
In which of the following species, correct direction of inductive effect is shown?
A)
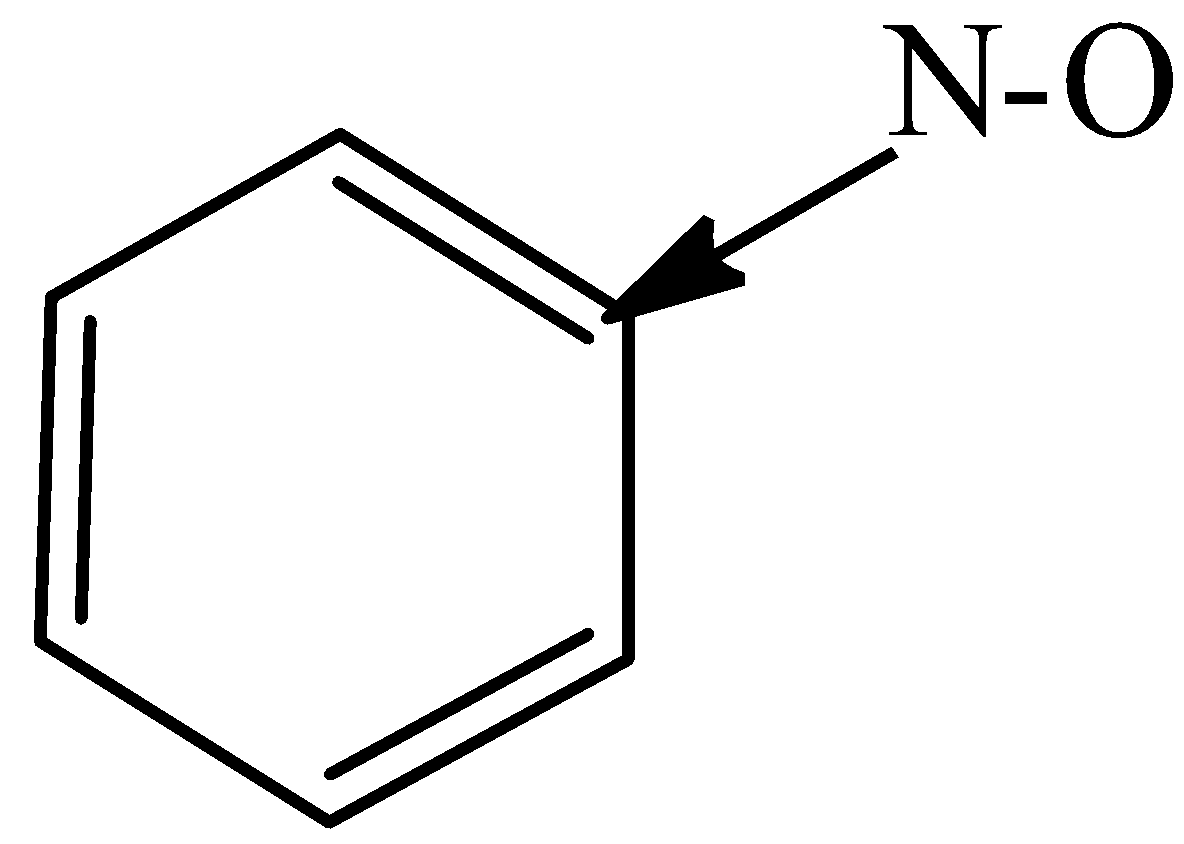
B)
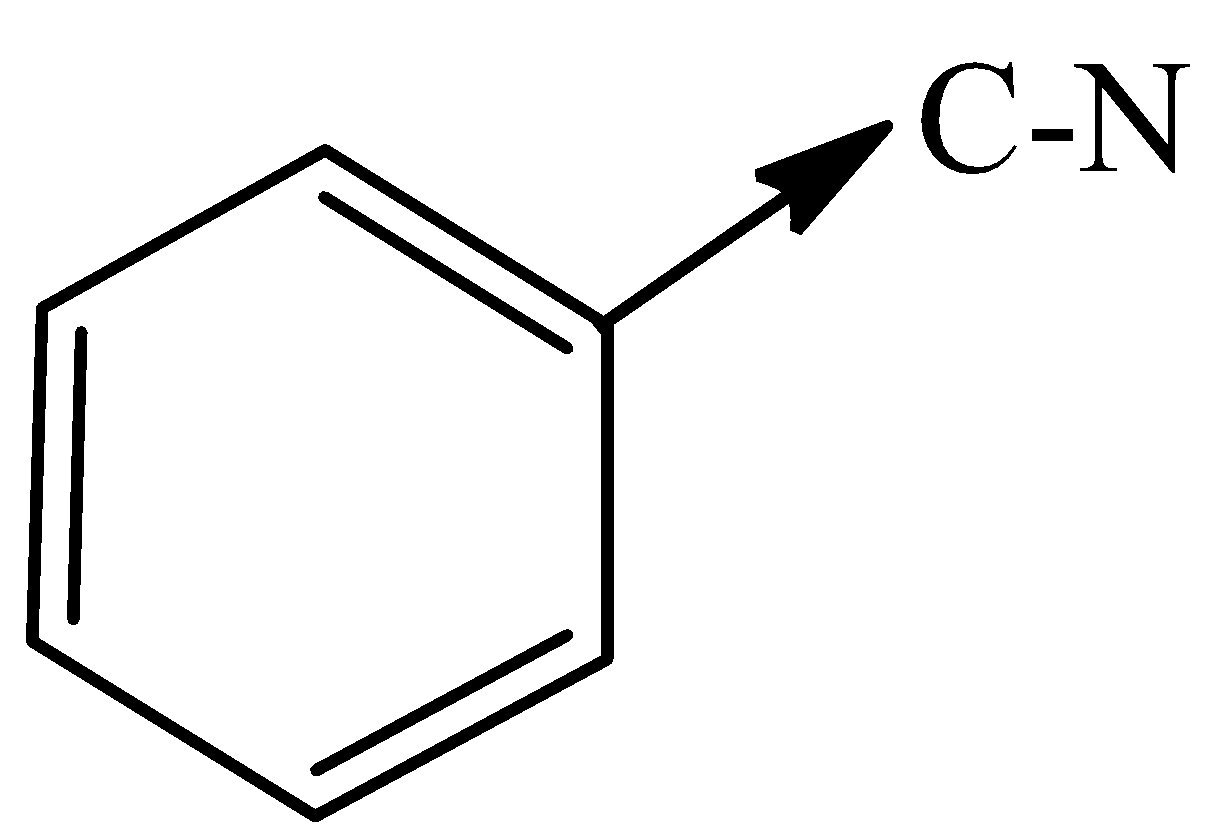
C)

D) None of the above.



Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: We know Inductive effect means the polarization of the sigma bond due to electron attracting and electron releasing effect of an adjacent atom.
\[C{H_3}^{\delta + + } - C{H_2}^{\delta + } - C{l^{\delta - }}\]
We have two types of inductive effect namely positive inductive effect (+I) and negative inductive effect (-I).
Complete step by step answer:
We know that an inductive effect is usually due to an electronegativity difference between the atoms at both the end of the bond. The more electronegative atom attracts the electrons in the bond towards itself creating bond polarity.
In the option both oxygen and nitrogen are more electronegative than carbon. They should pull the electrons and the arrow must be pointed towards nitrogen. Thus, the direction of the arrow is wrong.
Therefore, the option A is wrong.
In options (B) and (C), both the carbons are attached to nitrogen and oxygen respectively which are more electronegative than carbon. The carbon bonded to the Oxygen and Nitrogen shall attain partial negative charge and pull the electrons toward it.
Therefore, the options (B) and (C) are correct.
Note:
Positive inductive effect:
An atom or a group which attracts electrons towards itself less than a hydrogen atom is known as an electron-donating group and they are said to have a positive inductive effect (+I). Some of the groups with +I effects are $ - C{H_3}$,$ - {C_2}{H_5}$,${\left( { - C{H_3}} \right)_3}$ etc…
Negative inductive effect:
An atom or a group which attracts electrons towards itself more strongly than a hydrogen atom is known as an electron attracting group and they are said to have a negative inductive effect (-I). Some of the groups with -I effects are $ - Cl$,$ - N{O_2}$,$ - Br$,$ - I$ etc…
