
Let $ A = \left\{ {10,11,12,13,14} \right\} $ ; $ B = \left\{ {0,1,2,3,5} \right\} $ and $ fi:A \to B,i = 1,2,3 $ . State the type of the function for the following (give reason):
1. $ {f_1} = \left\{ {\left( {10,1} \right),\left( {11,2} \right),\left( {12,3} \right),\left( {13,5} \right),\left( {14,3} \right)} \right\} $
2. $ {f_2} = \left\{ {\left( {10,1} \right),\left( {11,1} \right),\left( {12,1} \right),\left( {13,1} \right),\left( {14,1} \right)} \right\} $
3. $ {f_3} = \left\{ {\left( {10,0} \right),\left( {11,1} \right),\left( {12,2} \right),\left( {13,3} \right),\left( {14,5} \right)} \right\} $
Answer
543.3k+ views
Hint: The given question is related to the concept of functions. If each element of non-empty set M, has only one range to a nonempty set N, then such a relation is called as function. It is represented as $ f:A \to B $ and the function is also known as mapping. There are different types of functions such as one-one function, many-one function, onto function as well as one-one and onto function. Here in order to solve this question, we must know the differ
Complete step by step answer:
Given is $ A = \left\{ {10,11,12,13,14} \right\} $ , $ B = \left\{ {0,1,2,3,5} \right\} $ and $ fi:A \to B,i = 1,2,3 $ .
$ {f_1} = \left\{ {\left( {10,1} \right),\left( {11,2} \right),\left( {12,3} \right),\left( {13,5} \right),\left( {14,3} \right)} \right\} $
So, let us map the given function,
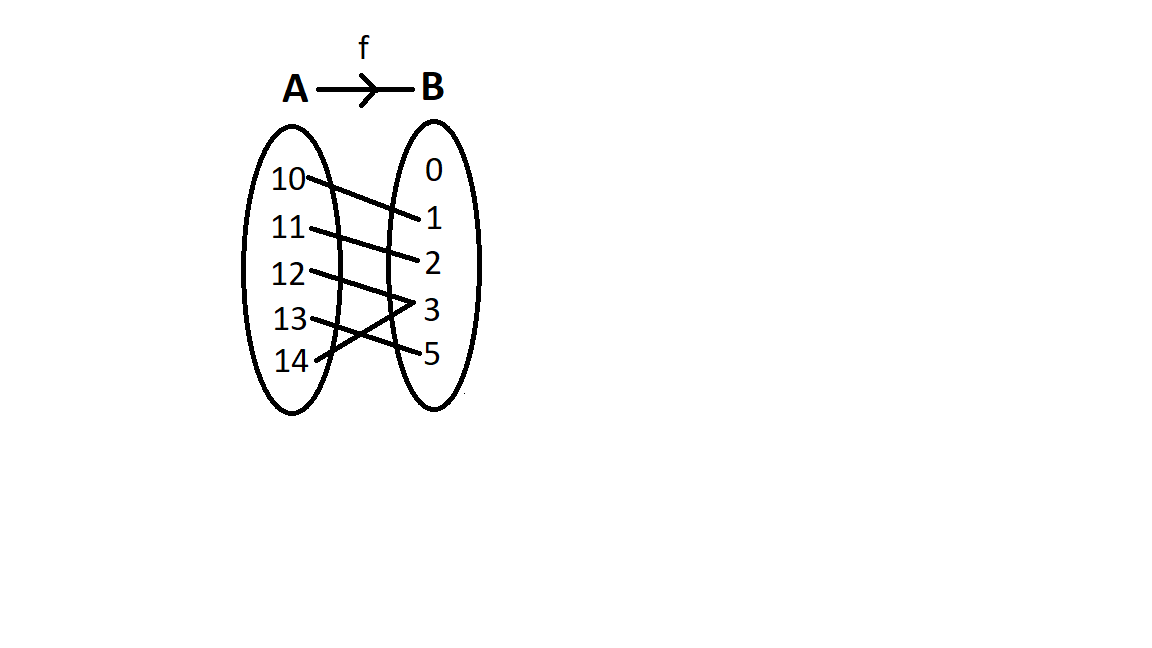
Since the elements $ 12 $ and $ 14 $ in A have the same image $ 3 $ in B. So, we can say that it is not one-one function. Moreover, the element $ 0 $ in B has no pre-image in A. Therefore, it is not onto function as well.
Hence, the given function is neither one-one nor onto function.
$ {f_2} = \left\{ {\left( {10,1} \right),\left( {11,1} \right),\left( {12,1} \right),\left( {13,1} \right),\left( {14,1} \right)} \right\} $
Let us map this function.
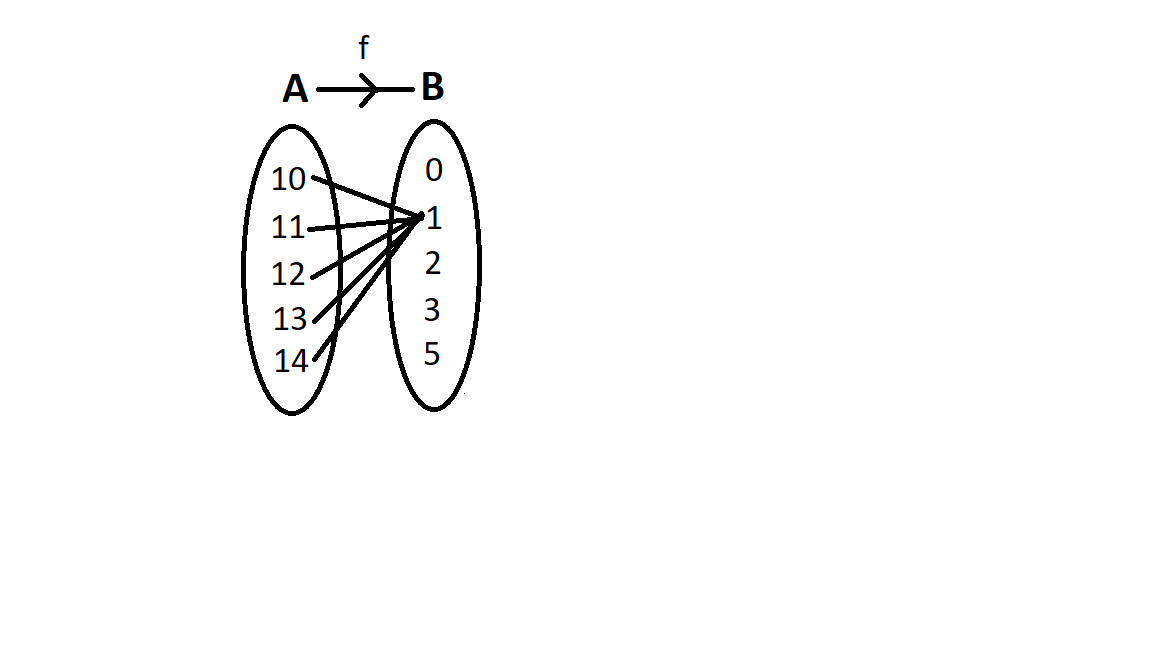
Since every element has the same image $ 1 $ in B, so, it is a constant function.
Hence, it is not onto function and is a constant function.
