
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is exhibited by?
A) O-nitrophenol
B) Catechol
C) Salicylic acid
D) All of these acid
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint:
Hydrogen bond is an additional linkage that occurs between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom like oxygen, nitrogen and fluorine. The hydrogen atom should be bonded to a highly electronegative element as well.
Complete step by step solution:
In intramolecular hydrogen bonding, as the name suggests, the polar hydrogen and the electronegative atom are present in the same molecule. When an intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed a five or six membered ring is formed. This ring formed must be planar and the interacting atoms should be placed in such a way that there is minimum strain during ring closure.
We consider, option A, that is, ortho-nitro phenol.
In the hydroxyl group, a hydrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom making it polar and suitable for hydrogen bonding. The nitro group present at the ortho position is in close proximity with the hydrogen atom. Also the hydrogen bond formation between the hydrogen and oxygen results in formation of a six membered planar ring.
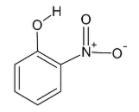
Thus, an intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed.
Now, considering option B, that is, catechol.
In catechol, we have a phenol molecule with a hydroxyl group at the ortho position. The hydrogen of one hydroxyl group will form a hydrogen bond with the oxygen atom of the other hydroxyl group forming a six membered planar ring.
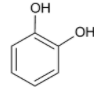
Thus, an intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed.
We consider option C, that is, salicylic acid
In salicylic acid hydrogen bonding can take place between the hydrogen and oxygen of the hydroxyl groups on the benzene ring and of the carboxylic acid group.
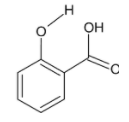
An intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed.
Thus we can conclude that intra molecular hydrogen bonding takes place in all the given compounds.
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note:
Hydrogen bonding between two atoms of the same molecule leads to unavailability of these atoms to bond with atoms of other molecules. As a result, the boiling points as well as solubility are less for such molecules as their atoms do not interact with the other molecules.
Hydrogen bond is an additional linkage that occurs between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom like oxygen, nitrogen and fluorine. The hydrogen atom should be bonded to a highly electronegative element as well.
Complete step by step solution:
In intramolecular hydrogen bonding, as the name suggests, the polar hydrogen and the electronegative atom are present in the same molecule. When an intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed a five or six membered ring is formed. This ring formed must be planar and the interacting atoms should be placed in such a way that there is minimum strain during ring closure.
We consider, option A, that is, ortho-nitro phenol.
In the hydroxyl group, a hydrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom making it polar and suitable for hydrogen bonding. The nitro group present at the ortho position is in close proximity with the hydrogen atom. Also the hydrogen bond formation between the hydrogen and oxygen results in formation of a six membered planar ring.

Thus, an intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed.
Now, considering option B, that is, catechol.
In catechol, we have a phenol molecule with a hydroxyl group at the ortho position. The hydrogen of one hydroxyl group will form a hydrogen bond with the oxygen atom of the other hydroxyl group forming a six membered planar ring.

Thus, an intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed.
We consider option C, that is, salicylic acid
In salicylic acid hydrogen bonding can take place between the hydrogen and oxygen of the hydroxyl groups on the benzene ring and of the carboxylic acid group.

An intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed.
Thus we can conclude that intra molecular hydrogen bonding takes place in all the given compounds.
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note:
Hydrogen bonding between two atoms of the same molecule leads to unavailability of these atoms to bond with atoms of other molecules. As a result, the boiling points as well as solubility are less for such molecules as their atoms do not interact with the other molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




