
In a fraction, twice the numerator is 2 more than the denominator. If 3 is added to the numerator and to the denominator, the new fraction is $\dfrac{2}{3}$. Find the original fraction.
Answer
628.5k+ views
Hint: Assume numerator of the fraction be x, and the denominator be y. Using the statement of the equation generates two linear equations in two variables. Solve for x,y using substitution method or matrix method or solve graphically to find the value of x and y.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the numerator of the original fraction be x, and the denominator of the original fraction be y.
Since twice numerator is 2 more than the denominator, we have
2x = y+2
Subtracting y+2 from both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 2x-y-2=y+2-y-2
i.e. 2x-y-2=0 (i)
Also, when 3 is added to the numerator, the numerator becomes x+3, and when 3 is added to the denominator, the denominator becomes y+3. Hence the fraction becomes $\dfrac{x+3}{y+3}$
So, according to question, we have
$\dfrac{x+3}{y+3}=\dfrac{2}{3}$
Cross multiplying, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 3(x+3) = 2(y+3)
Using the distributive property of multiplication over addition i.e. a(b+c) = ab+ac, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 3x+9=2y+6
Subtracting 2y+6 from both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 3x+9-(2y+6)=2y+6-(2y+6)
i.e. 3x-2y+3=0 (ii)
Hence we have the following system of equations,
2x-y-2=0
3x-2y+3=0.
From equation (i) we have
2x-y-2=0
Adding y on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 2x-2 = y (iii)
Substituting the value of y in equation (ii) we get
$\Rightarrow$ 3x-2(2x-2) +3= 0
i.e. 3x-4x+4+3=0
i.e. -x+7=0
Adding x on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$ -x+7+x=0+x
i.e. x = 7.
Substituting the value of x in (iii) we get
$\Rightarrow$ y = 2(7)-2 = 14 -2 = 12.
Hence the original fraction is $\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{7}{12}$
Note: [1] We can also solve the given system graphically.
Plotting these lines on a graph, we get the following graph
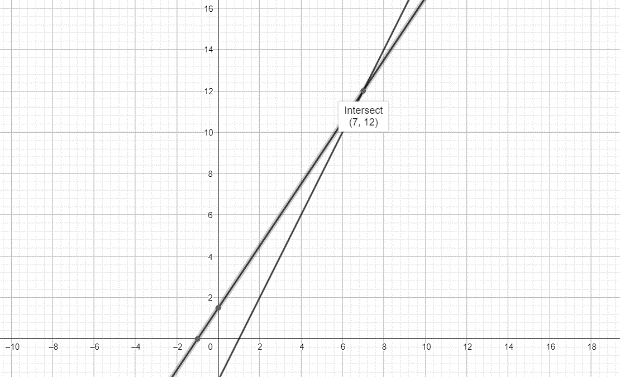
As is evident from the graph, the lines intersect at the point (7,12).
Hence x = 7 and y = 12, which is the same as obtained above.
[2] Alternatively, we can represent the given system as AX=B, where
$\text{A=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & -1 \\
3 & -2 \\
\end{matrix} \right],\text{X=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
x \\
y \\
\end{matrix} \right],\text{B=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 \\
-3 \\
\end{matrix} \right]$
So, we have augmented matrix [A|B] is given by
\[\text{C=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & -1 & 2 \\
3 & -2 & -3 \\
\end{matrix} \right]\]
Applying the row transformation ${{\text{R}}_{2}}\to 2{{\text{R}}_{2}}-3{{\text{R}}_{1}}$, we get
\[\text{C=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & -1 & 2 \\
0 & -1 & -12 \\
\end{matrix} \right]\]
Hence we have -y = -12, i.e. y = 12 and 2x-y = 2
i.e. 2x = 2+12
2x = 14
Dividing both sides by 2, we get
x =7
Hence we have x= 7 and y = 12, which is the same as obtained above.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the numerator of the original fraction be x, and the denominator of the original fraction be y.
Since twice numerator is 2 more than the denominator, we have
2x = y+2
Subtracting y+2 from both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 2x-y-2=y+2-y-2
i.e. 2x-y-2=0 (i)
Also, when 3 is added to the numerator, the numerator becomes x+3, and when 3 is added to the denominator, the denominator becomes y+3. Hence the fraction becomes $\dfrac{x+3}{y+3}$
So, according to question, we have
$\dfrac{x+3}{y+3}=\dfrac{2}{3}$
Cross multiplying, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 3(x+3) = 2(y+3)
Using the distributive property of multiplication over addition i.e. a(b+c) = ab+ac, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 3x+9=2y+6
Subtracting 2y+6 from both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 3x+9-(2y+6)=2y+6-(2y+6)
i.e. 3x-2y+3=0 (ii)
Hence we have the following system of equations,
2x-y-2=0
3x-2y+3=0.
From equation (i) we have
2x-y-2=0
Adding y on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$ 2x-2 = y (iii)
Substituting the value of y in equation (ii) we get
$\Rightarrow$ 3x-2(2x-2) +3= 0
i.e. 3x-4x+4+3=0
i.e. -x+7=0
Adding x on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$ -x+7+x=0+x
i.e. x = 7.
Substituting the value of x in (iii) we get
$\Rightarrow$ y = 2(7)-2 = 14 -2 = 12.
Hence the original fraction is $\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{7}{12}$
Note: [1] We can also solve the given system graphically.
Plotting these lines on a graph, we get the following graph
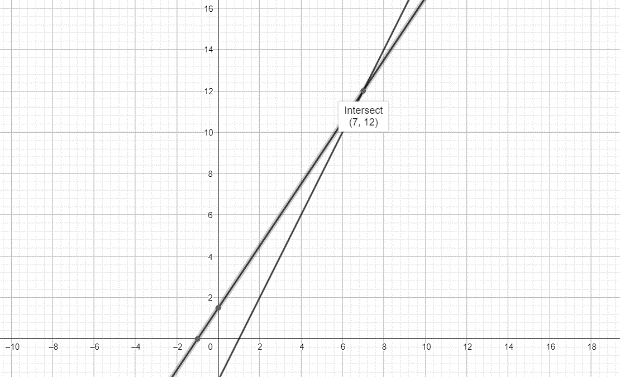
As is evident from the graph, the lines intersect at the point (7,12).
Hence x = 7 and y = 12, which is the same as obtained above.
[2] Alternatively, we can represent the given system as AX=B, where
$\text{A=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & -1 \\
3 & -2 \\
\end{matrix} \right],\text{X=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
x \\
y \\
\end{matrix} \right],\text{B=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 \\
-3 \\
\end{matrix} \right]$
So, we have augmented matrix [A|B] is given by
\[\text{C=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & -1 & 2 \\
3 & -2 & -3 \\
\end{matrix} \right]\]
Applying the row transformation ${{\text{R}}_{2}}\to 2{{\text{R}}_{2}}-3{{\text{R}}_{1}}$, we get
\[\text{C=}\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & -1 & 2 \\
0 & -1 & -12 \\
\end{matrix} \right]\]
Hence we have -y = -12, i.e. y = 12 and 2x-y = 2
i.e. 2x = 2+12
2x = 14
Dividing both sides by 2, we get
x =7
Hence we have x= 7 and y = 12, which is the same as obtained above.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are gulf countries and why they are called Gulf class 8 social science CBSE

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE

In Indian rupees 1 trillion is equal to how many c class 8 maths CBSE

Who created the image of Bharat Mata for the first class 8 social science CBSE

What is the Balkan issue in brief class 8 social science CBSE





