
In presence of U.V. light bromination of benzene produces:
A.${C_6}{H_5}Br$
B.${C_6}{H_6}B{r_6}$
C.o & p Dibromobenzene
D.No reaction will be take place
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: In the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light or heat, the reaction of a halogen with an alkane results in the formation of a haloalkane (alkyl halide). The phenomenon is explained by the reaction mechanism. The mechanism to halogenate. The carbon-hydrogen bonds are low-polarity covalent bonds in the methane molecule.
Complete answer:
-In presence of U.V. Light bromination of benzene produces ${C_6}{H_6}B{r_6}$ or 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane. Three molecules of bromine are added across the carbon-carbon triple bond.
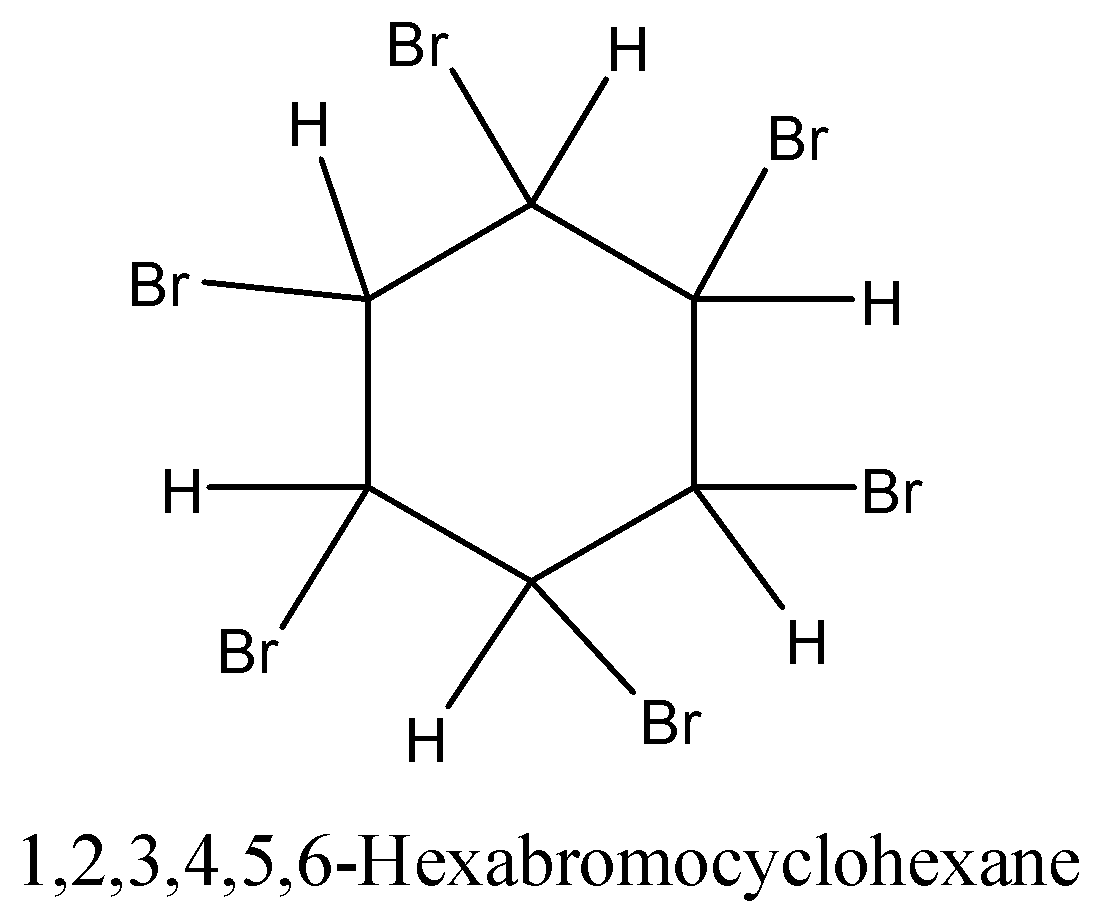
-In the presence of ultraviolet light (but without a catalyst present), hot benzene will also undergo an additional reaction with chlorine or bromine. The ring delocalization is permanently broken and a chlorine or bromine atom adds on to each carbon atom.
-For example, if you bubble chlorine gas through hot benzene exposed to UV light for an hour, you get 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane.
