
How many isomers of \[{C_5}{H_{11}}OH\;\] will be primary alcohols?
A. 5
B. 4
C. 3
D. 2
Answer
570k+ views
Hint:Isomers refer to the organic molecules having the similar molecular formula but distinct arrangement of atoms in space. There are generally two types of isomers i.e. (i) Constitutional isomers which refer to the molecules of different connectivity and (ii) stereoisomers which refer to the molecules of same connectivity but the parts are oriented distinctly in space.
Complete answer:
The given compound i.e. \[{C_5}{H_{11}}OH\;\] (pentanol) is an alcohol with 5 numbers of carbon atoms. The structure of pentanol is shown below:
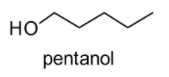
Since the given compound i.e. hexane possess only one functional group i.e. (\[ - OH\]), we can create its structural or constitutional isomers. We can form the structural isomers of pentanol because there is a possibility of branching in the carbon chains of pentanol. By switching the methyl groups (i.e. \[C{H_3}\]) and hydrogen atoms and also the hydroxyl group (\[ - OH\]) on the main carbon chain, we can change the way the atoms are bonded with each other. In the present case, we can observe a total of 8 structural isomers of pentanol i.e. 1-pentanol, 2-pentanol, 3-pentanol, 2-methylbutan-1-ol, 3-methylbutan-1-ol, 2-methylbutan-2-ol, 2-methylbutan-3-ol and 2,2-dimethylpropanol as demonstrated below:
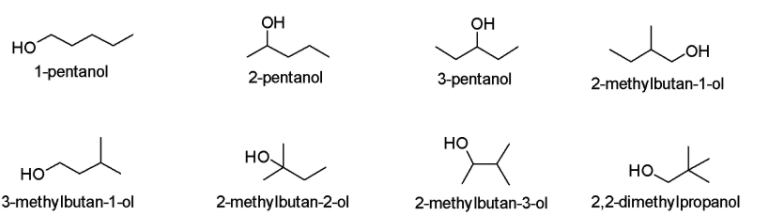
Therefore, as clear from the aforementioned structures, four isomers of \[{C_5}{H_{11}}OH\;\]will be primary alcohols.
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note:
In order to determine whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers, you can count the number of each atom in both of the molecules and check how the atoms are being arranged. Always remember that as the number of carbon atoms in an alkane increases, the number of its structural (or constitutional) isomers also increases.
Complete answer:
The given compound i.e. \[{C_5}{H_{11}}OH\;\] (pentanol) is an alcohol with 5 numbers of carbon atoms. The structure of pentanol is shown below:

Since the given compound i.e. hexane possess only one functional group i.e. (\[ - OH\]), we can create its structural or constitutional isomers. We can form the structural isomers of pentanol because there is a possibility of branching in the carbon chains of pentanol. By switching the methyl groups (i.e. \[C{H_3}\]) and hydrogen atoms and also the hydroxyl group (\[ - OH\]) on the main carbon chain, we can change the way the atoms are bonded with each other. In the present case, we can observe a total of 8 structural isomers of pentanol i.e. 1-pentanol, 2-pentanol, 3-pentanol, 2-methylbutan-1-ol, 3-methylbutan-1-ol, 2-methylbutan-2-ol, 2-methylbutan-3-ol and 2,2-dimethylpropanol as demonstrated below:

Therefore, as clear from the aforementioned structures, four isomers of \[{C_5}{H_{11}}OH\;\]will be primary alcohols.
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note:
In order to determine whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers, you can count the number of each atom in both of the molecules and check how the atoms are being arranged. Always remember that as the number of carbon atoms in an alkane increases, the number of its structural (or constitutional) isomers also increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




