
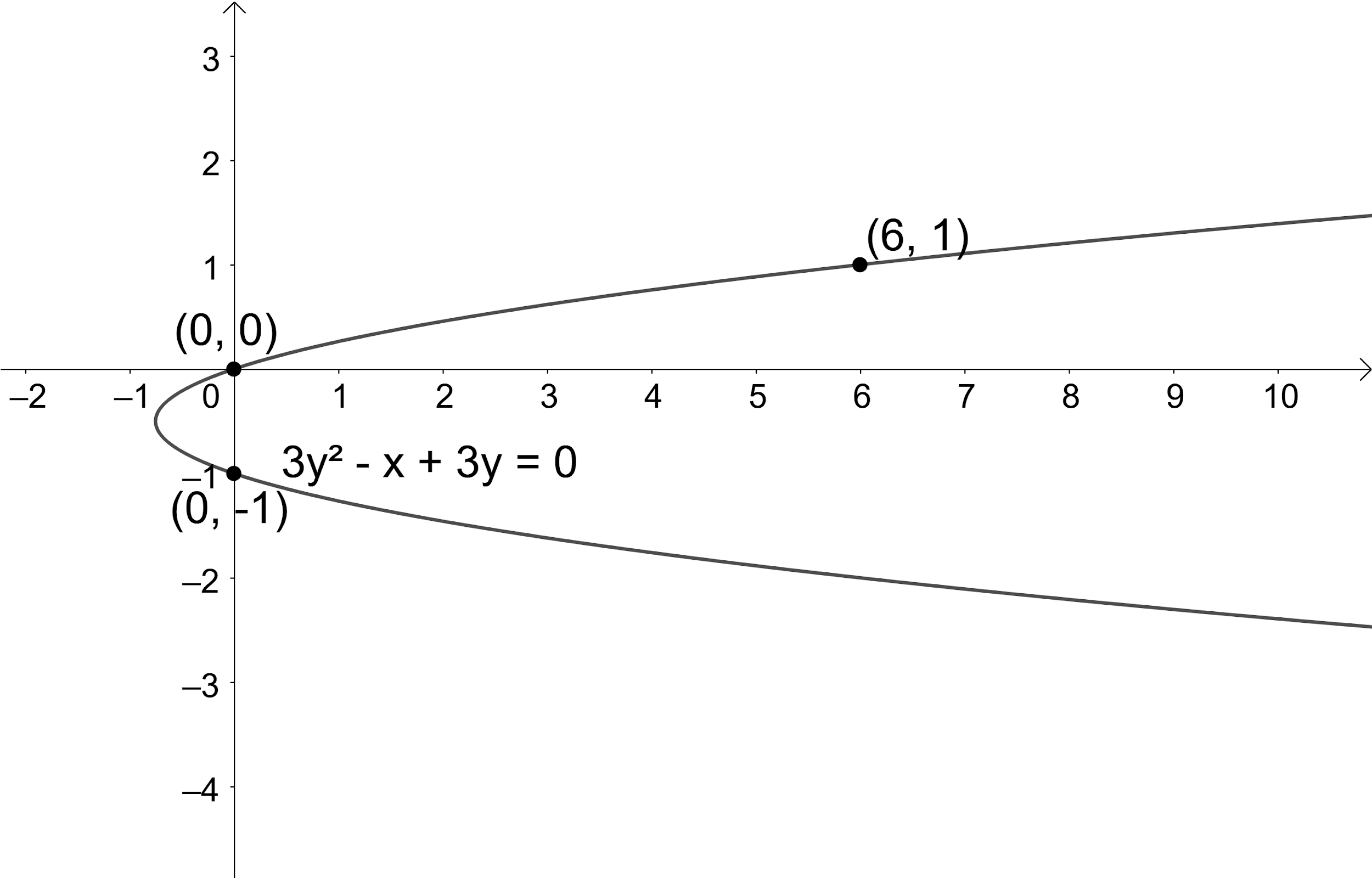
If the axis of the parabola is horizontal and it passes through the points $\left( 0,0 \right)$, $\left( 0,-1 \right)$ and $\left( 6,1 \right)$, then find its equation?
(a) ${{y}^{2}}+3y-x-4=0$
(b) ${{y}^{2}}+3y+x-4=0$
(c) ${{y}^{2}}-3y-x-4=0$.
(d) None of these
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by recalling the general equation of the parabola whose axis is horizontal as ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$. We then substitute the points $\left( 0,0 \right)$, $\left( 0,-1 \right)$ and $\left( 6,1 \right)$ each at once to get the relations between ‘h’, ‘k’ and ‘a’. We then make the necessary calculations between these three relations to get the values of ‘h’, ‘k’ and ‘a’. We then substitute these values in the general equation of parabola to get the required equation.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that the axis of the parabola is horizontal and we need to find the equation of parabola if it passes through the points $\left( 0,0 \right)$, $\left( 0,-1 \right)$ and $\left( 6,1 \right)$.
We know that the general equation of the parabola is ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$, if the axis of the parabola is horizontal.
Let us substitute the point $\left( 0,0 \right)$ in the parabola ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$.
So, we get ${{\left( 0-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 0-h \right)$.
$\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}=-4ah$ ---(1).
Let us substitute the point $\left( 0,-1 \right)$ in the parabola ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$.
So, we get ${{\left( -1-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 0-h \right)$.
$\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+2k+1=-4ah$.
From equation (1) we get ${{k}^{2}}+2k+1={{k}^{2}}$.
$\Rightarrow 2k+1=0$.
$\Rightarrow 2k=-1$.
$\Rightarrow k=\dfrac{-1}{2}$ ---(2).
Let us substitute equation (2) in equation (1), we get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=-4ah$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4}=-4ah$.
$\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{-1}{16a}$ ---(3).