$ {f_3} = \left\{ {\left( {10,0} \right),\left( {11,1} \right),\left( {12,2} \right),\left( {13,3} \right),\left( {14,5} \right)} \right\} $
Now we map this function.
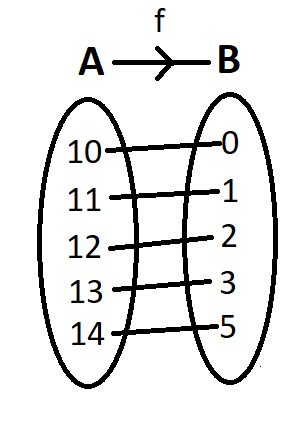
Since every element has a unique image and domain = codomain.
Hence, it is both one-one and onto function.
Note: In order to solve these types of questions students should be clear with the concepts of relations and functions. The different types of functions should be known to them. The only mistake which students tend to make is in the mapping of the functions. Students should try and avoid making such mistakes.
Complete step by step answer:
Given is $ A = \left\{ {10,11,12,13,14} \right\} $ , $ B = \left\{ {0,1,2,3,5} \right\} $ and $ fi:A \to B,i = 1,2,3 $ .
$ {f_1} = \left\{ {\left( {10,1} \right),\left( {11,2} \right),\left( {12,3} \right),\left( {13,5} \right),\left( {14,3} \right)} \right\} $
So, let us map the given function,

Since the elements $ 12 $ and $ 14 $ in A have the same image $ 3 $ in B. So, we can say that it is not one-one function. Moreover, the element $ 0 $ in B has no pre-image in A. Therefore, it is not onto function as well.
Hence, the given function is neither one-one nor onto function.
$ {f_2} = \left\{ {\left( {10,1} \right),\left( {11,1} \right),\left( {12,1} \right),\left( {13,1} \right),\left( {14,1} \right)} \right\} $
Let us map this function.

Since every element has the same image $ 1 $ in B, so, it is a constant function.
Hence, it is not onto function and is a constant function.
$ {f_3} = \left\{ {\left( {10,0} \right),\left( {11,1} \right),\left( {12,2} \right),\left( {13,3} \right),\left( {14,5} \right)} \right\} $
Now we map this function.

Since every element has a unique image and domain = codomain.
Hence, it is both one-one and onto function.
Note: In order to solve these types of questions students should be clear with the concepts of relations and functions. The different types of functions should be known to them. The only mistake which students tend to make is in the mapping of the functions. Students should try and avoid making such mistakes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




