
What is isomer? Write the isomer of butane with structural formula.
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: Structural isomers are those which have the same molecular formula but different bonding patterns and atomic organization. Butane is an organic compound with 4 carbon atoms attached with single bonds. So, just see the number of arrangements that can be formed by butane.
Complete step by step answer:
-Isomers are molecules which have identical chemical formulas but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. The two main forms of isomerism are:
-structural isomerism or constitutional isomerism in which bonds differ
-stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism where orientation of atoms differs.
-structural isomers are those isomers where the molecular formula remains same, only their bonding patterns and atomic organisation differs.
-Butane is a 4 carbon organic compound and since the suffix is –ane we can say that there are only single bonds (it is a saturated molecule). There are no double or triple bonds (it is not unsaturated).
-It’s molecular formula is: ${C_4}{H_{10}}$.
-Butane can form 2 structural isomers: 1) n-butane
2) isobutene (2-methylpropane)
1) n-butane or butane: In this first arrangement all the 4 carbon atoms are arranged one after the other to form a single chain with no branching. It is known as n-butane and its molecular formula is ${C_4}{H_{10}}$.
Its structural formula is:
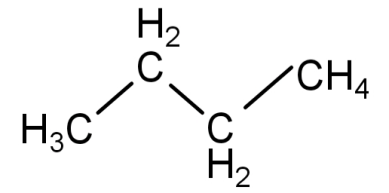
2) isobutane or 2-methylpropane: in this type of arrangement 3 carbon atoms are arranged in a straight chain and the 4th carbon atom is attached to the 2nd carbon atom of the straight chain to form a branch. This is known as isobutane and the IUPAC name is 2-methylpropane. Its molecular formula is ${C_4}{H_{10}}$.
Its structural formula is:
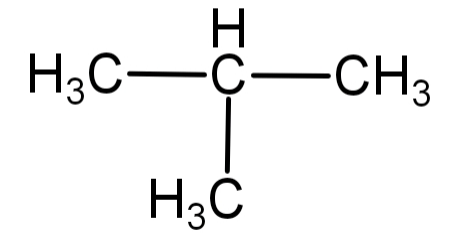
-For butane only 2 patterns of bond arrangements can be formed. Hence butane has 2 structural isomers: 1) n-butane (butane)
2) isobutene (2-methylpropane)
Note: Just be careful while drawing the structures and naming them.Never make the mistake of thinking that both the structural isomers are the same. They have the same molecular formula but different structure which causes them to have different chemical properties, different boiling point, melting point, etc.
Complete step by step answer:
-Isomers are molecules which have identical chemical formulas but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. The two main forms of isomerism are:
-structural isomerism or constitutional isomerism in which bonds differ
-stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism where orientation of atoms differs.
-structural isomers are those isomers where the molecular formula remains same, only their bonding patterns and atomic organisation differs.
-Butane is a 4 carbon organic compound and since the suffix is –ane we can say that there are only single bonds (it is a saturated molecule). There are no double or triple bonds (it is not unsaturated).
-It’s molecular formula is: ${C_4}{H_{10}}$.
-Butane can form 2 structural isomers: 1) n-butane
2) isobutene (2-methylpropane)
1) n-butane or butane: In this first arrangement all the 4 carbon atoms are arranged one after the other to form a single chain with no branching. It is known as n-butane and its molecular formula is ${C_4}{H_{10}}$.
Its structural formula is:

2) isobutane or 2-methylpropane: in this type of arrangement 3 carbon atoms are arranged in a straight chain and the 4th carbon atom is attached to the 2nd carbon atom of the straight chain to form a branch. This is known as isobutane and the IUPAC name is 2-methylpropane. Its molecular formula is ${C_4}{H_{10}}$.
Its structural formula is:

-For butane only 2 patterns of bond arrangements can be formed. Hence butane has 2 structural isomers: 1) n-butane (butane)
2) isobutene (2-methylpropane)
Note: Just be careful while drawing the structures and naming them.Never make the mistake of thinking that both the structural isomers are the same. They have the same molecular formula but different structure which causes them to have different chemical properties, different boiling point, melting point, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




