
In which stage of meiosis, crossing over takes place?
(a)Pachytene
(b)Leptotene
(c)Metaphase
(d)Anaphase
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: In this stage of meiosis formation of recombination nodules is observed. At the end of this phase synaptonemal complex starts dissolving. The name of this stage means ‘thick thread’. Nicking of DNA chromosomes is also seen in this stage.
Complete answer:
During meiosis I in prophase I, crossing over takes place. Prophase I can further be divided into leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
The pairing of chromosomes is a characteristic feature of meiosis which distinguishes it from Mitosis, Homologous chromosomes pair during the prophase I of meiosis I.
The prophase I stage of meiosis can be elaborated into the following substages- leptotene zygotene pachytene diplotene and diakinesis.
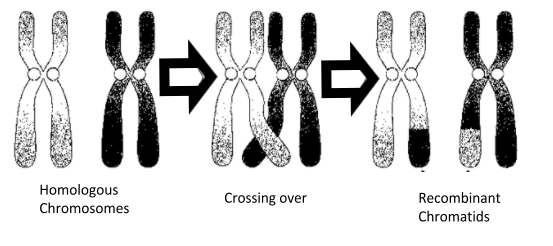
In the leptotene stage chromosomes coil, in the zygotene stage, the chromosomes pair, and a crossing occurs during the pachytene stage between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
Crossing over is a process where homologous chromosomes pair up with each other and exchange different segments of genetic material (DNA) to form a Recombinant chromosome.
Diplotene is characterized by the appearance of Chiasma, on the locations at which crossing over has occurred. In diakinesis, the chiasma undergoes terminalisation, and both the homologous chromosomes separate.
So, the correct answer is, “Pachytene.”
Note:
Recombination involves a mutual exchange of the segments of non-sister chromatids between homologous chromosomes. It takes place by breakage and reunion of chromatid segments. Breakage, called nicking, is completed by an enzyme endonuclease and reunion, termed annealing, is assisted by an enzyme ligase
In humans, the meiosis is seen in the haploid gamete cell. Variation occurs due to meiosis, as crossing over and random orientation of homologous pairs is seen in metaphase I.
Complete answer:
During meiosis I in prophase I, crossing over takes place. Prophase I can further be divided into leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
The pairing of chromosomes is a characteristic feature of meiosis which distinguishes it from Mitosis, Homologous chromosomes pair during the prophase I of meiosis I.
The prophase I stage of meiosis can be elaborated into the following substages- leptotene zygotene pachytene diplotene and diakinesis.

In the leptotene stage chromosomes coil, in the zygotene stage, the chromosomes pair, and a crossing occurs during the pachytene stage between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
Crossing over is a process where homologous chromosomes pair up with each other and exchange different segments of genetic material (DNA) to form a Recombinant chromosome.
Diplotene is characterized by the appearance of Chiasma, on the locations at which crossing over has occurred. In diakinesis, the chiasma undergoes terminalisation, and both the homologous chromosomes separate.
So, the correct answer is, “Pachytene.”
Note:
Recombination involves a mutual exchange of the segments of non-sister chromatids between homologous chromosomes. It takes place by breakage and reunion of chromatid segments. Breakage, called nicking, is completed by an enzyme endonuclease and reunion, termed annealing, is assisted by an enzyme ligase
In humans, the meiosis is seen in the haploid gamete cell. Variation occurs due to meiosis, as crossing over and random orientation of homologous pairs is seen in metaphase I.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




