
If a tower is 30m high, casts a shadow of $10\sqrt{3}m$ long on the ground, then finds the value of angle of elevation of sun?
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint: The tower, the shadow and the line joining the top of the tower to the end of the shadow constructs a right angled triangle. We know the length of the base and the height of the triangle then using $\tan \theta $, we can find the angle of elevation of the sun.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that the height of the tower is 30m and the length of the shadow is $10\sqrt{3}m$.
The below diagram is showing the height of the tower (AB), the shadow of the tower (BC) and angle of inclination of the sun is given by $\theta $.
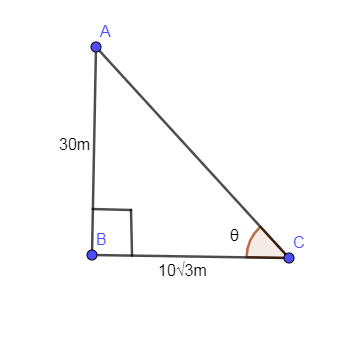
In the above right angled triangle, right angled at B,
$\tan \theta =\dfrac{P}{B}$
In the above formula, “P” stands for perpendicular corresponding to angle $\theta $ and “B” stands for the base corresponding to angle $\theta $ so using this formula in the above triangle.
In the above triangle, $P=30m;B=10\sqrt{3}m$so substituting these values in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{30}{10\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3}}=\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
We know that, $\tan \theta =\sqrt{3}$ when $\theta ={{60}^{0}}$ so the above equation is reduced to:
$\theta ={{60}^{0}}$
From the above solution, we have found the angle of elevation of the sun is ${{60}^{0}}$.
Note: The point to be noted here is that the shadow lies on the floor so the shadow in the diagram is BC not AC. You might get confused that the shadow is AC but it is BC and the angle of elevation of the sun is $\angle ACB$ not $\angle BAC$.
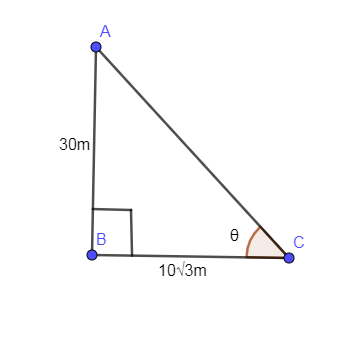
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that the height of the tower is 30m and the length of the shadow is $10\sqrt{3}m$.
The below diagram is showing the height of the tower (AB), the shadow of the tower (BC) and angle of inclination of the sun is given by $\theta $.

In the above right angled triangle, right angled at B,
$\tan \theta =\dfrac{P}{B}$
In the above formula, “P” stands for perpendicular corresponding to angle $\theta $ and “B” stands for the base corresponding to angle $\theta $ so using this formula in the above triangle.
In the above triangle, $P=30m;B=10\sqrt{3}m$so substituting these values in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{30}{10\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3}}=\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
We know that, $\tan \theta =\sqrt{3}$ when $\theta ={{60}^{0}}$ so the above equation is reduced to:
$\theta ={{60}^{0}}$
From the above solution, we have found the angle of elevation of the sun is ${{60}^{0}}$.
Note: The point to be noted here is that the shadow lies on the floor so the shadow in the diagram is BC not AC. You might get confused that the shadow is AC but it is BC and the angle of elevation of the sun is $\angle ACB$ not $\angle BAC$.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




