
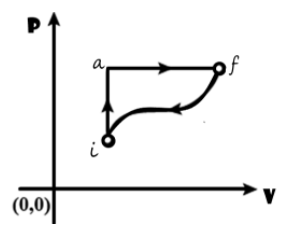
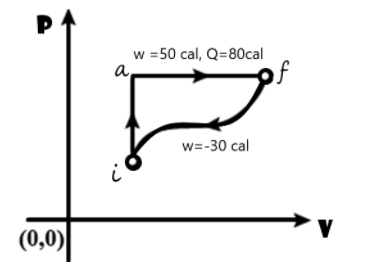
In the diagram shown $\text{ }{{\text{Q}}_{\text{iaf}}}\text{ = 80 cal }$and $\text{ }{{\text{W}}_{\text{iaf}}}\text{ = 50 cal }$.If $\text{ W= }-30\text{ cal }$ for the curved path fi, the value of Q for path fi will be
A) 60 cal
B) 30 cal
C) $\text{ }-30\text{ }$ Cal
D) $\text{ }-60\text{ }$Cal

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: According to the first law of thermodynamics, the change in the internal enthalpy U of the system is related to the heat q absorbed or release and work done w.The relation is as shown below:
$\text{ }\Delta \text{U = Q + W }$
Since internal enthalpy U is a state function, it is immaterial which path has been taken by the system to undergo the change from one state to another. In the P-V plot, increases in volume on pressure are an expansion of gas, and a decrease in the volume is compression of the gas.
Complete step by step solution:
We are provided with the following data:
Heat Q for the path iaf is given as ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{iaf}}}$80 cal
Work done W for the path iaf is given as 50 cal
Work W for the curved path fi is given as $\text{ }-30\text{ }$ cal
We are interested to find out the value of heat Q for the path fi
From the given plot of pressure P against the volume V, the initial state ‘i’ changes to the final state ‘f’ via two pathways .These are path iaf and path if.
According to the first law of thermodynamics, let $\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{fi }}}$ be the change in the internal energy of the system long the path fi .here system undergoes the change in state from f to i. Suppose the system undergoes the change in the state from f to i, then the heat of the system is equal to q, and then during the change, the volume decreases thus the work is done by the system on the surrounding. Thus internal enthalpy of a system for the path iaf is written as,
$\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{iaf}}}\text{ = Q }-\text{W }$
Let's substitute the values in the equation. we have,
$\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{iaf}}}\text{ = 80}-50\text{ }\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{fi}}}\text{ }=\text{ 30 cal }$
Therefore, the internal enthalpy for the path fi is 30 cal.
Since the enthalpy is a state function, the internal enthalpy from the path iaf and by the path fi is equal but opposite in sign. Thus for path fi, the internal enthalpy is \[\text{ }\Delta {{\text{U}}_{\text{fi}}}\text{ = }-30\text{ cal }\]
We are interested in determining the heat change along the fi path. Form first law of thermodynamic equation heat is written as,
$\text{ Q = }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{fi}}}-\text{W }$
Substitute the values in the above equation. We have,
$\text{ Q = }-30-30\text{ = }-60\text{ cal }$
Therefore, the heat change for the path is equal to \[-60\]cal.
Hence, (D) is the correct option.
Note: Note that, if the work is done by the surrounding on the system (i.e. compression of gas) then the w is taken as the positive, and for isothermal process the relation becomes$\text{ Q = }-\text{W }$. In the P-V plot, compression is expressed by the change in system from final to initial state.
However, when work is done by the system on the surrounding (i.e. expansion) the w is taken as the negative, and for an isothermal process the relation becomes$\text{ Q = W }$. In the P-V plot, expansion is expressed by the change in system from initial to the final state.
$\text{ }\Delta \text{U = Q + W }$
Since internal enthalpy U is a state function, it is immaterial which path has been taken by the system to undergo the change from one state to another. In the P-V plot, increases in volume on pressure are an expansion of gas, and a decrease in the volume is compression of the gas.
Complete step by step solution:
We are provided with the following data:
Heat Q for the path iaf is given as ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{iaf}}}$80 cal
Work done W for the path iaf is given as 50 cal
Work W for the curved path fi is given as $\text{ }-30\text{ }$ cal
We are interested to find out the value of heat Q for the path fi
From the given plot of pressure P against the volume V, the initial state ‘i’ changes to the final state ‘f’ via two pathways .These are path iaf and path if.

According to the first law of thermodynamics, let $\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{fi }}}$ be the change in the internal energy of the system long the path fi .here system undergoes the change in state from f to i. Suppose the system undergoes the change in the state from f to i, then the heat of the system is equal to q, and then during the change, the volume decreases thus the work is done by the system on the surrounding. Thus internal enthalpy of a system for the path iaf is written as,
$\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{iaf}}}\text{ = Q }-\text{W }$
Let's substitute the values in the equation. we have,
$\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{iaf}}}\text{ = 80}-50\text{ }\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{fi}}}\text{ }=\text{ 30 cal }$
Therefore, the internal enthalpy for the path fi is 30 cal.
Since the enthalpy is a state function, the internal enthalpy from the path iaf and by the path fi is equal but opposite in sign. Thus for path fi, the internal enthalpy is \[\text{ }\Delta {{\text{U}}_{\text{fi}}}\text{ = }-30\text{ cal }\]
We are interested in determining the heat change along the fi path. Form first law of thermodynamic equation heat is written as,
$\text{ Q = }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{U}}_{\text{fi}}}-\text{W }$
Substitute the values in the above equation. We have,
$\text{ Q = }-30-30\text{ = }-60\text{ cal }$
Therefore, the heat change for the path is equal to \[-60\]cal.
Hence, (D) is the correct option.
Note: Note that, if the work is done by the surrounding on the system (i.e. compression of gas) then the w is taken as the positive, and for isothermal process the relation becomes$\text{ Q = }-\text{W }$. In the P-V plot, compression is expressed by the change in system from final to initial state.
However, when work is done by the system on the surrounding (i.e. expansion) the w is taken as the negative, and for an isothermal process the relation becomes$\text{ Q = W }$. In the P-V plot, expansion is expressed by the change in system from initial to the final state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




