
In the Rosenmund’s reaction,
$RCOCl+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{Pd/BaS{{O}_{4}}}RCHO+HCl$
Here $BaS{{O}_{4}}$ :
(a)- promotes the catalytic activity of Pd
(b)- removes the HCl formed in the reaction
(c)- deactivates palladium
(d)- activates palladium
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes in the presence of palladium and barium sulfate. Palladium is a strong reducing agent. It reduces the aldehydes to further alcohol. So, it has to be stopped at the stage of the aldehydes.
Complete answer:
Acid chlorides are easily reduced to the corresponding aldehydes by passing hydrogen gas through boiling xylene solution of the acid chloride in presence of Pd catalyst supported over $BaS{{O}_{4}}$ and partially poisoned by the addition of sulfur and quinoline.
The reactions are given below:
Acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes.
$RCOCl+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow[Boiling\text{ }xylene]{Pd,BaS{{O}_{4}},S}RCHO+HCl$
Example: Acetyl chloride is converted into acetaldehyde.
$C{{H}_{3}}COCl+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow[Boiling\text{ }xylene]{Pd,BaS{{O}_{4}},S}C{{H}_{3}}CHO+HCl$
Benzoyl chloride is converted into benzaldehyde.
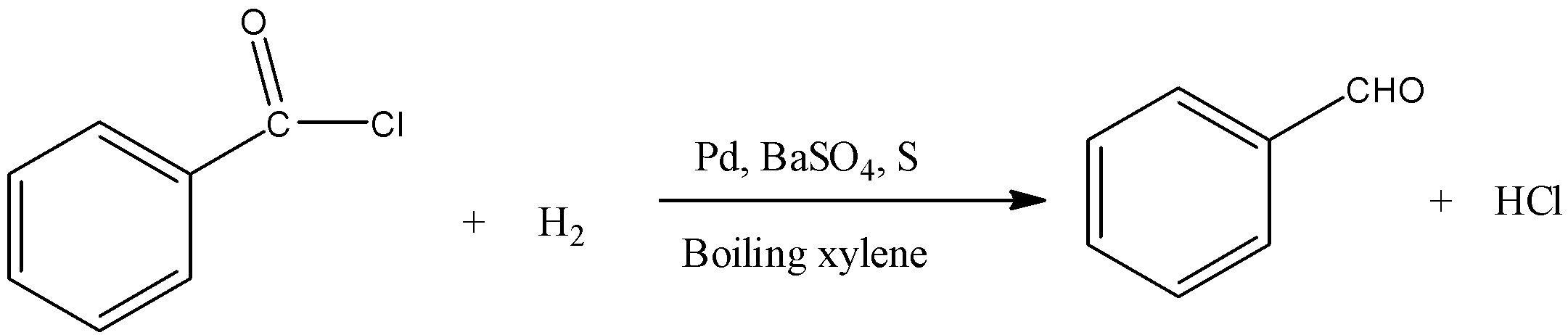
Normally, aldehydes are further reduced to primary alcohols. But the addition of $BaS{{O}_{4}}$ and sulfur (or quinoline) poisons the palladium catalyst and thus does not permit the further reduction of aldehydes to alcohols.
Hence the correct answer is an option (c)- deactivates palladium.
Additional information:
Acid chlorides can be converted into aldehydes by lithium-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride $[LiAlH{{(O-t-Bu)}_{3}}]$ at 196K.
The reaction is given below:
$RCOCl\xrightarrow[{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}]{LiAlH{{(O-t-Bu)}_{3}},dry\text{ }ether,196K}RCHO$
It may be noted that $[LiAlH{{(O-t-Bu)}_{3}}]$is less reactive than $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ because the electron-withdrawing t-butoxy group stabilizes the negatively charged aluminium ion. Therefore, it reduces the more reactive acid chlorides to aldehydes but does not reduce the less reactive aldehydes to primary alcohols.
Note: With the rosenmund reaction formaldehyde cannot be prepared since formyl chloride, $HCOCl$ is unstable to room temperature. This reaction is used only for the preparation of aldehydes but not for ketones.
Complete answer:
Acid chlorides are easily reduced to the corresponding aldehydes by passing hydrogen gas through boiling xylene solution of the acid chloride in presence of Pd catalyst supported over $BaS{{O}_{4}}$ and partially poisoned by the addition of sulfur and quinoline.
The reactions are given below:
Acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes.
$RCOCl+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow[Boiling\text{ }xylene]{Pd,BaS{{O}_{4}},S}RCHO+HCl$
Example: Acetyl chloride is converted into acetaldehyde.
$C{{H}_{3}}COCl+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow[Boiling\text{ }xylene]{Pd,BaS{{O}_{4}},S}C{{H}_{3}}CHO+HCl$
Benzoyl chloride is converted into benzaldehyde.

Normally, aldehydes are further reduced to primary alcohols. But the addition of $BaS{{O}_{4}}$ and sulfur (or quinoline) poisons the palladium catalyst and thus does not permit the further reduction of aldehydes to alcohols.
Hence the correct answer is an option (c)- deactivates palladium.
Additional information:
Acid chlorides can be converted into aldehydes by lithium-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride $[LiAlH{{(O-t-Bu)}_{3}}]$ at 196K.
The reaction is given below:
$RCOCl\xrightarrow[{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}]{LiAlH{{(O-t-Bu)}_{3}},dry\text{ }ether,196K}RCHO$
It may be noted that $[LiAlH{{(O-t-Bu)}_{3}}]$is less reactive than $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ because the electron-withdrawing t-butoxy group stabilizes the negatively charged aluminium ion. Therefore, it reduces the more reactive acid chlorides to aldehydes but does not reduce the less reactive aldehydes to primary alcohols.
Note: With the rosenmund reaction formaldehyde cannot be prepared since formyl chloride, $HCOCl$ is unstable to room temperature. This reaction is used only for the preparation of aldehydes but not for ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




