
Is the magnetic field inside a current carrying solenoid constant at all points?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint:Here in order to begin with answering the question we will start by knowing what does the term “solenoid” means and then we will know what happens to the magnetic field inside a current carrying solenoid.
Complete answer:
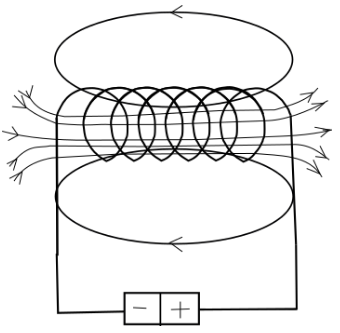
A solenoid is a coil of several circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped tightly in a cylinder shape. The field pattern is identical to that of a magnetic field around a bar magnet.The solenoid's one end acts as a magnetic north pole, while the other acts as a magnetic south pole.
Within the solenoid, the field lines are in the shape of parallel straight lines. This means that the magnetic field within the solenoid is the same at all points. That is, the field within the solenoid is uniform. Since the lines are entirely parallel to each other, the magnetic field in the solenoid remains constant.
The applied current and the number of turns per unit length are proportional to the magnetic field within a solenoid. The field strength is independent of the solenoid's diameter, and the field strength is independent of the location inside the solenoid, i.e. the field inside the solenoid is constant. Except for the fact that magnetic fields are stronger near the poles, the magnetic field within a solenoid is constant as the lines pass from north to south in a uniform manner of the same magnitude without causing any deflection.
Note:Solenoids are mostly used to generate magnetic fields or as electromagnets, and they have a wide range of applications. A solenoid is made up of tightly woven wire loops in the shape of a helix, with each loop having its own magnetic field (magnetic moment or magnetic dipole moment).
Complete answer:

A solenoid is a coil of several circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped tightly in a cylinder shape. The field pattern is identical to that of a magnetic field around a bar magnet.The solenoid's one end acts as a magnetic north pole, while the other acts as a magnetic south pole.
Within the solenoid, the field lines are in the shape of parallel straight lines. This means that the magnetic field within the solenoid is the same at all points. That is, the field within the solenoid is uniform. Since the lines are entirely parallel to each other, the magnetic field in the solenoid remains constant.
The applied current and the number of turns per unit length are proportional to the magnetic field within a solenoid. The field strength is independent of the solenoid's diameter, and the field strength is independent of the location inside the solenoid, i.e. the field inside the solenoid is constant. Except for the fact that magnetic fields are stronger near the poles, the magnetic field within a solenoid is constant as the lines pass from north to south in a uniform manner of the same magnitude without causing any deflection.
Note:Solenoids are mostly used to generate magnetic fields or as electromagnets, and they have a wide range of applications. A solenoid is made up of tightly woven wire loops in the shape of a helix, with each loop having its own magnetic field (magnetic moment or magnetic dipole moment).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




