
Isopropyl alcohol on oxidation forms:
a) Ethylene
b) Acetone
c) Ether
d) Acetaldehyde
Answer
551.1k+ views
Hint: Iso group can be defined as the structural isomer of a straight chain alkane where the second carbon will be attached to a methyl group. When any functional group is attached to the second carbon, the hydrocarbon will be called as a secondary carbon.
Complete step by step solution:
Alcohols are the functional group where the hydrocarbon is attached to the $ - OH $ group. The hydrocarbons can include alkanes, alkenes, aromatic compounds, etc.
When we oxidise the alcohols we get an aldehyde or a ketone depending on the type of carbon where the alcoholic group is attached.
A Primary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to only one carbon. For example, $ \Propan - 1 - ol $ that can be represented as
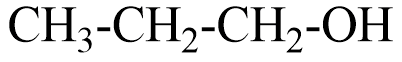
A secondary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to two carbons in the structure. For example, $ Bu\tan - 2 - ol $ that can be represented as

A tertiary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to three carbons in the structure. For example, $ 2 - Methylpropan - 2 - ol $ that can be represented as
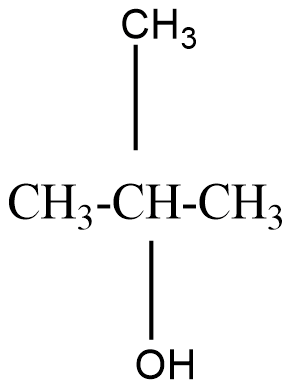
On oxidation of primary alcohol we get an aldehyde. But on oxidising a secondary alcohol, a ketone is usually formed.
The structure of isopropyl alcohol can be represented as-
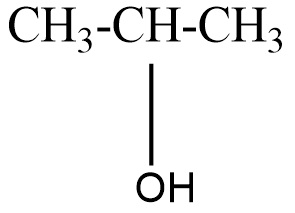
On oxidation of isopropyl alcohol, a secondary alcohol we get a ketone namely, acetone.
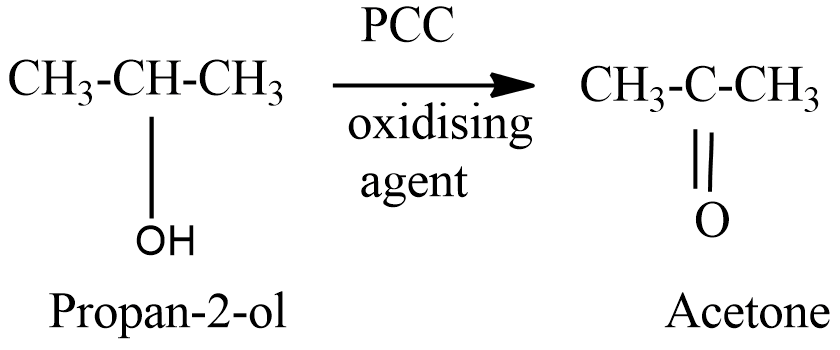
Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
There are different oxidising agents that can be used to oxidise particularly aldehyde and ketones, for example $ Cr{O_3} $ , PCC. PCC is used particularly to oxidise alcohol into ketone. On oxidising a carbonyl compound (aldehyde and ketone) the formation of carboxylic acid can be seen.
Complete step by step solution:
Alcohols are the functional group where the hydrocarbon is attached to the $ - OH $ group. The hydrocarbons can include alkanes, alkenes, aromatic compounds, etc.
When we oxidise the alcohols we get an aldehyde or a ketone depending on the type of carbon where the alcoholic group is attached.
A Primary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to only one carbon. For example, $ \Propan - 1 - ol $ that can be represented as
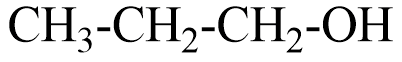
A secondary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to two carbons in the structure. For example, $ Bu\tan - 2 - ol $ that can be represented as

A tertiary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to three carbons in the structure. For example, $ 2 - Methylpropan - 2 - ol $ that can be represented as
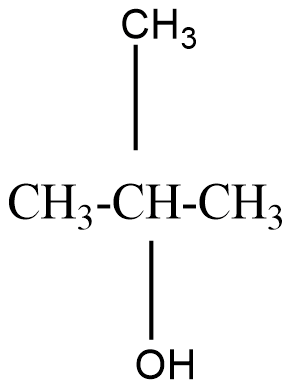
On oxidation of primary alcohol we get an aldehyde. But on oxidising a secondary alcohol, a ketone is usually formed.
The structure of isopropyl alcohol can be represented as-

On oxidation of isopropyl alcohol, a secondary alcohol we get a ketone namely, acetone.

Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
There are different oxidising agents that can be used to oxidise particularly aldehyde and ketones, for example $ Cr{O_3} $ , PCC. PCC is used particularly to oxidise alcohol into ketone. On oxidising a carbonyl compound (aldehyde and ketone) the formation of carboxylic acid can be seen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




