P atoms) (Oxidation state of P) + (Number of O atoms) (Oxidation state of O) + (Number of H atom)(oxidation state of H atom)= 0
2 (Oxidation state of P) + 6(-2)+ 4(+1) = 0
Oxidation state of P = +4
Thus, Hypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) matches with 1, 2, 4 from list II.
Hence, for hypophosphoric acid A-1, 2, 4 is the correct answer.
B. The structure of Isohypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) is as follows:

From the structure of isohypophosphoric acid we can say that there is a P-O-P bond present in it. However, there is no P-P bond in it.
As isohypophosphoric acid contains the \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond it is known as reducing.
Both P atoms are surrounded by different groups so the oxidation state of both P atoms is different.
The oxidation state of P atom bonded to H atom is +3 while the oxidation state of another P atom is +5.
Thus, isohypophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\]) matches with 3,5 from list II.
Hence, for isohypophosphoric acid B-3,5 is the correct answer.
C. The structure of pyrophosphorous acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_5}\]) is as follows:

From the structure of pyrophosphorous acid, we can say that there is a P-O-P bond present in it. However, there is no P-P bond in it.
As of pyrophosphorous acid contains the \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond it is known as reducing.
In pyrophosphorous acid, both P atoms are surrounded by the same groups. The oxidation state of both P atoms is +3.
Thus, of pyrophosphorous acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_5}\]) matches with 3,5 from list II.
Hence, for pyrophosphorous acid C-3,5 is the correct answer.
D. The structure of pyrophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7}\]) is as follows:

From the structure of pyrophosphoric acid, we can say that there is a P-O-P bond present in it. However, there is no P-P bond in it.
As pyrophosphoric acid does not contain \[{\text{ P - H}}\] bond it is known as non-reducing.
In pyrophosphoric acid, both P atoms are surrounded by the same groups. The oxidation state of both P atoms is +5.
Thus, of pyrophosphoric acid (\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7}\]) matches with 1,5 from list II.
Hence, for pyrophosphoric acid D-1,5 is the correct answer.
Thus, correct option is (a) A-1, 2, 4; B-3, 5; C-3, 5; D-1, 5
Note:
Acids are proton donor species. Proton bonded to the oxygen atom is known as an acidic proton. Proton bonded directly to the central atom is known as reducing proton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




