
In a common emitter transistor circuit, the base current is $40\,\mu A$, then ${V_{BE}}$ is
(A) $2\,V$
(B) $0.2\,V$
(C) $0.8\,V$
(D) zero

Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint
When the transistor is working in the common emitter mode, then the base emitter voltage is determined by using the base bias formula of the common emitter transistor. And by using the given information the base emitter voltage is determined.
The base bias formula of the common emitter transistor is given by,
$\Rightarrow {V_{CC}} - {I_B}{R_B} - {V_{BE}} = 0$
Where, ${V_{CC}}$ is the supplied voltage to the transistor, ${I_B}$ is the base current, ${R_B}$ is the resistance of the base and ${V_{BE}}$ is the voltage in the base emitter.
Complete step by step answer
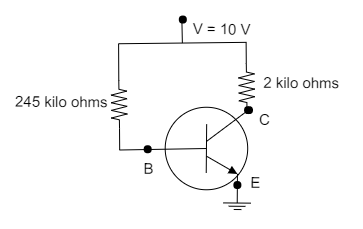
Given that, The base current is, ${I_B} = 40\,\mu A$
The voltage supplied to the transistor is, ${V_{CC}} = 10\,V$
The resistance in the base is, ${R_B} = 245\,k\Omega $
The resistance in the collector is, ${R_C} = 2\,k\Omega $
Now, The base bias formula of the common emitter transistor is given by,
$\Rightarrow {V_{CC}} - {I_B}{R_B} - {V_{BE}} = 0\,...................\left( 1 \right)$
By taking the voltage of the base emitter in one side and the other terms in the other side, then the equation (1) is written as,
$\Rightarrow {V_{CC}} - {I_B}{R_B} = {V_{BE}}$
Now substituting the voltage supplied to the transistor, base current and resistance of the base in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow 10 - \left( {40 \times 245 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right) = {V_{BE}}$
Now multiplying the terms inside the bracket, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow 10 - \left( {9800 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right) = {V_{BE}}$
Now moving the decimal of the term inside the bracket, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow 10 - \left( {9.8} \right) = {V_{BE}}$
On subtracting the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow {V_{BE}} = 0.2\,V$
Thus, the above equation shows the voltage of the base emitter.
Hence, the option (B) is the correct answer.
Note
The common emitter type of biasing arrangement uses two resistors as a potential divider network across the supply with their centre point supplying the required Base bias voltage to the transistor. Voltage divider biasing is commonly used in the design of bipolar transistor amplifier circuits.
When the transistor is working in the common emitter mode, then the base emitter voltage is determined by using the base bias formula of the common emitter transistor. And by using the given information the base emitter voltage is determined.
The base bias formula of the common emitter transistor is given by,
$\Rightarrow {V_{CC}} - {I_B}{R_B} - {V_{BE}} = 0$
Where, ${V_{CC}}$ is the supplied voltage to the transistor, ${I_B}$ is the base current, ${R_B}$ is the resistance of the base and ${V_{BE}}$ is the voltage in the base emitter.
Complete step by step answer
Given that, The base current is, ${I_B} = 40\,\mu A$
The voltage supplied to the transistor is, ${V_{CC}} = 10\,V$
The resistance in the base is, ${R_B} = 245\,k\Omega $
The resistance in the collector is, ${R_C} = 2\,k\Omega $
Now, The base bias formula of the common emitter transistor is given by,
$\Rightarrow {V_{CC}} - {I_B}{R_B} - {V_{BE}} = 0\,...................\left( 1 \right)$
By taking the voltage of the base emitter in one side and the other terms in the other side, then the equation (1) is written as,
$\Rightarrow {V_{CC}} - {I_B}{R_B} = {V_{BE}}$
Now substituting the voltage supplied to the transistor, base current and resistance of the base in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow 10 - \left( {40 \times 245 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right) = {V_{BE}}$
Now multiplying the terms inside the bracket, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow 10 - \left( {9800 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}} \right) = {V_{BE}}$
Now moving the decimal of the term inside the bracket, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow 10 - \left( {9.8} \right) = {V_{BE}}$
On subtracting the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$\Rightarrow {V_{BE}} = 0.2\,V$
Thus, the above equation shows the voltage of the base emitter.
Hence, the option (B) is the correct answer.
Note
The common emitter type of biasing arrangement uses two resistors as a potential divider network across the supply with their centre point supplying the required Base bias voltage to the transistor. Voltage divider biasing is commonly used in the design of bipolar transistor amplifier circuits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




