
In a Plano-convex lens, the radius of curvature is $10cm$. If the plane side is silvered, then the focal length will be, (refractive index=1.5)
A. $20cm$
B. $10cm$
C. $15cm$
D. $5cm$
Answer
614.1k+ views
Hint: In a plano-convex lens, one of the sides is curved while the other side is flat. If the flat side is silvered, the lens will act as a concave mirror. The radius of curvature of a plane or flat surface is taken as infinite.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
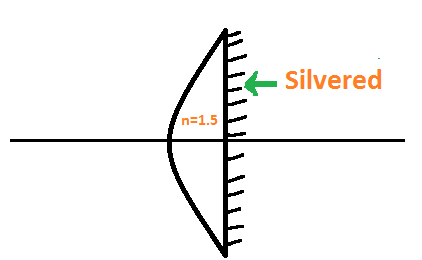
In our question, we are given a plano-convex lens which is silvered on the plane side. The radius of curvature of the curved side is given to be $10cm$. A plane convex lens which is silvered on one of the sides will act as a concave mirror. The effective focal length of this configuration is given by,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2}{{{f}_{l}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{m}}}$….. equation (1)
Where,
${{f}_{l}}$ is the focal length of the non-silvered surface (curved surface in our case)
${{f}_{m}}$ is the focal length of the mirror (silvered surface)
So we know that the focal length of a mirror ${{f}_{m}}$ is half the radius of curvature of the mirror, so we can write ${{f}_{m}}=\dfrac{{{R}_{m}}}{2}$. Here in the case of a plane silvered surface the radius of curvature is very high and taken as infinity. So ${{f}_{m}}$ will also be infinity.
The focal length of a curved surface of a lens is given by the lens makers formula,
$\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{l}}}=\left( \mu -1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{R} \right)$
Where, $\mu $ is the refractive index of the lens material. R is the radius of curvature of the curved surface.
So substituting the values of ${{f}_{m}}$ and ${{f}_{l}}$ in equation (1), we get,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}+\dfrac{1}{\infty }$
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}$
Substituting the values of refractive index and radius of curvature in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2\left( 1.5-1 \right)}{10}=\dfrac{2\times 0.5}{10}$
$\therefore f=10cm$
So the focal length of the plano convex lens silvered at the plane side and having a radius of curvature $10cm$ is $f=10cm$. (Option (B) )
Note: A light incident on a convex lens which is silvered experiences one reflection at the silvered side and two refractions at the non-silvered side.
If the plane surface had not been silvered, the focal length of the plano-convex lens would be 20cm.
The focal length of a lens increases when it is kept in a medium which has a refractive index higher than the refractive index of air. Example – A convex lens kept in water.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:

In our question, we are given a plano-convex lens which is silvered on the plane side. The radius of curvature of the curved side is given to be $10cm$. A plane convex lens which is silvered on one of the sides will act as a concave mirror. The effective focal length of this configuration is given by,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2}{{{f}_{l}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{m}}}$….. equation (1)
Where,
${{f}_{l}}$ is the focal length of the non-silvered surface (curved surface in our case)
${{f}_{m}}$ is the focal length of the mirror (silvered surface)
So we know that the focal length of a mirror ${{f}_{m}}$ is half the radius of curvature of the mirror, so we can write ${{f}_{m}}=\dfrac{{{R}_{m}}}{2}$. Here in the case of a plane silvered surface the radius of curvature is very high and taken as infinity. So ${{f}_{m}}$ will also be infinity.
The focal length of a curved surface of a lens is given by the lens makers formula,
$\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{l}}}=\left( \mu -1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{R} \right)$
Where, $\mu $ is the refractive index of the lens material. R is the radius of curvature of the curved surface.
So substituting the values of ${{f}_{m}}$ and ${{f}_{l}}$ in equation (1), we get,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}+\dfrac{1}{\infty }$
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}$
Substituting the values of refractive index and radius of curvature in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2\left( 1.5-1 \right)}{10}=\dfrac{2\times 0.5}{10}$
$\therefore f=10cm$
So the focal length of the plano convex lens silvered at the plane side and having a radius of curvature $10cm$ is $f=10cm$. (Option (B) )
Note: A light incident on a convex lens which is silvered experiences one reflection at the silvered side and two refractions at the non-silvered side.
If the plane surface had not been silvered, the focal length of the plano-convex lens would be 20cm.
The focal length of a lens increases when it is kept in a medium which has a refractive index higher than the refractive index of air. Example – A convex lens kept in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




