
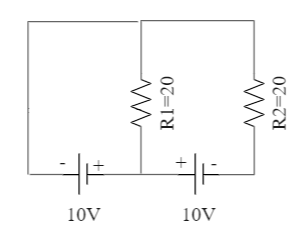
In the given circuit, the cells have zero internal resistance. The currents (in Amperes) passing through resistance $ {R_1} $ and $ {R_2} $ respectively are
A. 2, 2
B. 0, 1
C. 1, 2
D. $ 0.5 $, 0

Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint
The current through a resistor is dependent on the potential difference across it and the resistance possessed by the resistor. The potential difference across two points varies depending on the orientation of the source used.
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R} $, where V is the voltage across the component in consideration and R is the total resistance. I am currently in Amperes.
Complete step by step answer
Here, we have two resistances that are connected to two different voltage supplies with different orientation. We are asked to determine the current flowing through the two due to this potential difference.
We know that a cell creates a potential difference across the electrical component, and hence the voltage across the two resistances depending on the different orientation of the cell will be:
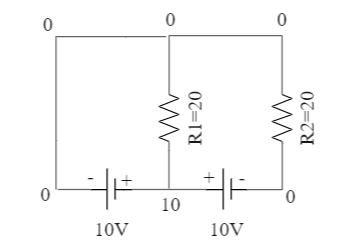
Now, we know that the current across a resistor is given by:
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R} $
So, for resistor $ {R_1} $ we have $ R = 20 $ and $ V = 10 $ :
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{10}}{{20}} = 0.5 $ A
And for resistor $ {R_2} $ we have $ R = 20 $ and $ V = 0 $ :
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{0}{{20}} = 0 $ A
Hence, the correct answer is option (D): $ 0.5 $, 0.
Note
The orientation of cells or voltage source plays an important role in current flow and potential difference across a component. For example, while trying to turn on a battery-powered charge, it will only work when the cells are correctly aligned with the positive and negative terminal of the components of the torch. When we insert the battery in an opposite direction, the current flowing across the circuit becomes 0 just as we saw for resistance 2.
The current through a resistor is dependent on the potential difference across it and the resistance possessed by the resistor. The potential difference across two points varies depending on the orientation of the source used.
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R} $, where V is the voltage across the component in consideration and R is the total resistance. I am currently in Amperes.
Complete step by step answer
Here, we have two resistances that are connected to two different voltage supplies with different orientation. We are asked to determine the current flowing through the two due to this potential difference.
We know that a cell creates a potential difference across the electrical component, and hence the voltage across the two resistances depending on the different orientation of the cell will be:

Now, we know that the current across a resistor is given by:
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R} $
So, for resistor $ {R_1} $ we have $ R = 20 $ and $ V = 10 $ :
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{10}}{{20}} = 0.5 $ A
And for resistor $ {R_2} $ we have $ R = 20 $ and $ V = 0 $ :
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{0}{{20}} = 0 $ A
Hence, the correct answer is option (D): $ 0.5 $, 0.
Note
The orientation of cells or voltage source plays an important role in current flow and potential difference across a component. For example, while trying to turn on a battery-powered charge, it will only work when the cells are correctly aligned with the positive and negative terminal of the components of the torch. When we insert the battery in an opposite direction, the current flowing across the circuit becomes 0 just as we saw for resistance 2.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




