
In paper chromatography, the stationary phase is a liquid.
(A) True
(B) False
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we first need to know what is paper chromatography. An analytical technique that is used to separate colored substances or chemicals is known as paper chromatography.
Complete answer:
Let us understand the principle of paper chromatography.
In paper chromatography, a solution is made to pass through sheets of paper that are adsorbent in nature.
From this, we can see that the solution or the liquid is the mobile phase whereas the paper or the absorbent is the stationary phase.
When the mobile phase (solution) moves through the stationary phase (paper) the colored components of the solution mixture are separated based on their affinity to adsorb on the stationary phase.
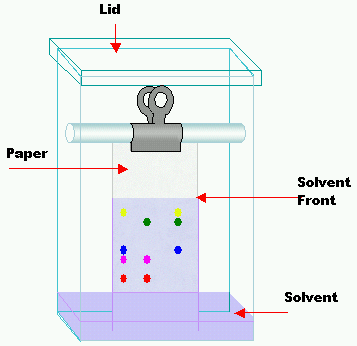
So the statement which says that in paper chromatography, the stationary phase is a liquid, So, option (B) False, is the correct option..
Additional Information:
Paper chromatography can be used to check for purity of compounds, detect adulterants, check for contaminants, determine drugs in animals and humans, carry out filtration, etc.
There are different methods of paper chromatography.
- Ascending paper chromatography in which the mobile phase moves upwards.
- Descending paper chromatography in which the mobile phase moves downwards due to gravitational pull.
- Ascending-Descending paper chromatography in which the mobile phase moves in two different directions after a fixed point.
- Two-dimensional paper chromatography
- Radial paper chromatography
Note:
It should be noted that various types of papers can be used for paper chromatography which has different rates of flow of mobile phase through it, pore size, thickness, adsorption and filtration capabilities, etc.
For example, cellulose papers, papers impregnated with oils, papers loaded with absorbent powders or ion-exchange celluloses, glass fiber type papers, etc.
Complete answer:
Let us understand the principle of paper chromatography.
In paper chromatography, a solution is made to pass through sheets of paper that are adsorbent in nature.
From this, we can see that the solution or the liquid is the mobile phase whereas the paper or the absorbent is the stationary phase.
When the mobile phase (solution) moves through the stationary phase (paper) the colored components of the solution mixture are separated based on their affinity to adsorb on the stationary phase.

So the statement which says that in paper chromatography, the stationary phase is a liquid, So, option (B) False, is the correct option..
Additional Information:
Paper chromatography can be used to check for purity of compounds, detect adulterants, check for contaminants, determine drugs in animals and humans, carry out filtration, etc.
There are different methods of paper chromatography.
- Ascending paper chromatography in which the mobile phase moves upwards.
- Descending paper chromatography in which the mobile phase moves downwards due to gravitational pull.
- Ascending-Descending paper chromatography in which the mobile phase moves in two different directions after a fixed point.
- Two-dimensional paper chromatography
- Radial paper chromatography
Note:
It should be noted that various types of papers can be used for paper chromatography which has different rates of flow of mobile phase through it, pore size, thickness, adsorption and filtration capabilities, etc.
For example, cellulose papers, papers impregnated with oils, papers loaded with absorbent powders or ion-exchange celluloses, glass fiber type papers, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