We also remember that an inductive effect is different from the resonance effect in which the sigma electrons, pi electrons and inductive effect are involved.
\[C{H_3}^{\delta + + } - C{H_2}^{\delta + } - C{l^{\delta - }}\]
We have two types of inductive effect namely positive inductive effect (+I) and negative inductive effect (-I).
Complete step by step answer:
We know that an inductive effect is usually due to an electronegativity difference between the atoms at both the end of the bond. The more electronegative atom attracts the electrons in the bond towards itself creating bond polarity.
In the option both oxygen and nitrogen are more electronegative than carbon. They should pull the electrons and the arrow must be pointed towards nitrogen. Thus, the direction of the arrow is wrong.
Therefore, the option A is wrong.
In options (B) and (C), both the carbons are attached to nitrogen and oxygen respectively which are more electronegative than carbon. The carbon bonded to the Oxygen and Nitrogen shall attain partial negative charge and pull the electrons toward it.
Therefore, the options (B) and (C) are correct.
Note:
Positive inductive effect:
An atom or a group which attracts electrons towards itself less than a hydrogen atom is known as an electron-donating group and they are said to have a positive inductive effect (+I). Some of the groups with +I effects are $ - C{H_3}$,$ - {C_2}{H_5}$,${\left( { - C{H_3}} \right)_3}$ etc…
Negative inductive effect:
An atom or a group which attracts electrons towards itself more strongly than a hydrogen atom is known as an electron attracting group and they are said to have a negative inductive effect (-I). Some of the groups with -I effects are $ - Cl$,$ - N{O_2}$,$ - Br$,$ - I$ etc…
We also remember that an inductive effect is different from the resonance effect in which the sigma electrons, pi electrons and inductive effect are involved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




