
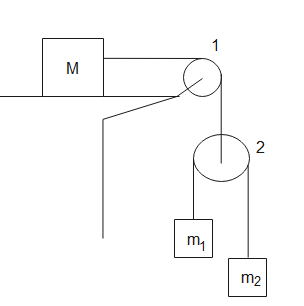
Ion the arrangement as shown below, ${{m}_{1}}=1kg$, ${{m}_{2}}=2kg$. Pulleys are massless and strings are light. For what value of $M$, the mass ${{m}_{1}}$ will move with constant velocity? (Neglect friction)
(1). $4kg$
(2). $8kg$
(3). $6kg$
(4). $10kg$

Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: The system of blocks and pulleys is isolated as no external forces are acting on it. All the forces acting between the elements of the system are internal forces. We can resolve forces along the different directions and use it to make equations. Using the equations, we can calculate the required parameter.
Formula Used:
${{m}_{1}}g=T$
${{m}_{2}}g-T={{m}_{2}}a$
$2T=M{{a}_{1}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given a system of three blocks attached to two pulleys, mass ${{m}_{1}}$ is moving with constant velocity, this means net forces acting on it are zero.
The forces acting on the system are as shown,
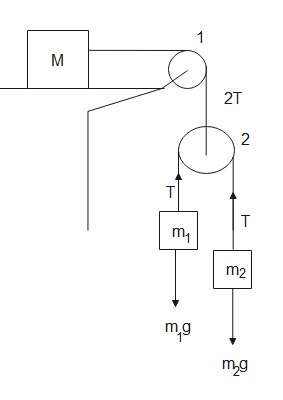
Forces acting on ${{m}_{1}}$ are-
${{m}_{1}}g=T$
From the above equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& T=1\times g \\
& \therefore T=g \\
\end{align}$
The forces acting on ${{m}_{2}}$ are
${{m}_{2}}g-T={{m}_{2}}a$
When we substitute given values in the above equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2\times g-g=2\times a \\
& \Rightarrow g=2a \\
& \therefore a=\dfrac{g}{2} \\
\end{align}$
${{m}_{2}}$ is moving with acceleration, $\dfrac{g}{2}$.
Let the mass $M$ move with acceleration, ${{a}_{1}}$ . so the whole system will move with acceleration ${{a}_{1}}$. The forces acting on the string will cause it to stretch, since there is no movement on the string, the accelerations cancel each other.
$\begin{align}
& a-{{a}_{1}}-{{a}_{1}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow a=2{{a}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}_{1}}=\dfrac{a}{2} \\
& \therefore {{a}_{1}}=\dfrac{g}{2} \\
\end{align}$
The forces acting on mass $M$ are-
$\begin{align}
& 2T=M{{a}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2T}{{{a}_{1}}}=M \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2\times g}{\dfrac{g}{2}}=M \\
& \therefore 4kg=M \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the mass of $M$ for which ${{m}_{1}}$ moves with constant velocity is $4kg$.
Hence, the correct option is (1).
Note:
The tension in a string is the pulling force acting on a string. It is the action-reaction pair of forces acting on the point at which a string is connected to an object. The pulleys and strings are considered massless. The action-reaction pairs follow Newton’s third law of motion, which states that forces acting between two bodies are equal and opposite. According to Newton’s second law of motion, a force is required to change the state of rest or motion of an object.
Formula Used:
${{m}_{1}}g=T$
${{m}_{2}}g-T={{m}_{2}}a$
$2T=M{{a}_{1}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given a system of three blocks attached to two pulleys, mass ${{m}_{1}}$ is moving with constant velocity, this means net forces acting on it are zero.
The forces acting on the system are as shown,

Forces acting on ${{m}_{1}}$ are-
${{m}_{1}}g=T$
From the above equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& T=1\times g \\
& \therefore T=g \\
\end{align}$
The forces acting on ${{m}_{2}}$ are
${{m}_{2}}g-T={{m}_{2}}a$
When we substitute given values in the above equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2\times g-g=2\times a \\
& \Rightarrow g=2a \\
& \therefore a=\dfrac{g}{2} \\
\end{align}$
${{m}_{2}}$ is moving with acceleration, $\dfrac{g}{2}$.
Let the mass $M$ move with acceleration, ${{a}_{1}}$ . so the whole system will move with acceleration ${{a}_{1}}$. The forces acting on the string will cause it to stretch, since there is no movement on the string, the accelerations cancel each other.
$\begin{align}
& a-{{a}_{1}}-{{a}_{1}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow a=2{{a}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}_{1}}=\dfrac{a}{2} \\
& \therefore {{a}_{1}}=\dfrac{g}{2} \\
\end{align}$
The forces acting on mass $M$ are-
$\begin{align}
& 2T=M{{a}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2T}{{{a}_{1}}}=M \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2\times g}{\dfrac{g}{2}}=M \\
& \therefore 4kg=M \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the mass of $M$ for which ${{m}_{1}}$ moves with constant velocity is $4kg$.
Hence, the correct option is (1).
Note:
The tension in a string is the pulling force acting on a string. It is the action-reaction pair of forces acting on the point at which a string is connected to an object. The pulleys and strings are considered massless. The action-reaction pairs follow Newton’s third law of motion, which states that forces acting between two bodies are equal and opposite. According to Newton’s second law of motion, a force is required to change the state of rest or motion of an object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