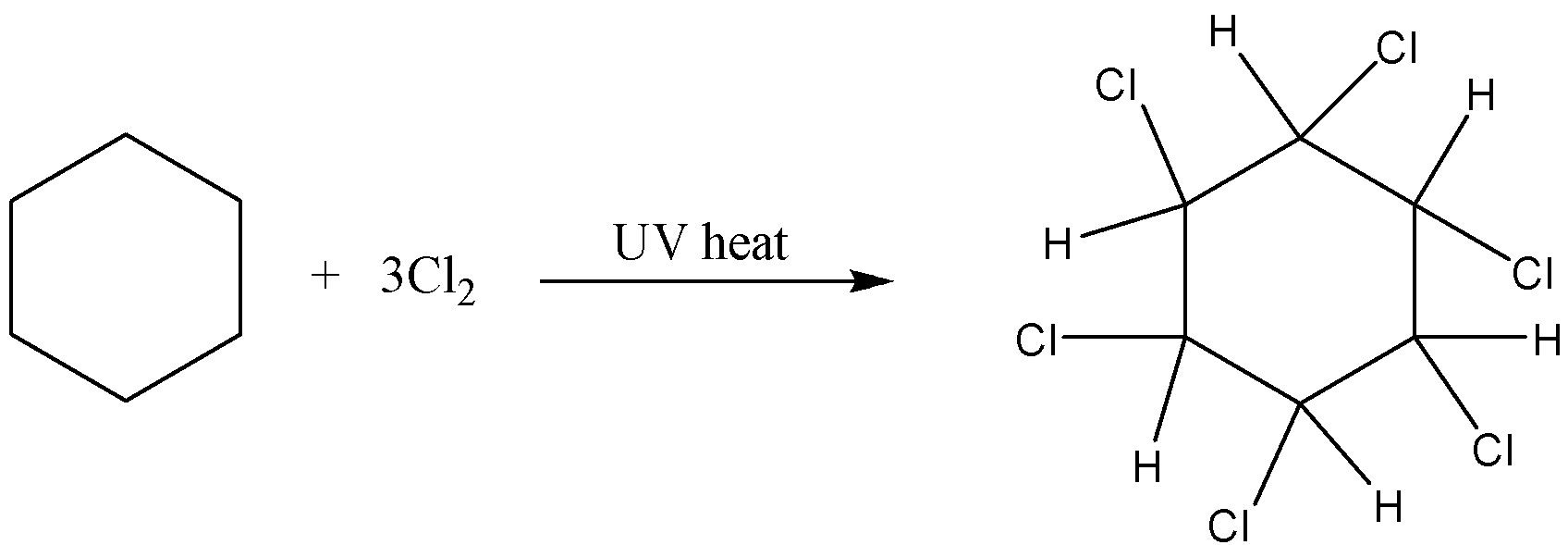
Bromine would behave similarly.
-The bromination of benzene is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. In the reaction, the electrophile (bromine) forms a sigma bond to the benzene ring, yielding an intermediate. Then a proton is removed from the intermediate to form a substituted benzene ring.
Thus, the correct answer is (B).
Note:
-There is no similar reaction between benzene and chlorine in which six chlorine atoms are added around the ring.
-Chlorine adds to benzene in the presence of ultraviolet light. With methylbenzene under those conditions, we get substitution in the methyl group. That is energetically easier because it doesn't involve breaking the delocalized electron system.
-Once all the hydrogens in the methyl group had been substituted, then there might be an addition to the ring as well.
Complete answer:
-In presence of U.V. Light bromination of benzene produces ${C_6}{H_6}B{r_6}$ or 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane. Three molecules of bromine are added across the carbon-carbon triple bond.

-In the presence of ultraviolet light (but without a catalyst present), hot benzene will also undergo an additional reaction with chlorine or bromine. The ring delocalization is permanently broken and a chlorine or bromine atom adds on to each carbon atom.
-For example, if you bubble chlorine gas through hot benzene exposed to UV light for an hour, you get 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane.

Bromine would behave similarly.
-The bromination of benzene is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. In the reaction, the electrophile (bromine) forms a sigma bond to the benzene ring, yielding an intermediate. Then a proton is removed from the intermediate to form a substituted benzene ring.
Thus, the correct answer is (B).
Note:
-There is no similar reaction between benzene and chlorine in which six chlorine atoms are added around the ring.
-Chlorine adds to benzene in the presence of ultraviolet light. With methylbenzene under those conditions, we get substitution in the methyl group. That is energetically easier because it doesn't involve breaking the delocalized electron system.
-Once all the hydrogens in the methyl group had been substituted, then there might be an addition to the ring as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




