
Kinetic energy of the system in centre of mass frame is-
(A). $\dfrac{3}{2}m\omega _{0}^{2}{{L}^{2}}$
(B). $\dfrac{1}{2}m\omega _{0}^{2}{{L}^{2}}$
(C). $\dfrac{1}{3}m\omega _{0}^{2}{{L}^{2}}$
(D). $\dfrac{4}{3}m\omega _{0}^{2}{{L}^{2}}$
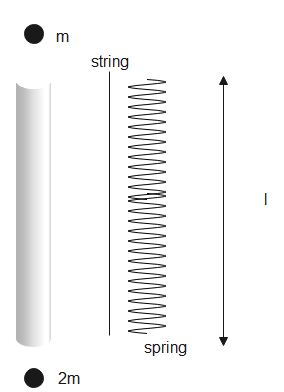
(a)
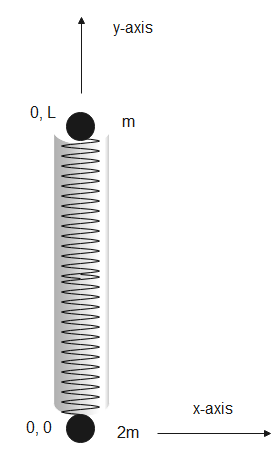
(b)


Answer
544.5k+ views
Hint: The system contains two masses connected to a cylinder with a spring of length L. The system will rotate about its centre of mass. The centre will lie more towards the heavier mass and the motion is purely rotational. The rotational kinetic energy is analogous to translational kinetic energy and it depends on the moment of inertia and rotational velocity.
Formulas used:
$y=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{y}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{y}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$
Complete answer:
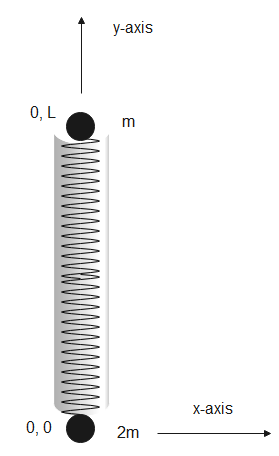
In the given figure, the cylinder will have only rotational kinetic energy.
The position of centre of mass for the frame is given by-
$y=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{y}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{y}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
Here, ${{m}_{1}},\,{{m}_{2}}$ are the masses of the different components of the system, ${{y}_{1}},\,{{y}_{2}}$ are the positions of the different components.
Given, $m$ at position $(0,0)$ and $2m$ at position $(0,L)$. We substitute given values in the above equation to get,
$\begin{align}
& y=\dfrac{m(0)+2m(L)}{m+2m} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2}{3}L \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the position of the centre of mass is at $(0,\dfrac{2}{3}L)$. The cylinder will rotate about its centre of mass. The centre of mass will be $\dfrac{2}{3}L$ distance away from $m$ and $\dfrac{1}{3}L$ distance away from $2m$.
The rotational kinetic energy is given by-
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$ - (1)
Here, $K$ is the kinetic energy
$I$ is the moment of inertia
$\omega $ is the angular velocity
The moment of inertia for the cylinder is $m{{L}^{2}}$. The total moment of inertia is the sum of moment of inertia of both masses. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& I={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow I=2m{{\left( \dfrac{L}{3} \right)}^{2}}+m{{\left( \dfrac{2L}{3} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \therefore I=\dfrac{2}{3}m{{L}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Let the initial angular velocity be ${{\omega }_{0}}$. We substitute the given values in eq (2) to get,
$\begin{align}
& K=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{2}{3}m{{L}^{2}}\omega _{0}^{2} \\
& \therefore K=\dfrac{1}{3}m{{L}^{2}}\omega _{0}^{2} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the system about its centre of mass is $\dfrac{1}{3}m{{L}^{2}}\omega _{0}^{2}$.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
The motion of the system was pure rotational. The centre of mass is the point of symmetry of the system. Since, the system lies entirely on the y-axis, its centre of mass will also lie on the y-axis. The moment of inertia is analogous to the mass. The system is an isolated system as no external force or torque is acting on it.
Formulas used:
$y=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{y}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{y}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$
Complete answer:

In the given figure, the cylinder will have only rotational kinetic energy.
The position of centre of mass for the frame is given by-
$y=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{y}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{y}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
Here, ${{m}_{1}},\,{{m}_{2}}$ are the masses of the different components of the system, ${{y}_{1}},\,{{y}_{2}}$ are the positions of the different components.
Given, $m$ at position $(0,0)$ and $2m$ at position $(0,L)$. We substitute given values in the above equation to get,
$\begin{align}
& y=\dfrac{m(0)+2m(L)}{m+2m} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2}{3}L \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the position of the centre of mass is at $(0,\dfrac{2}{3}L)$. The cylinder will rotate about its centre of mass. The centre of mass will be $\dfrac{2}{3}L$ distance away from $m$ and $\dfrac{1}{3}L$ distance away from $2m$.
The rotational kinetic energy is given by-
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$ - (1)
Here, $K$ is the kinetic energy
$I$ is the moment of inertia
$\omega $ is the angular velocity
The moment of inertia for the cylinder is $m{{L}^{2}}$. The total moment of inertia is the sum of moment of inertia of both masses. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& I={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow I=2m{{\left( \dfrac{L}{3} \right)}^{2}}+m{{\left( \dfrac{2L}{3} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \therefore I=\dfrac{2}{3}m{{L}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Let the initial angular velocity be ${{\omega }_{0}}$. We substitute the given values in eq (2) to get,
$\begin{align}
& K=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{2}{3}m{{L}^{2}}\omega _{0}^{2} \\
& \therefore K=\dfrac{1}{3}m{{L}^{2}}\omega _{0}^{2} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the system about its centre of mass is $\dfrac{1}{3}m{{L}^{2}}\omega _{0}^{2}$.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
The motion of the system was pure rotational. The centre of mass is the point of symmetry of the system. Since, the system lies entirely on the y-axis, its centre of mass will also lie on the y-axis. The moment of inertia is analogous to the mass. The system is an isolated system as no external force or torque is acting on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