Let us substitute the point $\left( 6,1 \right)$ in the parabola ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$.
So, we get ${{\left( 1-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 6-h \right)$.
From equations (2) and (3), we get ${{\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 6-\left( \dfrac{-1}{16a} \right) \right)$.
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 6+\dfrac{1}{16a} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{4}=24a+\dfrac{1}{4}$.
$\Rightarrow 2=24a$.
$\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{1}{12}$ ---(4).
Let us substitute equation (4) in equation (3).
So, we get $h=\dfrac{-1}{16\left( \dfrac{1}{12} \right)}=\dfrac{-3}{4}$ ---(5).
Let us substitute the values of ‘h’, ‘k’ and ‘a’ obtained from equations (2), (4) and (5) in ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$.
So, we get ${{\left( y+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( \dfrac{1}{12} \right)\left( x+\dfrac{3}{4} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+y+\dfrac{1}{4}=\left( \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\left( x+\dfrac{3}{4} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow 3{{y}^{2}}+3y+\dfrac{3}{4}=x+\dfrac{3}{4}$.
$\Rightarrow 3{{y}^{2}}+3y-x=0$.
So, we have found the equation of the parabola as $3{{y}^{2}}+3y-x=0$.
So, the correct answer is “Option d”.
Note: We can also take the general equation of the parabola whose axis is horizontal (axis is parallel to x-axis) as $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$ which can be solved as shown below.
Let us substitute the point $\left( 0,0 \right)$ in $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$.
So, we get $0=a{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( 0 \right)+c$.
$\Rightarrow 0=0+0+c$.
$\Rightarrow c=0$ ---(6).
Let us substitute the point $\left( 0,-1 \right)$ in $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$.
So, we get $0=a{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( -1 \right)+c$.
From equation (6).
$\Rightarrow 0=a-b+0$.
$\Rightarrow a-b=0$ ---(7).
Let us substitute the point $\left( 6,1 \right)$ in $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$.
So, we get $6=a{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( 1 \right)+c$.
From equation (6).
$\Rightarrow 6=a+b+0$.
$\Rightarrow a+b=6$ ---(8).
On solving equations (7) and (8), we get $a=3$ and $b=3$.
So, we get the equation of the parabola as $x=3{{y}^{2}}+3y+0$.
$\Rightarrow 3{{y}^{2}}+3y-x=0$.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that the axis of the parabola is horizontal and we need to find the equation of parabola if it passes through the points $\left( 0,0 \right)$, $\left( 0,-1 \right)$ and $\left( 6,1 \right)$.

We know that the general equation of the parabola is ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$, if the axis of the parabola is horizontal.
Let us substitute the point $\left( 0,0 \right)$ in the parabola ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$.
So, we get ${{\left( 0-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 0-h \right)$.
$\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}=-4ah$ ---(1).
Let us substitute the point $\left( 0,-1 \right)$ in the parabola ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$.
So, we get ${{\left( -1-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 0-h \right)$.
$\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+2k+1=-4ah$.
From equation (1) we get ${{k}^{2}}+2k+1={{k}^{2}}$.
$\Rightarrow 2k+1=0$.
$\Rightarrow 2k=-1$.
$\Rightarrow k=\dfrac{-1}{2}$ ---(2).
Let us substitute equation (2) in equation (1), we get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=-4ah$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4}=-4ah$.
$\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{-1}{16a}$ ---(3).
Let us substitute the point $\left( 6,1 \right)$ in the parabola ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$.
So, we get ${{\left( 1-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 6-h \right)$.
From equations (2) and (3), we get ${{\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 6-\left( \dfrac{-1}{16a} \right) \right)$.
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( 6+\dfrac{1}{16a} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{4}=24a+\dfrac{1}{4}$.
$\Rightarrow 2=24a$.
$\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{1}{12}$ ---(4).
Let us substitute equation (4) in equation (3).
So, we get $h=\dfrac{-1}{16\left( \dfrac{1}{12} \right)}=\dfrac{-3}{4}$ ---(5).
Let us substitute the values of ‘h’, ‘k’ and ‘a’ obtained from equations (2), (4) and (5) in ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$.
So, we get ${{\left( y+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( \dfrac{1}{12} \right)\left( x+\dfrac{3}{4} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+y+\dfrac{1}{4}=\left( \dfrac{1}{3} \right)\left( x+\dfrac{3}{4} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow 3{{y}^{2}}+3y+\dfrac{3}{4}=x+\dfrac{3}{4}$.
$\Rightarrow 3{{y}^{2}}+3y-x=0$.
So, we have found the equation of the parabola as $3{{y}^{2}}+3y-x=0$.
So, the correct answer is “Option d”.
Note: We can also take the general equation of the parabola whose axis is horizontal (axis is parallel to x-axis) as $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$ which can be solved as shown below.
Let us substitute the point $\left( 0,0 \right)$ in $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$.
So, we get $0=a{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( 0 \right)+c$.
$\Rightarrow 0=0+0+c$.
$\Rightarrow c=0$ ---(6).
Let us substitute the point $\left( 0,-1 \right)$ in $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$.
So, we get $0=a{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( -1 \right)+c$.
From equation (6).
$\Rightarrow 0=a-b+0$.
$\Rightarrow a-b=0$ ---(7).
Let us substitute the point $\left( 6,1 \right)$ in $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$.
So, we get $6=a{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( 1 \right)+c$.
From equation (6).
$\Rightarrow 6=a+b+0$.
$\Rightarrow a+b=6$ ---(8).
On solving equations (7) and (8), we get $a=3$ and $b=3$.
So, we get the equation of the parabola as $x=3{{y}^{2}}+3y+0$.
$\Rightarrow 3{{y}^{2}}+3y-x=0$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




