
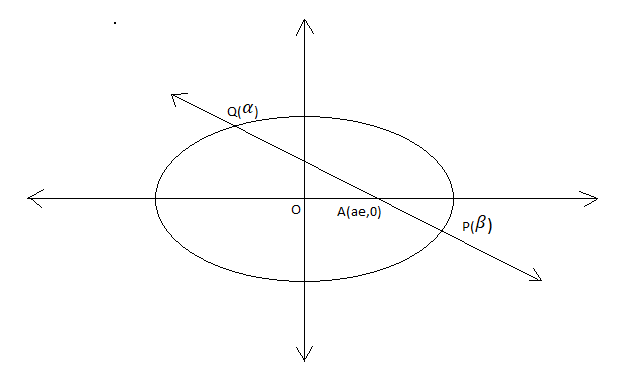
If the chord through the points whose eccentric angles are \[\alpha \] and \[\beta \] on the ellipse \[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\] passes through the focus (ae, 0), then the value of \[\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2}\] is:
A. \[\dfrac{e+1}{e-1}\]
B. \[\dfrac{e-1}{e+1}\]
C. \[\dfrac{e+1}{e-2}\]
D. none
Answer
619.8k+ views
Hint: We will first write the equation of the chord to the ellipse with given eccentric angles and then we will put the point (ae, 0) in the equation as it is passing through it so it will satisfy the equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the eccentric angle of chord as \[\alpha \] and \[\beta \] on the ellipse \[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\].
The eccentric angle of a point on an ellipse with semi major axes of length and semi minor axes of length is the angle in the parametrization.
Now the equation of chord to the ellipse with eccentric angle \[\alpha \] and \[\beta \] is as follows:
\[\dfrac{x}{a}\cos \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2}+\dfrac{y}{b}\sin \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2}=\cos \dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2}\]
It is given that it passes through (ae, 0).
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{ae}{a}\cos \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2}+\dfrac{0}{b}\sin \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2}=\cos \dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2} \\
& e\cos \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2}+\dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)=\cos \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2}-\dfrac{\beta }{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now we are using the trigonometric identity which is given as below.
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \left( A+B \right)=\cos A\cos B-\sin A\sin B \\
& C=\cos \left( A-B \right)=\cos A\cos B+\sin A\sin B \\
& \Rightarrow e\left( \cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}-\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\sin \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)=\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}+\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\sin \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now taking the term \[\left( \cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)\] as common from both sides of the equality, we get as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& e\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}\left( 1-\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\sin \dfrac{\beta }{2}}{\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}} \right)=\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}\left( 1+\dfrac{sin\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\sin \dfrac{\beta }{2}}{\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}} \right) \\
& e\left( 1-\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)=1+\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
& e-e\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2}=1+\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
& e-1=(1+e)\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
& \dfrac{e-1}{1+e}=\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we have proved that \[\dfrac{e-1}{1+e}\] = \[\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2}\].
Hence the correct answer of the above mentioned question is option B.
Note: Be careful while substituting the values of \[\left( \cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}+\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)\] and \[\left( \cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}-\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)\] as there is a chance that you might put the wrong sign.
Also, be careful while choosing the option sometime when you choose option A in spite of option B.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the eccentric angle of chord as \[\alpha \] and \[\beta \] on the ellipse \[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\].
The eccentric angle of a point on an ellipse with semi major axes of length and semi minor axes of length is the angle in the parametrization.
Now the equation of chord to the ellipse with eccentric angle \[\alpha \] and \[\beta \] is as follows:
\[\dfrac{x}{a}\cos \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2}+\dfrac{y}{b}\sin \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2}=\cos \dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2}\]
It is given that it passes through (ae, 0).
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{ae}{a}\cos \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2}+\dfrac{0}{b}\sin \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2}=\cos \dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2} \\
& e\cos \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2}+\dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)=\cos \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2}-\dfrac{\beta }{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now we are using the trigonometric identity which is given as below.
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \left( A+B \right)=\cos A\cos B-\sin A\sin B \\
& C=\cos \left( A-B \right)=\cos A\cos B+\sin A\sin B \\
& \Rightarrow e\left( \cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}-\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\sin \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)=\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}+\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\sin \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now taking the term \[\left( \cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)\] as common from both sides of the equality, we get as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& e\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}\left( 1-\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\sin \dfrac{\beta }{2}}{\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}} \right)=\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}\left( 1+\dfrac{sin\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\sin \dfrac{\beta }{2}}{\cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2}} \right) \\
& e\left( 1-\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)=1+\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
& e-e\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2}=1+\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
& e-1=(1+e)\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
& \dfrac{e-1}{1+e}=\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we have proved that \[\dfrac{e-1}{1+e}\] = \[\tan \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\tan \dfrac{\beta }{2}\].
Hence the correct answer of the above mentioned question is option B.
Note: Be careful while substituting the values of \[\left( \cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}+\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)\] and \[\left( \cos \dfrac{\alpha }{2}-\cos \dfrac{\beta }{2} \right)\] as there is a chance that you might put the wrong sign.
Also, be careful while choosing the option sometime when you choose option A in spite of option B.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




