
In the following compounds
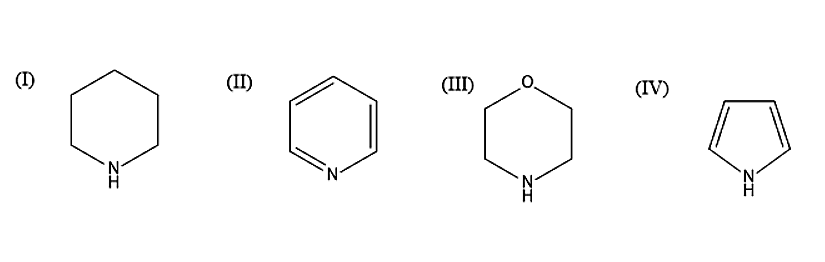
The order of basicity is
(A) IV > I > III > II
(B) III > I > IV > II
(C) II > I > III > IV
(D) I > III > II > IV

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: In order to find the order of the basicity of the given compounds, we must first have an exact idea about what a basicity is. Basicity depends on the tendency of a molecule to donate electron pairs. Presence of the lone pairs of electrons plays a very crucial role in the basicity of the compound.
Complete Solution :
- Let us first see the basics. Basicity is the measure of the electron donating power of the molecule. When more lone pairs are donated, then the basic character will be more. When the base is strong, electron donation will be easier. Lone pairs will be having a negative charge and in order to stabilize the compound, the lone pair is donated and it will come in conjugation to form a stable compound. Now let us move on to the structures given. When there is more resonance structure, basicity will be less. Compound IV will be least basic because the lone pair of electrons present on the Nitrogen atom is involved in delocalisation, in order to form resonance structure. In the remaining compound the lone pairs in the Nitrogen atoms are localised. In the compound I and III, the Nitrogen atom is \[s{p^3}\] hybridised, while in the compound II, the Nitrogen atom is \[s{p^2}\] hybridised. When the s character is more, then the compound is least basic. As we know that in compound II, the Nitrogen atom is \[s{p^2}\] hybridised and therefore it is least basic, because it has more s character compared to I and III. Due to the negative inductive effect, the oxygen atom will pull the electrons towards itself. Thus, the electrons will move away from the Nitrogen atom. Therefore, the compound III is less basic than the compound I. Hence the compound I is more basic.
The order of basicity is given as I > III > II > IV.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Certain points to note while determining the order of basicity of the compounds. When there is delocalisation of the electron of a compound, then the compound will be less basic. When the s character of the Nitrogen atom is more, then it is also less basic.
Complete Solution :
- Let us first see the basics. Basicity is the measure of the electron donating power of the molecule. When more lone pairs are donated, then the basic character will be more. When the base is strong, electron donation will be easier. Lone pairs will be having a negative charge and in order to stabilize the compound, the lone pair is donated and it will come in conjugation to form a stable compound. Now let us move on to the structures given. When there is more resonance structure, basicity will be less. Compound IV will be least basic because the lone pair of electrons present on the Nitrogen atom is involved in delocalisation, in order to form resonance structure. In the remaining compound the lone pairs in the Nitrogen atoms are localised. In the compound I and III, the Nitrogen atom is \[s{p^3}\] hybridised, while in the compound II, the Nitrogen atom is \[s{p^2}\] hybridised. When the s character is more, then the compound is least basic. As we know that in compound II, the Nitrogen atom is \[s{p^2}\] hybridised and therefore it is least basic, because it has more s character compared to I and III. Due to the negative inductive effect, the oxygen atom will pull the electrons towards itself. Thus, the electrons will move away from the Nitrogen atom. Therefore, the compound III is less basic than the compound I. Hence the compound I is more basic.
The order of basicity is given as I > III > II > IV.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Certain points to note while determining the order of basicity of the compounds. When there is delocalisation of the electron of a compound, then the compound will be less basic. When the s character of the Nitrogen atom is more, then it is also less basic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




