
Linked genes separate due to
(a)Recombination
(b)Mutation
(c)Crossing over
(d)None of the above
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Due to the exchange of chromosome segments, related genes separate. If the number of created progenies is more like parents (greater than 50 percent) it means the genes are linked. This event has a significant effect of rising the number of phenotypes that occur in a population.
Complete answer:
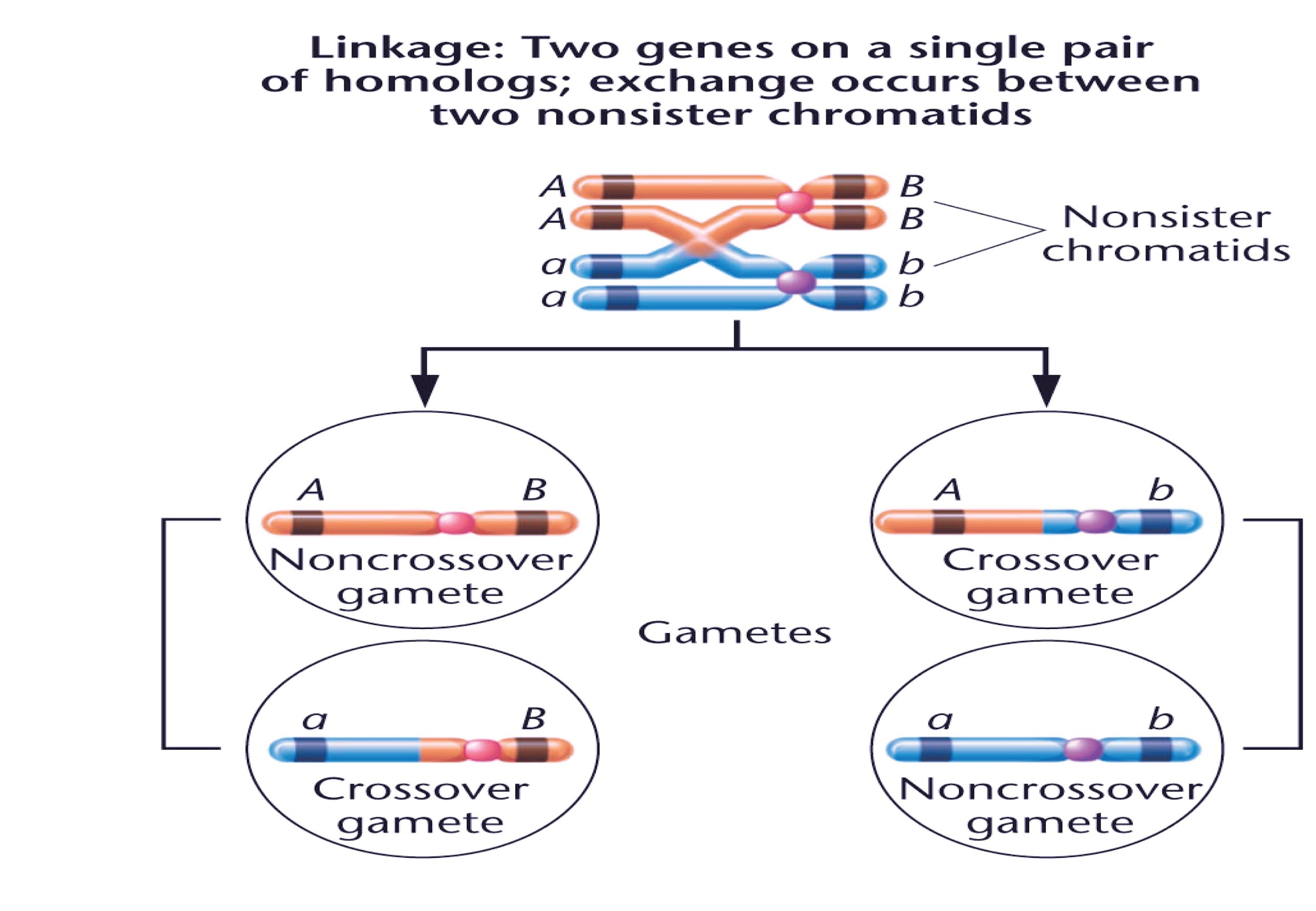
Linked genes are called genes that are found on the same chromosome. Unless they are split by crossing-over, alleles for these genes appear to segregate together during meiosis. When chromosomes cross over, during prophase I of meiosis, two separate chromosomes exchange bits of genetic material. If the linked genes on the chromosome are far apart, crossing over is more likely to split them.
Crossing-over occurs during meiosis I when two homologous chromosomes swap genetic material. The closer two genes are to a chromosome, the less likely their alleles are to be split by cross-over.
Additional Information: A DNA segment may code for eye color on each chromosome portion, for instance, while one chromosome may code for brown eyes and the other for blue eyes. The expressed eye color depends on which gene is dominant. Very frequently, this event happens between different alleles coding for the same gene.
For normal segregation of chromosomes during meiosis, crossing over is necessary. Crossing over also accounts for genetic differences, since the chromatids kept together by the centromere are no longer similar because of the exchanging of genetic material during crossing over.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Crossing over’.
Note: The propensity of DNA sequences that seem to be similar together on a chromosome that are inherited together during the process of meiosis is called genetic linkage. Crossing over is the exchange of chromosome segments during the development of gametes between non-sister chromatids. The result is that the alleles on parental chromosomes are assorted (shuffled) so that the gametes bear gene combinations that are distinct from either parent.
Complete answer:
Linked genes are called genes that are found on the same chromosome. Unless they are split by crossing-over, alleles for these genes appear to segregate together during meiosis. When chromosomes cross over, during prophase I of meiosis, two separate chromosomes exchange bits of genetic material. If the linked genes on the chromosome are far apart, crossing over is more likely to split them.
Crossing-over occurs during meiosis I when two homologous chromosomes swap genetic material. The closer two genes are to a chromosome, the less likely their alleles are to be split by cross-over.
Additional Information: A DNA segment may code for eye color on each chromosome portion, for instance, while one chromosome may code for brown eyes and the other for blue eyes. The expressed eye color depends on which gene is dominant. Very frequently, this event happens between different alleles coding for the same gene.
For normal segregation of chromosomes during meiosis, crossing over is necessary. Crossing over also accounts for genetic differences, since the chromatids kept together by the centromere are no longer similar because of the exchanging of genetic material during crossing over.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Crossing over’.
Note: The propensity of DNA sequences that seem to be similar together on a chromosome that are inherited together during the process of meiosis is called genetic linkage. Crossing over is the exchange of chromosome segments during the development of gametes between non-sister chromatids. The result is that the alleles on parental chromosomes are assorted (shuffled) so that the gametes bear gene combinations that are distinct from either parent.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




