
In a meter-bridge, the balancing length from the left end when standard resistance of 1 $\Omega$ is in the right gap is found to be 20 cm. The value of unknown resistance is
(A) 0.25 $\Omega$
(B) 0.4 $\Omega$
(C) 0.5 $\Omega$
(D) 4 $\Omega$
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: A meter bridge has an arrangement similar to Wheatstone bridge and is made up of a wire of uniform thickness upon which when the jockey of the galvanometer is placed, gets divided into 2 different resistances. The unknown resistance is found as the ratio of the two lengths times known resistance.
Formula used:
On the condition of balancing of bridge, the relationship among various resistance goes as follows:
$\dfrac{X}{R} = \dfrac{L}{100 - L}$
Complete answer:
Just like a Wheatstone bridge that has four arms, the metre bridge has that total four resistances. One resistance is given through a resistance box R which is the known resistance. One wire of unknown resistance is attached at X, one wire of length one meter is connected on a wooden board that gets divided into two different resistances of values rL and r(100-L). L is the length from one of the ends of the wire and r is the resistance per unit length of the wire.
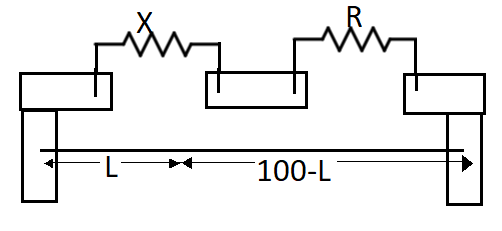
We are given the balancing length L = 20 cm from the left and also the value of resistance R = 1 $ \Omega$ on the standard resistance side. Now, we substitute these values in the formula to find the value of X, so that we get:
$X = \dfrac{20}{80} \times 1 \Omega = 0.25 \Omega$.
Therefore, when we connect an unknown resistance on the X and a standard resistance of value 1$\Omega$ that shows a balance point at 20 cm from the left, we find the value of unknown resistance at X to be $0.25 \Omega$ .
The correct answer is option (A).
Note:
Meter bridge is specifically used for determining the value of unknown resistance X. In a bridge, the ratios of two adjoining resistances on the opposite side are equal like here we have X:rL =R:r(100-L). One has to be careful about the notations.
Formula used:
On the condition of balancing of bridge, the relationship among various resistance goes as follows:
$\dfrac{X}{R} = \dfrac{L}{100 - L}$
Complete answer:
Just like a Wheatstone bridge that has four arms, the metre bridge has that total four resistances. One resistance is given through a resistance box R which is the known resistance. One wire of unknown resistance is attached at X, one wire of length one meter is connected on a wooden board that gets divided into two different resistances of values rL and r(100-L). L is the length from one of the ends of the wire and r is the resistance per unit length of the wire.

We are given the balancing length L = 20 cm from the left and also the value of resistance R = 1 $ \Omega$ on the standard resistance side. Now, we substitute these values in the formula to find the value of X, so that we get:
$X = \dfrac{20}{80} \times 1 \Omega = 0.25 \Omega$.
Therefore, when we connect an unknown resistance on the X and a standard resistance of value 1$\Omega$ that shows a balance point at 20 cm from the left, we find the value of unknown resistance at X to be $0.25 \Omega$ .
The correct answer is option (A).
Note:
Meter bridge is specifically used for determining the value of unknown resistance X. In a bridge, the ratios of two adjoining resistances on the opposite side are equal like here we have X:rL =R:r(100-L). One has to be careful about the notations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




