
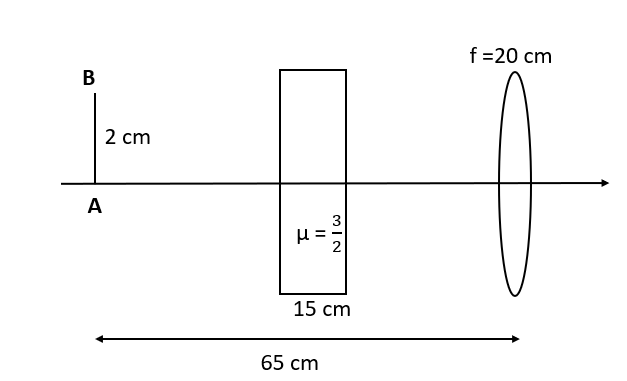
In the given figure, the image of object AB observed by observer is:

Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: The image distance can be measured with the information of object length and focal length with the aid of the lens formula. In optics, the connection between the image distance (i), the object distance (u), and the focal length (f) are provided by the formula identified as the Lens formula. The lens formula is suitable for convex and concave lenses. These lenses have almost negligible thickness.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given: A plate of thickness $t = 15 cm$ is inserted in between the lens.
Refractive index of plate is $\mu = \dfrac{3}{2}$
Object’s distance, $u = 65 cm$
Focal length, $f = 20 cm$
There is shift in the object distance due to insertion of plate.
Shift, $s = t \left(1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu} \right)$
After putting the value of thickness and refractive index. We get,
$s = 15 \left(1 - \dfrac{2}{3} \right) = 5 cm$
We need to subtract shift distance from object’s distance.
Then, object distance will be $65 – 5 = 60 cm$
Apply Len’s formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Put $f = 20 cm; u =- 60 cm $
$\dfrac{1}{20} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{-60}$
$\dfrac{1}{20} - \dfrac{1}{60} = \dfrac{1}{v}$
$ \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{3-1}{60}$
We get, $v = 30 cm$.
Hence, the image of object AB observed by the observer is $30 cm$.
Note: The lens formula applies to all sites with suitable sign conventions. This lens formula applies to both the convex and concave lens. If the equation explains a negative image length, then the image is a practical image on the corresponding side of the lens while the object. If this equation gives a negative focal length, then the lens is a divergent lens rather than the convergent lens. This equation is utilized to obtain image distance for both real or virtual images.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given: A plate of thickness $t = 15 cm$ is inserted in between the lens.
Refractive index of plate is $\mu = \dfrac{3}{2}$
Object’s distance, $u = 65 cm$
Focal length, $f = 20 cm$
There is shift in the object distance due to insertion of plate.
Shift, $s = t \left(1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu} \right)$
After putting the value of thickness and refractive index. We get,
$s = 15 \left(1 - \dfrac{2}{3} \right) = 5 cm$
We need to subtract shift distance from object’s distance.
Then, object distance will be $65 – 5 = 60 cm$
Apply Len’s formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Put $f = 20 cm; u =- 60 cm $
$\dfrac{1}{20} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{-60}$
$\dfrac{1}{20} - \dfrac{1}{60} = \dfrac{1}{v}$
$ \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{3-1}{60}$
We get, $v = 30 cm$.
Hence, the image of object AB observed by the observer is $30 cm$.
Note: The lens formula applies to all sites with suitable sign conventions. This lens formula applies to both the convex and concave lens. If the equation explains a negative image length, then the image is a practical image on the corresponding side of the lens while the object. If this equation gives a negative focal length, then the lens is a divergent lens rather than the convergent lens. This equation is utilized to obtain image distance for both real or virtual images.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




