
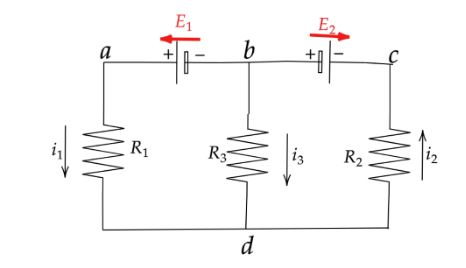
In Figure, what is the potential difference ${V_d} - {V_c}$ between point d and c if ${E_1} = 0.4V$, ${E_2} = 1.0V$ ,${R_1} = {R_2} = 10\Omega $, and ${R_3} = 5.0\Omega $, and the battery is ideal.

Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: Here we have to find the potential difference between the two terminals d and c. First we will find the values of their difference current in diffract branches of the circuit using the given information. Then after taking two different paths one is branch d to b to c and the other one is d to c hence from that we will get two same potential difference values for both the way.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given problem we have a figure where ${E_1} = 4.0V$, ${E_2} = 1.0V$ ,${R_1} = {R_2} = 10\Omega $, and ${R_3} = 5.0\Omega $, and the battery is ideal.Now we need to calculate the value of potential difference ${V_d} - {V_c}$ between point d and c.Now from the above given figure we can write,
${i_1} = \dfrac{{{E_1}\left( {{R_2} + {R_3}} \right) - {E_2}{R_3}}}{{{R_1}{R_2} + {R_2}{R_3} + {R_1}{R_3}}}$
We know,
${E_1} = 4.0V$
$\Rightarrow {E_2} = 1.0V$
$\Rightarrow {R_1} = {R_2} = 10\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_3} = 5.0\Omega $
Now putting the given values we will get,
${i_1} = \dfrac{{\left( {4.0V} \right)\left( {10\Omega + 5\Omega } \right) - \left( {1.0V} \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right)}}{{\left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {10\Omega } \right) + \left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right) + \left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right)}}$
On further solving and simplifying we will get,
${i_1} = 0.275A$
Similarly from the figure we can write,
${i_2} = \dfrac{{{E_1}{R_3} - {E_2}\left( {{R_1} + {R_2}} \right)}}{{{R_1}{R_2} + {R_2}{R_3} + {R_1}{R_3}}}$
We know,
${E_1} = 4.0V$
$\Rightarrow {E_2} = 1.0V$
$\Rightarrow {R_1} = {R_2} = 10\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_3} = 5.0\Omega $
Now putting the given values we will get,
${i_2} = \dfrac{{\left( {4.0V} \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right) - \left( {1.0V} \right)\left( {10\Omega + 5\Omega } \right)}}{{\left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {10\Omega } \right) + \left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right) + \left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right)}}$
On further solving and simplifying we will get,
${i_2} = 0.025A$
Now from the figure we can write,
${i_3} = {i_2} - {i_1} = 0.025A - 0.275A = - 0.250A$
Now to find the potential differ,
We can two different oath two calculate the potential difference
Case I:From point d to b to c we will get,
${V_d} + {i_3}{R_3} + {E_2} = {V_c}$
We know,
${i_3} = - 0.250A$
$\Rightarrow {R_3} = 5.0\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {E_2} = 1.0V$
Now putting the known value we will get,
${V_d} + \left( { - 0.250A} \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right) + 1.0V = {V_c}$
On soling we will get,
${V_d} - 0.250V = {V_c}$
On rearranging we will get,
${V_d} - {V_c} = 0.250V$
Case II: From point d to c we will get,
${V_d} - {i_2}{R_2} = {V_c}$
We know,
${i_2} = 0.025A$
$\Rightarrow {R_2} = 10\Omega $
Now putting the known value we will get,
${V_d} - \left( {0.025A} \right)\left( {10\Omega } \right) = {V_c}$
On soling we will get,
${V_d} - 0.250V = {V_c}$
On rearranging we will get,
$\therefore {V_d} - {V_c} = 0.250V$
Hence,the potential difference ${V_d} - {V_c}$ between point d and c is 0.250 V.
Note: Remember that potential difference is the difference in the amount of energy that a charge carrier has between two points in a circuit as in this equation the two points are d and c. Note that whatever the path the current has travelled, the potential difference between that point will always remain the same and it is measured in terms of voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given problem we have a figure where ${E_1} = 4.0V$, ${E_2} = 1.0V$ ,${R_1} = {R_2} = 10\Omega $, and ${R_3} = 5.0\Omega $, and the battery is ideal.Now we need to calculate the value of potential difference ${V_d} - {V_c}$ between point d and c.Now from the above given figure we can write,
${i_1} = \dfrac{{{E_1}\left( {{R_2} + {R_3}} \right) - {E_2}{R_3}}}{{{R_1}{R_2} + {R_2}{R_3} + {R_1}{R_3}}}$
We know,
${E_1} = 4.0V$
$\Rightarrow {E_2} = 1.0V$
$\Rightarrow {R_1} = {R_2} = 10\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_3} = 5.0\Omega $
Now putting the given values we will get,
${i_1} = \dfrac{{\left( {4.0V} \right)\left( {10\Omega + 5\Omega } \right) - \left( {1.0V} \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right)}}{{\left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {10\Omega } \right) + \left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right) + \left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right)}}$
On further solving and simplifying we will get,
${i_1} = 0.275A$
Similarly from the figure we can write,
${i_2} = \dfrac{{{E_1}{R_3} - {E_2}\left( {{R_1} + {R_2}} \right)}}{{{R_1}{R_2} + {R_2}{R_3} + {R_1}{R_3}}}$
We know,
${E_1} = 4.0V$
$\Rightarrow {E_2} = 1.0V$
$\Rightarrow {R_1} = {R_2} = 10\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {R_3} = 5.0\Omega $
Now putting the given values we will get,
${i_2} = \dfrac{{\left( {4.0V} \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right) - \left( {1.0V} \right)\left( {10\Omega + 5\Omega } \right)}}{{\left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {10\Omega } \right) + \left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right) + \left( {10\Omega } \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right)}}$
On further solving and simplifying we will get,
${i_2} = 0.025A$
Now from the figure we can write,
${i_3} = {i_2} - {i_1} = 0.025A - 0.275A = - 0.250A$
Now to find the potential differ,
We can two different oath two calculate the potential difference
Case I:From point d to b to c we will get,
${V_d} + {i_3}{R_3} + {E_2} = {V_c}$
We know,
${i_3} = - 0.250A$
$\Rightarrow {R_3} = 5.0\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {E_2} = 1.0V$
Now putting the known value we will get,
${V_d} + \left( { - 0.250A} \right)\left( {5\Omega } \right) + 1.0V = {V_c}$
On soling we will get,
${V_d} - 0.250V = {V_c}$
On rearranging we will get,
${V_d} - {V_c} = 0.250V$
Case II: From point d to c we will get,
${V_d} - {i_2}{R_2} = {V_c}$
We know,
${i_2} = 0.025A$
$\Rightarrow {R_2} = 10\Omega $
Now putting the known value we will get,
${V_d} - \left( {0.025A} \right)\left( {10\Omega } \right) = {V_c}$
On soling we will get,
${V_d} - 0.250V = {V_c}$
On rearranging we will get,
$\therefore {V_d} - {V_c} = 0.250V$
Hence,the potential difference ${V_d} - {V_c}$ between point d and c is 0.250 V.
Note: Remember that potential difference is the difference in the amount of energy that a charge carrier has between two points in a circuit as in this equation the two points are d and c. Note that whatever the path the current has travelled, the potential difference between that point will always remain the same and it is measured in terms of voltage.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




