
If the critical point as well as the stationary point of the function $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}}{x}$ is $x=a$, then find the value of $a$.
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: We first explain the process of finding critical point as well as the stationary point. We find the concept of those points being similar to finding extremum points. The solution of the slope of the curve being equal to 0 gives us the solution of the problem.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the critical point as well as the stationary point for $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}}{x}$. The point is the same at $x=a$. We need to find the value for $a$.
Critical point can be defined as the point $\left( p,f\left( p \right) \right)$ of \[f\left( x \right)\] if \[f\left( p \right)\] exists and either \[{{f}^{'}}\left( p \right)\] does not exist or \[{{f}^{'}}\left( p \right)=0\].
On the other hand, $\left( p,f\left( p \right) \right)$ is a stationary point of \[f\left( x \right)\] if \[f\left( p \right)\] and \[{{f}^{'}}\left( p \right)\] exist and satisfies \[{{f}^{'}}\left( p \right)=0\].
To find these points we need to find the first order derivative or the slope of the curve.
For our given function $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}}{x}$, we can differentiate it to ${{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{df}{dx}$.
We get ${{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{x{{e}^{x}}-{{e}^{x}}}{{{x}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}\left( x-1 \right)}{{{x}^{2}}}$.
We equate it with 0 to find both the critical as well as the stationary point.
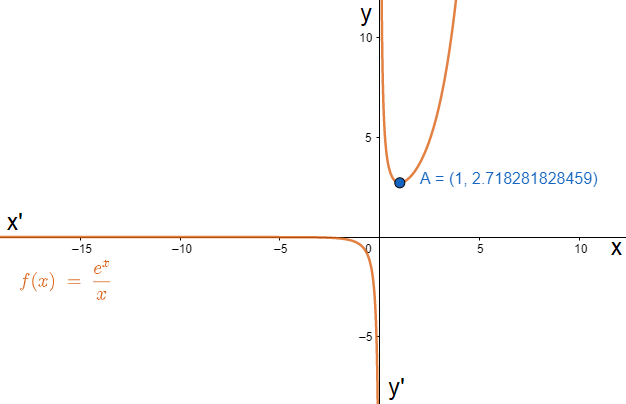
So, $\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}\left( x-1 \right)}{{{x}^{2}}}=0\Rightarrow x=1$. The point is $A\left( 1,e \right)$. This is not equal to $x=0$ at which the functions $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}}{x}$ and ${{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}\left( x-1 \right)}{{{x}^{2}}}$ both are undefined.
Therefore, the value of $a$ is 1.
Note: We need to remember the concept of extremum and point of stationary is quite similar. The slopes decide the concavity and its change. We also need to remember that if a function is undefined at some value of x, then the point can be no stationary point.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the critical point as well as the stationary point for $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}}{x}$. The point is the same at $x=a$. We need to find the value for $a$.
Critical point can be defined as the point $\left( p,f\left( p \right) \right)$ of \[f\left( x \right)\] if \[f\left( p \right)\] exists and either \[{{f}^{'}}\left( p \right)\] does not exist or \[{{f}^{'}}\left( p \right)=0\].
On the other hand, $\left( p,f\left( p \right) \right)$ is a stationary point of \[f\left( x \right)\] if \[f\left( p \right)\] and \[{{f}^{'}}\left( p \right)\] exist and satisfies \[{{f}^{'}}\left( p \right)=0\].
To find these points we need to find the first order derivative or the slope of the curve.
For our given function $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}}{x}$, we can differentiate it to ${{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{df}{dx}$.
We get ${{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{x{{e}^{x}}-{{e}^{x}}}{{{x}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}\left( x-1 \right)}{{{x}^{2}}}$.
We equate it with 0 to find both the critical as well as the stationary point.
So, $\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}\left( x-1 \right)}{{{x}^{2}}}=0\Rightarrow x=1$. The point is $A\left( 1,e \right)$. This is not equal to $x=0$ at which the functions $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}}{x}$ and ${{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{x}}\left( x-1 \right)}{{{x}^{2}}}$ both are undefined.
Therefore, the value of $a$ is 1.

Note: We need to remember the concept of extremum and point of stationary is quite similar. The slopes decide the concavity and its change. We also need to remember that if a function is undefined at some value of x, then the point can be no stationary point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




