
What is the major product of the given reaction.
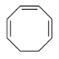 $+\,B{{r}_{2}}\left( 1\,mole \right)\xrightarrow{CC{{l}_{4}}}$
$+\,B{{r}_{2}}\left( 1\,mole \right)\xrightarrow{CC{{l}_{4}}}$
A.
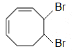
B.
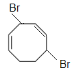
C.
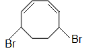
D.
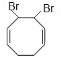





Answer
555.6k+ views
Hint: The given reaction is based on the concept of bromination of cycloalkenes in the presence of inorganic solvent. Whenever alkenes are treated with bromine in the presence of inorganic solvent (here carbon tetrachloride) then vicinal dibromides are formed as a product of the reaction.
Complete answer:
Cycloalkenes reacts with bromine in the presence of tetrachloromethane. In this reaction the double bond is broken and bromine atoms get attached to the alkenes in the vicinal positions.
During this reaction the alkenes lose their red color of the solution and turn into a colorless solution. This is even a test for the unsaturation of the alkenes.
In the given question, a cycloalkene named $1,3,5tricyclooctatriene$ is reacting with bromine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride.
Let us see the mechanism of the reaction.
This reaction is a simple electrophilic addition reaction. The mechanism is an follows:
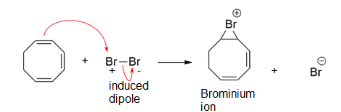
Step 1: We know that bromine is a highly polarizable molecule. The pi bond in the $1,3,5tricyclooctatriene$induces a dipole in the approaching bromine molecule. Thus a dipole is induced in the bromine molecule. We call it “induced dipole”.
As a first step one of the atom of bromine molecule gets attached to both of the carbon atoms, with a positive charge developed in it. This results in the formation of bromonium ions. The reacts is shown as below:
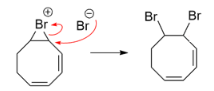
Step 2: Now the bromonium ion is attacked by the bromide anion from the backside and this results in the formation of vicinal dibromides from the cycloalkenes. The steps are represented as follows:
Thus we see that the product thus formed is similar to option A.
Hence, option A. is the correct option.
Note: It should be noted that in the entire reaction carbon tetrachloride is merely used as an inorganic solvent and it does not affect the reaction and its mechanism. Halogens, other from the bromine such as fluorine, chlorine and iodine also undergo the reaction through the same mechanism.
Complete answer:
Cycloalkenes reacts with bromine in the presence of tetrachloromethane. In this reaction the double bond is broken and bromine atoms get attached to the alkenes in the vicinal positions.
During this reaction the alkenes lose their red color of the solution and turn into a colorless solution. This is even a test for the unsaturation of the alkenes.
In the given question, a cycloalkene named $1,3,5tricyclooctatriene$ is reacting with bromine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride.
Let us see the mechanism of the reaction.
This reaction is a simple electrophilic addition reaction. The mechanism is an follows:
Step 1: We know that bromine is a highly polarizable molecule. The pi bond in the $1,3,5tricyclooctatriene$induces a dipole in the approaching bromine molecule. Thus a dipole is induced in the bromine molecule. We call it “induced dipole”.
As a first step one of the atom of bromine molecule gets attached to both of the carbon atoms, with a positive charge developed in it. This results in the formation of bromonium ions. The reacts is shown as below:

Step 2: Now the bromonium ion is attacked by the bromide anion from the backside and this results in the formation of vicinal dibromides from the cycloalkenes. The steps are represented as follows:

Thus we see that the product thus formed is similar to option A.
Hence, option A. is the correct option.
Note: It should be noted that in the entire reaction carbon tetrachloride is merely used as an inorganic solvent and it does not affect the reaction and its mechanism. Halogens, other from the bromine such as fluorine, chlorine and iodine also undergo the reaction through the same mechanism.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




